UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10‑K
|
☒ |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019
OR
|
☐ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number: 001‑35527
Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc.
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Delaware |
2834 |
87-0419387 |
|
(State or Other Jurisdiction of |
(Primary Standard Industrial |
(I.R.S. Employer |
|
Incorporation or Organization) |
Classification Code Number) |
Identification No.) |
21250 Hawthorne Boulevard, Suite 800, Torrance, California 90503
(Address of principal executive offices, including zip code)
(310) 214‑0065
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
SECURITIES REGISTERED PURSUANT TO SECTION 12(b) OF THE ACT:
|
Title of each class |
Trading Symbol(s) |
Name of each exchange on which registered |
|
None. |
|
|
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well‑known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically every Interactive Data File required to be submitted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S‑T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit such files). Yes ☐ No ☒
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non‑accelerated filer, a smaller reporting company, or emerging growth company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” “smaller reporting company” and “emerging growth company” in Rule 12b‑2 of the Exchange Act:
|
Large accelerated filer |
☐ |
|
|
Accelerated filer |
☐ |
|
Non‑accelerated filer |
☒ |
|
|
Smaller reporting company |
☒ |
|
Emerging growth company |
☐ |
|
|
|
|
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b‑2 of the Act). Yes ☐ No ☒
The aggregate market value of shares of common stock held by non‑affiliates of the registrant as of June 30, 2020, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter, was $58,283,977 based upon the closing price of the common stock as reported on the OTCQB.
There were 48,987,189 shares of common stock outstanding as of January 5, 2021.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
|
ITEM |
|
|
PAGE |
|
|
4 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
ITEM 1. |
6 |
||
|
ITEM 1A. |
20 |
||
|
ITEM 1B. |
46 |
||
|
ITEM 2. |
46 |
||
|
ITEM 3. |
47 |
||
|
ITEM 4. |
47 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
ITEM 5. |
48 |
||
|
ITEM 6. |
48 |
||
|
ITEM 7. |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
49 |
|
|
ITEM 7A. |
58 |
||
|
ITEM 8. |
58 |
||
|
ITEM 9. |
CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE |
58 |
|
|
ITEM 9A. |
59 |
||
|
ITEM 9B. |
61 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
ITEM 10. |
62 |
||
|
ITEM 11. |
65 |
||
|
ITEM 12. |
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
70 |
|
|
ITEM 13. |
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE |
72 |
|
|
ITEM 14. |
73 |
||
|
|
|
||
|
ITEM 15. |
75 |
||
|
82 |
|||
2
CAUTIONARY STATEMENT REGARDING FORWARD‑LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report contains some statements that are not purely historical and that are considered “forward‑looking statements” within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, which we refer to as the Securities Act, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, which we refer to as the Exchange Act. Such forward‑looking statements express our management’s expectations, beliefs, and intentions regarding the future. The words “anticipates,” “believes,” “continue,” “could,” “estimates,” “expects,” “intends,” “may,” “might,” “plans,” “possible,” “potential,” “predicts,” “projects,” “seeks,” “should,” “will,” “would” and similar expressions and variations, or comparable terminology, or the negatives of any of the foregoing, may identify forward‑looking statements, but the absence of these words does not mean that a statement is not forward‑looking.
The forward‑looking statements contained in this Annual Report are based on current expectations and beliefs concerning future developments that are difficult to predict. We cannot guarantee future performance, or that future developments affecting our company will be those currently anticipated. These forward‑looking statements involve a number of risks, uncertainties (some of which are beyond our control) or other assumptions that may cause actual results or performance to be materially different from those expressed or implied by these forward‑looking statements, including the factors referenced in this Annual Report under the sections entitled “Business,” “Risk Factors” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
All forward‑looking statements attributable to us are expressly qualified in their entirety by these risks and uncertainties, and you should not place undue reliance on any forward‑looking statement. We undertake no obligation to update or revise any forward‑looking statement, except as may be required under applicable securities laws.
3
This Annual Report on Form 10-K:
|
|
(a) |
Restates the Consolidated Balance Sheet of EMI Holding, Inc., or EMI, the accounting acquirer in the reverse recapitalization transaction effected on July 17, 2019, and the related Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss, Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows and Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) for the year ended December 31, 2018 and the nine months ended September 30, 2019. |
|
|
(b) |
Amends “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” as it relates to the year ended December 31, 2018. |
|
|
(c) |
Restates the “Unaudited Quarterly Financial Information” for the quarter ended September 30, 2019. |
Background on the Restatement
As previously disclosed in the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 8, 2020, the board of directors of the Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. (“we,” “us,” “our,” “Emmaus” or the “Company”), based on the recommendation of the audit committee, concluded that, because of errors identified in the previously issued financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2018 as well as EMI Holding’s unaudited consolidated financial statements for the three months ended March 31, 2019, the three and six months ended June 30, 2019 and our previously filed unaudited consolidated financial statements for three and nine months ended September 30, 2019, the Company would restate the previously issued financial statements.
These errors were discovered during the preparation of this Annual Report and the audit of the Company’s financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2019. We have determined that these errors were the result of material weaknesses in internal control over financial reporting as described in management’s report on internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2019 in Part II—Item 9A – Controls and Procedures of this Annual Report.
The restated financial statements correct the following errors:
|
|
1. |
The misclassification as equity of warrants issued by EMI in October of 2018, which warrants should have been accounted for as liabilities based upon fair value. |
|
|
2. |
The erroneous consolidation as a Variable Interest Entity, or VIE, of EMI’s interest in EJ Holdings, Inc., which should have been accounted for based upon the equity method. |
|
|
3. |
The mistreatment of the fair value of cashless exercise warrants originally recorded in the Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss, which fair value should have been recorded in additional paid-in capital in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. |
|
|
4. |
In addition to the errors described above, the restated financial statements also include adjustments to correct certain immaterial errors identified during the audit of the Company’s financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2019. Cumulatively through September 30, 2019, the restatement had the following effects on net loss (in thousands): |
|
|
|
Warrant Derivative Liability |
|
|
Consolidation of VIE |
|
Fair Value of Warrants |
|
|
Other |
|
|
Tax Effect of |
|
|
Total (Increase) Decrease |
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
Adjustments |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
in Net Loss |
|
|||||||||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2018 |
|
$ |
|
2,425 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
|
(18,345 |
) |
|
$ |
|
1,264 |
|
|
$ |
|
(33 |
) |
|
$ |
|
(14,689 |
) |
|
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2019 |
|
|
|
7,222 |
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
(1,757 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
5,465 |
|
|||
|
|
|
$ |
|
9,647 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
|
(18,345 |
) |
|
$ |
|
(493 |
) |
|
$ |
|
(33 |
) |
|
$ |
|
(9,224 |
) |
4
The following table sets forth the effects of the restatement on affected items within the previously reported Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss (in thousands, except per share data):
|
|
|
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2019 |
|
|
Year Ended December 31, 2018 |
|
||
|
Gross profit |
As Originally Reported |
$ |
16,687 |
|
|
$ |
14,313 |
|
|
|
Adjustments |
|
(1,498 |
) |
|
|
1,153 |
|
|
|
As Restated |
$ |
15,189 |
|
|
$ |
15,466 |
|
|
Loss from operations |
As Originally Reported |
$ |
(4,791 |
) |
|
$ |
(10,100 |
) |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
(421 |
) |
|
|
1,646 |
|
|
|
As Restated |
$ |
(5,212 |
) |
|
$ |
(8,454 |
) |
|
Net loss |
As Originally Reported |
$ |
(58,943 |
) |
|
$ |
(57,898 |
) |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
5,465 |
|
|
|
(14,689 |
) |
|
|
As Restated |
$ |
(53,478 |
) |
|
$ |
(72,587 |
) |
|
Net loss per common share - basic and diluted |
As Originally Reported |
$ |
(1.46 |
) |
|
$ |
(1.57 |
) |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
0.14 |
|
|
|
(0.40 |
) |
|
|
As Restated |
$ |
(1.32 |
) |
|
$ |
(1.97 |
) |
The adjustments resulting from the restatement are more fully discussed in Note 3, Restatement of Previously Issued Financial Statements, of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report. For further information regarding the effects of the accounting errors identified and the restatement adjustments, see Part II—Item 7—Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations included in this Annual Report. For a description of the control deficiencies identified by management and management’s plan to remediate those deficiencies, see Part II—Item 9A—Controls and Procedures.
Previously filed annual reports on Form 10-K of EMI and quarterly reports on Form 10-Q of EMI and the Company for the periods affected by the restatement have not been amended and the financial information included therein is superseded in its entirety by the restatements included in this Form 10-K. Accordingly, investors should no longer rely upon the previously released financial statements for these periods and any earnings releases or other communications relating to these periods, and, for these periods, investors should rely solely on the financial statements and other financial data for the relevant periods included in this Annual Report. See Note 15, Unaudited Quarterly Financial Statements, of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report for the impact of these adjustments for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2019. Our quarterly reports for 2020 will also include restated results for the corresponding interim periods of fiscal 2019. All amounts in this Annual Report on Form10-K give effect to the restatement adjustments.
5
In this Annual Report, the terms, “we,” “us,” “our” or the “Company” refer to Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc., and its subsidiaries.
As reported in more detail in our Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 22, 2019, as amended by our Form 8-K/A filed on August 14, 2019, on July 17, 2019, we completed our merger transaction with EMI Holding, Inc., formerly known as Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. (“EMI”), in accordance with the terms of the Agreement and Plan of Merger and Reorganization, dated as of January 4, 2019, among us, Athena Merger Subsidiary, Inc., and EMI, as amended by Amendment No. 1 thereto, dated as of May 10, 2019, which we refer to as the merger agreement. Pursuant to the merger agreement, Athena Merger Subsidiary, Inc. merged into EMI, with EMI surviving as our wholly owned subsidiary. On July 17, 2019, immediately after completion of the merger, we changed our name to “Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc.”
The merger was treated as a reverse recapitalization transaction under the acquisition method of accounting in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. For accounting purposes, EMI is considered to have acquired us. The merger is intended to qualify as a tax-free reorganization for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
Overview
We are a commercial-stage biopharmaceutical company engaged in the discovery, development, marketing and sale of innovative treatments and therapies, primarily for rare and orphan diseases. On July 7, 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, approved our lead product, Endari® (prescription grade L-glutamine oral powder), which is indicated to reduce the acute complications of sickle cell disease (“SCD”) in adult and pediatric patients five years of age and older. Endari® has received Orphan Drug designation from the FDA and Orphan Medical designation from the European Commission, which designations afford marketing exclusivity for Endari® for a seven-year period in the U.S. and ten-year period in the European Union, respectively, following marketing approval.
We commenced commercialization of Endari® in the U.S. in January 2018 in collaboration with a contract sales organization. Since January 2020, we have relied upon our internal commercial sales team. Endari® is reimbursable by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and every state provides coverage for Endari® for outpatient prescriptions to all eligible Medicaid enrollees within their state Medicaid programs. We have agreements in place with the nation’s leading distributors, as well as physician group purchasing organizations and pharmacy benefits managers, making Endari® available at selected retail and specialty pharmacies nationwide. We expect net revenue to increase as we expand our commercialization of Endari® in the United States and grow or commence early access programs and eventual marketing and commercialization of Endari® outside the United States.
SCD is a rare, debilitating and lifelong hereditary blood disorder that affects approximately 100,000 patients in the U.S. and up to 25 million patients worldwide, the majority of which are of African descent. Approximately one in every 365 African-American children are born with SCD. FDA approval of Endari® was based upon the results of a 48-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-center Phase 3 clinical trial evaluating the effects of Endari®, as compared to placebo in 230 adults and children with SCD. The results demonstrated that Endari® reduced the frequency of sickle cell crises by 25% and hospitalizations by 33%. Additional findings included a 41% decrease in cumulative hospital days and greater than 60% fewer incidents of acute chest syndrome in patients treated with Endari®. In addition, the FDA has acknowledged that the clinical benefit of Endari® was observed irrespective of hydroxyurea use, which supports the use of Endari® as a monotherapy or in combination with hydroxyurea as safe and effective treatment options for patients with SCD.
The safety of Endari® was based upon data from 298 patients, 187 treated with Endari® and 111 patients treated with placebo in Phase 2 and Phase 3 studies. Endari®’s safety profile was similar to that of placebo and Endari® was well-tolerated in pediatric and adult patients alike. The most common adverse reactions, occurring in more than 10% of patients treated with Endari®, were constipation, nausea, headache, abdominal pain, cough, pain in extremity, back pain, and chest pain (non-cardiac).
On July 4, 2018, the FDA acknowledged receipt of our investigational new drug application, or IND, for the treatment of diverticulosis using the same prescription grade L-glutamine oral powder (PGLG) used in Endari®. We subsequently received a “Study May Proceed” letter from the FDA. In April 2019, we commenced a Pilot/Phase 1 study of the safety and efficacy of PGLG oral powder in diverticulosis. The study will evaluate the change in the number and size of colonic diverticula and assess safety in a total of up to 10 to 15 patients at multiple study sites. The COVID-19 pandemic has slowed
6
the progress of clinical trials in the pharmaceutical industry, in general. However, patient enrollment has now been completed.
On August 5, 2020, we announced preliminary top-line data for two patients who had most recently completed the first six months of the scheduled twelve months of treatment in a pilot study of diverticulosis. The following table summarizes the data:
Number of diverticula in the sigmoid colon following six months treatment on PGLG
|
Patient |
Baseline |
Six Months |
Percentage Reduction |
|
52 year old female |
8 |
4 |
50% |
|
59 year old female |
7 |
0 |
100% |
In each of these patients, the investigator also noted the appearance of healthier mucosa with pinkish coloration compared to the baseline. There were no safety concerns reported by the patients. Our study observations are focused on diverticula in the sigmoid colon, the most frequent site for diverticulitis.
An Emmaus-led team at The Lundquist Institute, formerly known as the Los Angeles Biomedical Research Institute, or TLI, an independent non-profit biomedical research organization academically affiliated with the David Geffen School of Medicine at University of California, at Los Angeles that works in partnership with Harbor-UCLA Medical Center, is conducting pre-clinical studies of Cultured Autologous Oral Mucosal Epithelial Cell Sheet, or CAOMECS, technology licensed by us from CellSeed Inc., a Japanese company, which we refer to as CellSeed. Our lead CAOMECS program is for the treatment of corneal diseases. The development of CAOMECS for treating corneal and other diseases is in the early stages.
Sickle Cell Disease—Market Overview
Sickle cell disease is a genetic blood disorder that affects 20 million - 25 million people worldwide and occurs with increasing frequency among those whose ancestors are from regions including sub-Saharan Africa, South America, the Caribbean, Central America, the Middle East, India and Mediterranean regions such as Turkey, Greece and Italy. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimates that there are as many as 100,000 patients with SCD in the United States, and we estimate there are approximately 80,000 patients in the EU. We estimate that there are over 100,000 SCD patients that could potentially be treated in the Persian Gulf States, as well as patients in other countries that comprise the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region.
SCD is characterized by the production of an altered form of hemoglobin which polymerizes and becomes fibrous, causing the red blood cells of patients with SCD to become sickle‑shaped, inflexible and adhesive rather than round, smooth and flexible. The complications associated with SCD occur when these inflexible and sticky cells block, or occlude, small blood vessels, which can then cause severe and chronic pain throughout the body due to insufficient oxygen being delivered to tissue, or ischemia, and inflammation. According to an article in Annals of Internal Medicine, “In the Clinic: Sickle Cell Disease” by M.H. Steinberg (September 2011), which we refer to as the Steinberg Article, this leads to long‑term organ damage, diminished exercise tolerance, increased risk of stroke and infection and decreased lifespan.
Sickle cell crisis, a broad term covering a range of disorders, is one of the most devastating complications of SCD. Types of sickle cell crisis include:
|
|
• |
Vaso‑occlusive crisis, characterized by obstructed blood flow to organs such as the bones, liver, kidneys, eyes or central nervous system; |
|
|
• |
Aplastic crisis, characterized by acute anemia typically due to viral infection; |
|
|
• |
Hemolytic crisis, characterized by accelerated red blood cell death and reduced hemoglobin; |
|
|
• |
Splenic sequestration crisis, characterized by painful enlargement of the spleen due to trapped red blood cells; and |
7
|
|
• |
Acute chest syndrome, a potentially life‑threatening obstruction of blood supply to the lungs characterized by fever, chest pain, cough, and lung infiltrates. |
According to the Steinberg Article, acute chest syndrome affects more than half of all patients with SCD and is a common reason for hospitalization. Other symptoms and complications of SCD include swelling of the hands and feet, infections, pneumonia, vision loss, leg ulcers, gall stones and stroke.
A crisis is characterized by excruciating musculoskeletal pain, visceral pain and pain in other locations. These crises occur periodically throughout the life of a person with SCD. In adults, the acute pain typically persists for five or ten days or longer, followed by a dull, aching pain generally ending only after several weeks and sometimes persisting between crises. According to the Steinberg Article, the frequency of sickle cell crises varies within patients with SCD from rare occurrences to occurrences several times a month. The frequency of crises tends to increase late in the second decade of life and to decrease after the fourth decade.
Treatment of sickle cell crises is burdensome and expensive for patients and payors, as it encompasses costs for hospitalization, urgent care and emergency room visits and prescription pain medication. Endari® enhances nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (“NAD”) synthesis to reduce excessive oxidative stress in sickle red blood cells, which is the cause of much of the damage leading to characteristic symptoms of SCD. We believe that Endari®, when taken daily, will decrease the incidence of sickle cell crisis by restoring the flexibility and function of red blood cells in patients with SCD. We believe that regular use of Endari® also will reduce the number of costly hospitalizations of patients with SCD, as well as unexpected urgent care and emergency room visits.
8
Limitations of the Current Standard of Care
Prior to the approval of Endari®, the only other FDA approved pharmaceutical targeting sickle cell crisis was hydroxyurea, which is available in both generic and branded formulations. Hydroxyurea, a drug originally developed as an anticancer chemotherapeutic agent, has been approved as a once‑daily oral treatment for reducing the frequency of sickle cell crisis and the need for blood transfusions in adult patients with recurrent moderate to severe sickle cell crisis. In December 2017, the FDA granted Addmedica a regular approval for hydroxyurea (Siklos) to reduce the frequency of painful crises and the need for blood transfusions in pediatric patients two years of age and older with sickle cell anemia with recurrent moderate to severe painful crises. While hydroxyurea has been shown to reduce the frequency of sickle cell crisis in some patient groups, it is not suitable for many patients due to significant toxicities and side effects. In particular, hydroxyurea can cause a severe decrease in the number of blood cells in a patient’s bone marrow, which may increase the risk that the patient will develop a serious infection or bleeding, or that the patient will develop certain cancers. Another potential treatment option for SCD, bone marrow transplant, is limited in its use due to the lack of availability of matched donors and the risk of serious complications, including graft versus host disease, infection and potentially death, as well as by its high cost.
Two new treatments for sickle cell disease were approved by the FDA at the end of 2019. Crizanlizumab, marketed under the brand name of Adakveo® by Novartis AG, is a humanized monoclonal antibody that binds to P-selectin. It was approved by the FDA on November 15, 2019 to reduce the frequency of vaso-occlusive crises in adults and pediatric patients aged 16 years and older with SCD. It is administered intravenously in two loading doses two weeks apart and every four weeks thereafter. Voxelotor, marketed under the brand name of Oxbryta™ by Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc., is an HbS polymerization inhibitor that reversibly binds to hemoglobin to stabilize the oxygenated hemoglobin state, thus shifting the oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve. Voxelotor was approved by the FDA on November 25, 2019 for the treatment of SCD in adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older.
Upon onset of sickle cell crisis, the current standard of care is focused on pain management, often with prescription narcotics or non-prescription oral medications taken at home. If the pain is not relieved, or if it progresses, patients may seek medical attention in a clinic or emergency department. Pain that is not controlled in these settings may require hospitalization for more potent pain medications, typically opioids administered intravenously. The patient must stay in the hospital to receive these intravenous pain medications until the sickle cell crisis resolves and the pain subsides. Other supportive measures during hospitalization may include hydration, supplemental oxygen and treatment of any concurrent infections or other conditions.
According to Hematology in Clinical Practice, by Robert S. Hillman et. al. (5th ed. 2011), sickle cell crisis, once it has started, almost always results in tissue damage at the affected site in the body, increasing the importance of preventative measures. While pain medications can be effective in managing pain during sickle cell crisis, they do not affect or resolve the underlying vascular occlusion, tissue ischemia or potential tissue damage. Additionally, opioid narcotics that are generally prescribed to treat pain can also lead to tissue or organ damage and resulting complications and morbidities, prolonged hospital stays and associated continuation of pain and suffering. Given the duration and frequency of sickle cell crises, addiction to these opioid narcotics is also a significant concern.
Endari®, Our Solution for SCD
We believe Endari® may provide a safe and effective means for reducing the frequency of sickle cell crises in patients with SCD and the need for costly hospital stays or treatment with highly addictive pain medications such as opioid narcotics. Published academic research has identified L-glutamine as a precursor to NAD, one of the major molecules that regulate and prevent oxidative damage in red blood cells. Several published studies have demonstrated that sickle red blood cells have a significantly increased rate of transport of L-glutamine, which appears to be driven by the cells’ synthesis of NAD to protect against oxidative damage and thereby leading to further improvement in their regulation of oxidative stress. In turn this makes sickle red blood cells less adhesive to cells of the interior wall of blood vessels, which suggests that there is decreased chance of blockage of blood vessels, especially small ones. In summary, improved regulation of oxidative stress appears to lead to less obstruction or blockage of small blood vessels, thereby alleviating a major cause of the pain and other problems associated with SCD.
In December 2013, we completed a Phase 3 prospective, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled, parallel group multicenter clinical trial to measure, over a 48-week time frame, as its primary outcome, the reduction in the number of occurrences of sickle cell crises experienced by patients in the trial. All participants other than those who received placebo, including children, received up to 30 grams of Endari® daily, dissolved in liquid, split between morning and evening; the same dosage as our Phase 2 clinical trial completed in 2009. Patients were randomized to the study treatment using a 2:1 ratio of Endari® to placebo. The randomization was stratified by investigational site and hydroxyurea usage.
9
The clinical trial evaluated the efficacy and safety of Endari® in 230 patients (5 to 58 years of age) with sickle cell anemia or sickle β°-thalassemia who had 2 or more painful crises within 12 months prior to enrollment. Eligible patients stabilized on hydroxyurea for at least 3 months continued their therapy throughout the study. The trial excluded patients who had received blood products within 3 weeks, had renal insufficiency or uncontrolled liver disease, or were pregnant (or planning pregnancy) or lactating. Study patients received Endari® or placebo for a treatment duration of 48 weeks followed by 3 weeks of tapering.
Efficacy was demonstrated by a reduction in the number of sickle cell crises through Week 48 and prior to the start of tapering among patients that received Endari® compared to patients who received placebo. A sickle cell crisis was defined as a visit to an emergency room/medical facility for sickle cell disease-related pain which was treated with a parenterally administered narcotic or parenterally administered ketorolac. In addition, the occurrence of acute chest syndrome, priapism, and splenic sequestration were considered sickle cell crises. Treatment with Endari® also resulted in fewer hospitalizations due to sickle cell pain at Week 48, fewer cumulative days in hospital and a lower incidence of acute chest syndrome.
Table 1. Results from the Endari® Clinical Trial in Sickle Cell Disease
|
|
Endari |
Placebo |
|
Event |
(n = 152) |
(n = 78) |
|
Median number of sickle cell crises (min, max)1 |
3 (0, 15) |
4 (0, 15) |
|
Median number of hospitalizations for sickle cell pain (min, max)1 |
2 (0, 14) |
3 (0, 13) |
|
Median cumulative days hospitalized (min, max)1, |
6.5 (0, 94) |
11 (0, 187) |
|
Median time (days) to first sickle cell crisis (95% CI) 1,2 |
84 (62, 109) |
54 (31, 73) |
|
Patients with occurrences of acute chest syndrome (%)1 |
13 (8.6%) |
18 (23.1%) |
1. Measured through 48 weeks of treatment
2. Hazard Ratio=0.69 (95% CI=0.52, 0.93), estimated based on unstratified Cox’s proportional model. Median time and 95% CI were estimated based on the Kaplan Meier method.
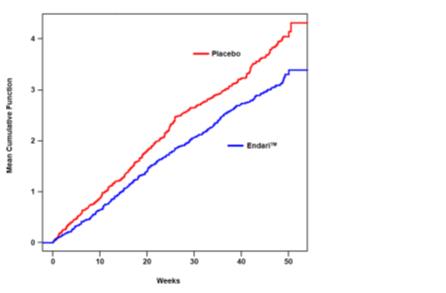
The recurrent crisis event time analysis (Figure 1) yielded an intensity rate ratio (IRR) value of 0.75 with 95% CI= (0.62, 0.90) and (0.55, 1.01) based on unstratified models using the Andersen-Gill and Lin, Wei, Yang and Ying methods, respectively in favor of Endari®, suggesting that over the entire 48- week period, the average cumulative crisis count was reduced by 25% from the Endari® group over the placebo group.
Figure 1. Recurrent Event Time for Sickle Cell Crises by Treatment Group

Endari® was studied in 2 placebo-controlled clinical trials (a phase 3 study, n=230 and a phase 2 study, n=70). In these trials, patients with sickle cell anemia or sickle β0-thalassemia were randomized to receive Endari® (n=187) or placebo (n=111) orally twice daily for 48 weeks followed by 3 weeks of tapering. Both studies included pediatric and adult patients (5-58 years of age) and 54% were female.
10
Treatment discontinuation due to adverse reactions was reported in 2.7% (n=5) of patients receiving Endari®. These adverse reactions included one case each of hypersplenism, abdominal pain, dyspepsia, burning sensation, and hot flash.
Serious adverse reactions were reported in both treatment groups, more frequently in the placebo group, and were consistent with the underlying disease.
Three deaths (3/187=1.6%) occurred during the study in the Endari® treatment group as compared to none in the placebo treatment group. None of the deaths were considered to be related to Endari® treatment. Adverse reactions occurring in greater than 10% of patients treated with Endari® are shown in Table 2 below.
Table 2. Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence > 10% in Clinical
|
Adverse reaction |
|
Endari N = 187 (%) |
|
Placebo N = 111 (%) |
|
|
Constipation |
|
21 |
|
18 |
|
|
Nausea |
|
19 |
|
14 |
|
|
Headache |
|
18 |
|
15 |
|
|
Abdominal Pain1 |
|
17 |
|
16 |
|
|
Cough |
|
16 |
|
14 |
|
|
Pain in extremity |
|
13 |
|
7 |
|
|
Back pain |
|
12 |
|
5 |
|
|
Chest pain |
|
12 |
|
8 |
|
1Abdominal pain = abdominal pain and abdominal pain, upper
Commercialization and Distribution
United States
In January 2018 we commenced commercialization of Endari® in the U.S utilizing a contract sales organization or CSO to support our internal sales activities. We terminated our relationship with the CSO in December 2019 and in January 2020 we internalized the sales function in order to have greater control over sales activities. Our in-house commercial team encompasses marketing, market access, patient support, and distribution support personnel. The sales team consists of sales representatives, sales management, and a National Sales Director. In February 2019 we established a Commercial Patient Assistance Program (C- PAP) to provide financial assistance to eligible patients who are unable to afford their monthly co-payments for Endari®.
Our sales and marketing efforts focus on the following groups: pediatric and adult hematologists who treat SCD patients with sickle cell disease, Community Based Organizations, or CBOs, government payors, insurance companies, and pharmacy benefit managers. SCD patients are primarily treated at specialized clinics located in children’s hospitals, university hospitals and community-based out-patient locations. The current focus of our sales team is as follows:
• educating prescribers and CBOs on the approved use and benefits of Endari®; and
• establishing collaborative relationships with CBOs and patient support groups that focus on SCD education and patient advocacy in their respective communities.
We have contracted with AmerisourceBergen Specialty Group (ASD Healthcare LLC and US Bioservices Corporation), AmerisourceBergen Corporation companies, McKesson Plasma and Biologics LLC, a McKesson Corporation company, and Cardinal Health 108, LLC, a Cardinal Health Inc. company, to distribute Endari® to selected pharmacies and hospitals. AmerisourceBergen Corporation, McKesson Corporation and Cardinal Health, Inc. are the three largest specialty distributors of prescription drugs in the U.S.
Our two largest distributors, ASD Healthcare and McKesson Plasma and Biologics LLC, each account for more than 20% of units sold for the year ended December 31, 2019. On a combined basis, the three distributors accounted for approximately 87% of our units sold in 2019.
11
Outside the United States
In July 2012, the European Commission, or EC, granted Orphan Drug Designation status in the European Union, or EU, for our prescription grade L-glutamine oral powder, to be known as Xyndari™ in the EU, for the treatment of SCD. In January 2018, the European Medicines Agency, or EMA, provided their agreement on the pediatric investigation plan, or PIP, for Xyndari™ and we filed with the MEA an application for marketing authorization, or MAA, in the EU. In May 2019, we announced that the EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use, or CHMP, adopted a negative opinion regarding our MAA based upon the CHMP’s position that our main clinical study did not conclusively support the efficacy of the treatment in SCD patients, although no safety concerns were raised. In light of the CHMP’s opinion, we withdrew our MAA in September 2019 to consider pursuing alternative decentralized and centralized regulatory pathways for obtaining marketing authorization in an effort to ensure access to Xyndari™ for patients afflicted by SCD.
We are in the process of meeting with the regulatory authorities at the EMA and perhaps in other EU member nations to determine whether there is a viable regulatory path forward for Xyndari™, including whether or what additional data might be necessary to support future MAAs. With Brexit in place, we will also work directly with the U.K.’s Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency, or MHRA, to determine the regulatory pathway for Xyndari™ in the U.K. We expect to provide an update in the first half of 2021 on the outcome of these efforts. On June 17, 2020 Endari® was approved for marketing in Israel by the Israeli Ministry of Health for the same indication approved under the FDA. On November 10, 2020, we announced the submission of a temporary license application for Endari® to the National Health Regulatory Authority in the Kingdom of Bahrain as a prerequisite for marketing authorization there. The temporary license will allow Endari® to be prescribed in the Kingdom pending marketing authorization. We are also currently engaged in marketing regulatory submissions in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia and other Gulf Coast Cooperation Council countries.
We have entered into exclusive distribution agreements with strategic partners to register, commercialize and distribute Endari® in the Gulf Cooperation Council countries and other countries throughout the MENA region in collaboration with our office in Dubai. Under the terms of the agreements the distributors generally are responsible for registration and will bear all or substantially all costs for commercialization in their respective countries in return for a share in net revenues from Endari® sales in the countries.
We also are party to an exclusive early access agreement with a strategic partner in the EU pursuant to which our partner distributes Endari® on an early access basis only in France and certain other EU member states. We also are in talks with potential strategic partners in other countries to establish similar early access programs while we consider seeking marketing authorization in one of more of such countries.
We also may seek future collaborations with other pharmaceutical or biotechnology companies and identify potential licensees and other international opportunities to commercialize Endari®, if approved by foreign regulatory authorities.
Diverticulosis, or the presence of colonic diverticula (i.e., pouches in the colon wall), is very common in industrialized nations, with its prevalence increasing with age. An estimated 40% of 60 year-olds and 70% of 80 year-olds have diverticulosis. Of these patients, 10% to 25% are expected to develop diverticulitis, or the advancement of peridiverticular inflammation and infection, resulting in abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, constipation, diarrhea, fever, and leukocytosis.
The pathogenesis of diverticulosis is believed to result from structural abnormalities of the colonic wall, disordered motility and low fiber diets. The relationships between glutamine and intestinal physiology have been extensively studied in inflammatory bowel diseases (i.e., ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease), short bowel syndrome and as a nutritional therapy for critical illnesses. Overall, glutamine elicits the following mechanisms of action within intestinal cells: promotion of enterocyte proliferation, regulation of tight junction proteins; suppression of pro-inflammatory signaling pathways; suppression of intestinal cell apoptosis and cellular stress; and microbiome regulation. Glutamine also helps to maintain intestinal tissue integrity through various signaling pathways.
12
See the discussion above of our Pilot/Phase 1 study of the safety and efficacy of prescription grade L-glutamine oral powder in diverticulosis.
We are party to a distributor agreement with Telcon pursuant to which we granted Telcon exclusive rights to our PGLG oral powder for the treatment of diverticulosis in South Korea, Japan and China. The agreement contemplates that Telcon will be responsible at its expense for obtaining marketing authorization assuming FDA approval is obtained and for all other commercial activities in the territories. In exchange for the exclusive rights, Telcon paid us a $10 million upfront fee, which is refundable in the event of termination of the distributor agreement for failure to obtain FDA approval, and agreed in the distributor agreement to purchase from us specified minimum quantities of the finished product.
CellSeed Collaboration
In June 2016, we entered into a non-exclusive agreement with the Japanese company, CellSeed, Inc. (“CellSeed”), and Dr. Kohji Nishida of the Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka University, Japan, for the development of Cultured Autologous Oral Mucosal Epithelial Cell Sheet (“CAOMECS”) for the treatment of corneal impairments in the United States. Under the agreement, we will be required to pay a single-digit royalty based upon net sales of the technology.
A cell sheet is a composite of cells grown and harvested in an intact sheet, rather than as individual cells. These cell sheets can be used for tissue transplantation or to engineer complex multilayer cell sheets composed of different types of cells. CellSeed’s technology involves culturing cells on a surface coated with the poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) temperature responsive polymer. The thinness of this polymer coating is measured at the nanometer scale. The cells cultured on this polymer can be harvested intact as a composite stratified cell sheet to transplant it precisely on the cornea. Using a patient’s own oral mucosal epithelial cells, we are working toward being able to grow and harvest a cell sheet for directly transplanting onto the cornea of the patient’s affected eye to repair the damaged cornea.
See the discussion above of preclinical studies on our lead CAOMECS program for treatment of corneal diseases.
Research and Development
We spent $2.2 million and $1.7 million, respectively, in 2019 and 2018 on research and development, primarily relating to our Pilot/Phase 1 diverticulosis study. None of these costs are borne or sponsored by our customers.
Raw Materials and Manufacturing
Our SCD treatment uses prescription grade L‑glutamine (“PGLG”), which differs from non‑prescription grade L‑glutamine available as a nutritional supplement. There are limited suppliers of PGLG, and we currently obtain all our PGLG, directly or indirectly, from a single supplier, Ajinomoto Health and Nutrition North America, Inc. (“Ajinomoto”), a subsidiary of Ajinomoto North American Holdings, Inc.
Ajinomoto provided PGLG to us free of charge for our clinical trials of Endari®, including our Phase 3 trial. In return, we have agreed to purchase from Ajinomoto substantially all our commercial needs for PGLG, subject to certain exceptions. We have no long-term supply agreement with Ajinomoto.
On June 12, 2017, we entered into an API supply agreement with Telcon RF Pharmaceutical, Inc. (formerly, Telcon, Inc.), a South Korea-based company, or Telcon, pursuant to which Telcon paid us approximately ₩36.0 billion KRW (approximately $31.8 million USD) in consideration of the right to supply 25% of our requirements for bulk containers of PGLG for a 15-year term. The amount was recorded as a deferred trade discount. On July 12, 2017, we entered into a raw material supply agreement with Telcon which revised certain terms of the API supply agreement, which we refer to as the “revised API agreement.” The revised API agreement is effective for a term of five years and will renew automatically for 10 successive one-year renewal periods, except as either party may determine. In the revised API agreement, we have agreed to purchase a total of 940,000 kilograms of PGLG at a fixed price of $50 per kilogram, or a total of $47.0 million, over the term of the agreement. In September 2018, we entered into an agreement with Ajinomoto and Telcon to facilitate Telcon’s purchase of PGLG from Ajinomoto for resale to us under the revised API agreement.
On June 27, 2019, we entered into an agreement with Telcon to adjust the price payable to Telcon under the revised API agreement from $50 per kilogram of PGLG to $100 kilogram from July 1, 2019 through June 30, 2020 with the price payable after June 30, 2020 to be subject to agreement between the parties. The PGLG raw material purchased from Telcon is recorded in inventory at net realizable value and the excess purchase price is recorded against deferred trade discount.
13
See Note 12 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements in this Annual Report for a discussion of our pledge of marketable securities and other collateral to secure our obligations under the revised API Agreement.
In December 2019, EJ Holdings, Inc., or EJ Holdings a Japanese corporation which is 40% owned by us, purchased from Kyowa Hakko Bio Co. Ltd., or Kyowa, a subsidiary of Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd., Kyowa’s phased-out facility in Ube, Japan, for the manufacture of L-glutamine and other amino acids. EJ Holdings is engaged in phasing in the plant, including obtaining FDA and other regulatory approvals for the manufacture of PGLG in accordance with current Good Manufacturing Practices (“cGMP”). Once the plant is active, we expect to enter into a long-term agreement with EJ Holdings for the supply of PGLG. EJ Holdings has had no revenues since its inception, has depended on loans from us to acquire the Ube plant and fund its operations and will continue to be dependent on loans from us or other financing unless and until its plant is activated and it can secure customers, including us, for its products. As of October 31, 2020, we had loaned EJ Holdings a total of $16.0 million, including $2.8 million of loans made pursuant to our written commitment dated October 28, 2020 to loan EJ Holdings a total of up to $6.5 million through the period ending March 31, 2021. In addition to loans from us, EJ Holdings may require substantial financing in order bring the Ube plant online. EJ Holdings has no commitments or understandings regarding any additional financing. Under the asset purchase agreement pursuant to which EJ Holdings purchased the Ube plant, Kyowa has the right to repurchase the plant at the purchase price, plus certain taxes, paid by EJ Holdings if the plant does not become operational within a reasonable period of time (not to exceed five years).
In May 2020 we entered into a memorandum of understanding and agreement, or MOU, with Japan Industrial Partners, Inc., or JIP, which owns 60% of the capital stock of EJ Holdings, to memorialize the parties’ intentions with respect to the business and operations of the Ube plant and ownership of EJ Holdings. The MOU contemplates, among other things, that we will continue to be the principal source of funding for EJ Holdings’ ownership and operation of the plant and that, subject to certain conditions, to the extent we provide additional funding our ownership interest in EJ Holdings is expected to increase according and that the composition of EJ Holdings’ board of directors and control of EJ Holdings would be modified consistent with the parties’ relative ownership interests. The MOU also contemplates that the Ube plant will eventually supply us with the plant’s output of amino acids and that the operation of the plant will be principally for our benefit and, as such, that major decisions affecting EJ Holdings and the Ube plant will be made by EJ Holdings’ board of directors in consultation with us. At present, JIP owns 60% of EJ Holdings and is entitled to designate a majority of EJ Holdings’ board of directors, its Chief Executive Officer and outside auditors, and as such, controls the management, business and operations of EJ Holdings.
Endari® and any other commercial products we develop must be manufactured and packaged by facilities that meet FDA requirements for cGMP. Ajinomoto and Packaging Coordinators, Inc., or PCI, of Rockville, Illinois, which packages Endari®, currently meet FDA cGMP for manufacture and packaging of our commercial supplies of Endari®. Previous compliance with cGMP; however, does not guarantee future compliance. We have no long-term agreement with Ajinomoto or PCI. We may seek to enter into long-term supply agreements and to establish one or more arrangements with alternative suppliers.
Competition
The biopharmaceutical industry is highly competitive and subject to rapid and significant technological change. We face potential competition from both large and small pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, academic institutions, governmental agencies (such as the National Institutes of Health) and public and private research institutions. Many of our competitors and potential competitors have far greater financial resources and expertise in research and development, manufacturing, preclinical testing, conducting clinical trials, obtaining regulatory approvals and marketing approved products. Smaller or early stage companies may also prove to be significant competitors, particularly through collaborative arrangements with large and established companies.
14
Any product candidates that we successfully develop and commercialize will compete with existing therapies and new therapies that may become available in the future. The key competitive factors affecting the success of each of our product candidates, if approved, are likely to be their safety, efficacy, convenience, price, the level of proprietary and generic competition, and the availability of coverage and reimbursement from government and other third‑party payors. Our commercial opportunity could be reduced or eliminated if our competitors develop and commercialize products that are safer or more effective, have fewer or less severe side effects, or are more convenient or less expensive than any products that we may develop. Our competitors may also obtain FDA or other regulatory approval for their products more rapidly than we may obtain approval for ours, which could result in their establishing a strong market position before we are able to enter the market.
Sickle Cell Disease
Endari® is approved as a therapy to reduce the acute complications of SCD in adult and pediatric patients 5 years of age and older. The other drugs which are indicated to reduce the frequency of sickle cell crisis are hydroxyurea (marketed as DROXIA or Hydrea by Bristol-Myers Squibb Company and available in generic form), which is approved to reduce the frequency of painful crises and need for blood transfusions in patients with sickle cell anemia for the treatment of adults with SCD; Voxelotor (marketed as Oxbryta™ by Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc.) tablets for the treatment of SCD in adults and children 12 years of age and older; and crizanlizumab (marketed as Adakveo® by Novartis International AG) intravenous infusion approved to reduce the frequency of VOCs in adult and pediatric patients ages 16 years and older with SCD. Several companies are also developing product candidates for chronic treatment in SCD. Several other companies are in clinical trials to investigate new mechanisms of action for the chronic treatment of SCD.
Endari® also faces potential competition from one-time therapies for treating patients with severe SCD, including LentiGlobin BB305, which is being developed by bluebird bio, Inc. to treat SCD by inserting a functional human beta-globin gene into a patient’s hematopoietic stem cells, or HSCs, ex vivo and then transplanting the modified HSCs into the patient’s bloodstream. Bluebird has indicated its plans to pursue an accelerated development and approval pathway for its gene therapy product in SCD. Others are seeking to develop one-time therapies such as hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, gene therapy and gene editing, including gene editing using CRISPR. Attempts to develop a cure for SCD through gene therapy are in the early stages, but if these attempts were to succeed and receive regulatory approval, it could adversely affect the market for Endari®.
We are also aware of efforts to develop cures for SCD through approaches such as bone marrow. Although bone marrow transplant is currently available for SCD patients, its use is limited by the lack of availability of matched donors and by the risk of serious complications, including graft versus host disease and infection.
Endari® also may compete with non-prescription grade L-glutamine, which is widely available as a dietary supplement at substantially lower prices than Endari®. Dietary supplements may be marketed without FDA approval, are generally not reimbursed by payors and are not subject to the rigorous quality control standards required by regulatory authorities for prescription drug products. Also, unlike prescription drugs, manufacturers of dietary supplements may not make claims that the supplements will cure, mitigate, treat or prevent disease, and we are not aware of any reports in peer-reviewed literature regarding the effectiveness of non-prescription grade L-glutamine supplements in treating SCD in controlled clinical trials.
Oral Mucosa Epithelial Cell Sheet
Currently, the treatment of limbal stem cell deficiency (“LSCD”) patients varies based on the severity of the LSCD. Treatment may include the use of non-invasive procedures such as autologous serum drops, therapeutic scleral lens and corneal scraping to more invasive surgical procedures such as limbal stem cells or oral mucosal stem cells graft. The source of the transplanted tissue can be from cells from the patient’s healthy eye, matched living donors or cadavers. Transplantation with cells other than from the patient’s own tissue can cause serious complications, including graft-versus-host disease. Using oral mucosal epithelial cells (“OMEC”) of the LSCD patients lessens these risks. Specifically, the use of OMEC eliminates the risk of graft rejection, permits treatment of bilateral LSCD patients and allows engineered corneal epithelial cell sheets to be transplanted on LSCD patients’ corneas.
The development of OMEC technology to treat LSCD is in the early stages. We are not aware of any FDA approved treatments using OMEC for LSCD.
Research institutions outside the United States (e.g., The Centre Hospitalier National d’Ophtalmologie des Quinze Vingts lin Paris, France; Royan Institute Teheran in the Islamic Republic of Iran and Hospital San Raffaele in Milan, Italy)
15
are researching the transplantation of corneal cells from patients’ healthy eyes to reverse LSCD. However, results from these clinical trials were not published yet. This approach only allows uni-lateral LSCD patients to be treated and risks damage to the patients’ one healthy corneas.
The use of OMEC is a promising alternative for treat LSCD. For example, the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in South Korea, the He Eye Hospital in China and the Adisak Wongkajornsilp, Siriraj Hospital in Thailand are conducting phase 2 clinical trials using the OMEC. While many research institutions as are conducting such trials, we are not aware of published results of these studies.
Our OMEC-based regenerative medicine technology eliminates risks associated with donor-dependent transplantation and has shown some promising results in pilot studies (animal serum dependent) done by other groups in Japan and Europe. Our novel and innovative cell sheet therapy utilizes xeno-free media that allows harvested cell sheets to retain intact basal membranes and extracellular matrix (fibronectin, laminin, collagen type IV), reducing the inherent risks of suturing during transplantation. Our cell sheet therapy also makes possible to layer different types of cell sheets by harvesting the cell sheet without the use of harmful enzymes (trypsin or dispase) that may damage the cell‑based therapy and potentially to construct in vitro stratified tissue equivalents by alternately layering different types of harvested cell sheets to provide regenerated tissue architectures, resembling human tissues. This technique holds promise for the study of cell‑cell communications and angiogenesis in reconstructed, three‑dimensional environments, as well as for tissues engineering with complex, multicellular architectures and drug-screening.
Government Regulation
The FDA has granted Endari Orphan Drug designation and the EC has granted L-glutamine Orphan Medicinal designation for the treatment of SCD.
Orphan Drug Designation. The FDA has authority under the U.S. Orphan Drug Act to grant Orphan Drug designation to a drug or biological product intended to treat a rare disease or condition. This law defines a rare disease or condition generally as one that affects fewer than 200,000 individuals in the United States, or more than 200,000 individuals in the United States and for which there is no reasonable expectation that the cost of the development and distribution of the orphan product in the United States will be recovered from sales of the product. Being granted Orphan Drug designation provides tax benefits to mitigate expenses of developing the orphan product. More importantly, Orphan Drug designation provides seven years of market exclusivity if the product receives the first FDA approval for the disease or condition for which it was granted such designation and the indication for which approval is granted matches the indication for which Orphan Drug designation was granted. During the seven-year exclusivity period, Orphan Drug exclusivity precludes FDA approval of a marketing application for the same product for the same indication. Orphan Drug exclusivity is limited and will not preclude the FDA from approving the same product for the same indication if the same product is shown to be clinically superior to the product previously granted exclusivity. For example, if the same product for the same indication is shown to have significantly fewer side effects, the FDA may approve the second product despite the Orphan Drug exclusivity granted to the first product. In addition, a product that is the same as the orphan product may receive approval for a different indication (whether orphan or not) during the exclusivity period of the orphan product. Also, Orphan Drug market exclusivity will not bar a different product intended to treat the same orphan disease or condition from obtaining its own Orphan Drug designation and Orphan Drug exclusivity.
Orphan Medicinal status in the EU has similar benefits, including a ten-year marketing exclusivity period following marketing authorization in the EU.
505(b)(2) Applications. Under Section 505(b)(2) of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (“FD&C Act”) , a person may submit a NDA for which one or more of the clinical studies relied upon by the applicant for approval were not conducted by or for the applicant and for which the applicant does not have a right of reference or use from the person by or for whom the clinical studies were conducted. Instead, a 505(b)(2) applicant may rely on published literature containing the specific information (e.g., clinical trials, animal studies) necessary to obtain approval of the application. The 505(b)(2) applicant may also rely on the FDA’s finding of safety and/or effectiveness of a drug previously approved by the FDA when the applicant does not own or otherwise have the right to access the data in that previously approved application. The 505(b)(2) pathway to marketing authorization thus allows an applicant to submit a NDA without having to conduct its own studies to obtain data that are already documented in published reports or previously submitted NDAs. In addition to relying on safety data from the Phase 2 and 3 studies of Endari® and our previously approved product, NutreStore, we intend to take advantage of the 505(b)(2) pathway to the extent published literature will further support any NDA for PGLG.
16
Regulation by United States and foreign governmental authorities is a significant factor in the development, manufacture and expected marketing of our product candidates and in our ongoing research and development activities. The nature and extent to which such regulation will apply to us will vary depending on the nature of the product candidates we seek to develop.
Human therapeutic products, such as drugs, biologics and cell-based therapies, are subject to rigorous preclinical and clinical testing and other preapproval requirements of the FDA and similar regulatory authorities in other countries. Various federal and state statutes and regulations govern and influence pre- and post-approval requirements related to research, testing, manufacturing, labeling, packaging, storage, distribution and record keeping of such products to ensure the safety and effectiveness for their intended uses. The process of obtaining marketing approval and ensuring post approval compliance with the FD&C Act for drugs and biologics (and applicable provisions of the Public Health Service Act for biologics), and the regulations promulgated thereunder, and other applicable federal and state statutes and regulations, requires substantial time and financial resources. Any failure by us or our collaborators to obtain, or any delay in obtaining, marketing approval could adversely affect the marketing of any of our product candidates, our ability to receive product revenues, and our liquidity and capital resources.
The manufacture of these products is subject to cGMP regulations. The FDA inspects manufacturing facilities for compliance with cGMP regulations before deciding whether to approve a product candidate for marketing.
The steps required by the FDA before a new product, such as a drug, biologic or cell-based therapy, may be marketed in the United States include:
|
|
● |
completion of preclinical studies (during this stage, the treatment is called a development candidate); |
|
|
● |
the submission to the FDA of a proposal for the design of a clinical trial program for studying in humans the safety and effectiveness of the product candidate. This submission is referred to as an IND. The FDA reviews the IND to ensure it adequately protects the safety and rights of trial participants and that the design of the studies is adequate to permit an evaluation of the product candidate’s safety and effectiveness. The IND becomes effective within thirty days after the FDA receives the IND, unless the FDA notifies the sponsor that the investigations described in the IND are deficient and cannot begin; |
|
|
● |
the conduct of adequate and well controlled clinical trials, usually completed in three phases, to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of the product candidate for its intended use; |
|
|
● |
the submission to the FDA of a marketing application, a NDA, if the product candidate is a drug, that provides data and other information to demonstrate the product is safe and effective for its intended use (“BLA”), if the product candidate is a biologic that provides data and other information to demonstrate that the product candidate is safe, pure, and potent; and |
|
|
● |
the review and approval of the NDA by the FDA before the product candidate may be distributed commercially as a product. |
In addition to obtaining FDA approval for each product candidate before we can market it as a product, the manufacturing establishment from which we obtain it must be registered and is subject to periodic FDA post approval inspections to ensure continued compliance with cGMP requirements. If, as a result of these inspections, the FDA determines that any equipment, facilities, laboratories, procedures or processes do not comply with applicable FDA regulations and the conditions of the product approval, the FDA may seek civil, criminal, or administrative sanctions and/or remedies against us, including the suspension of the manufacturing operations, recalls, the withdrawal of approval and debarment. Manufacturers must expend substantial time, money and effort in the area of production, quality assurance and quality control to ensure compliance with these standards.
Preclinical testing includes laboratory evaluation of the safety of a product candidate and characterization of its formulation. Preclinical testing is subject to Good Laboratory Practice (“GLP”) regulations. Preclinical testing results are submitted to the FDA as a part of an IND which must become effective prior to commencement of clinical trials. Clinical trials are typically conducted in three sequential phases following submission of an IND. In Phase 1, the product candidate under investigation (and therefore often called an investigational product) is initially administered to a small group of humans, either patients or healthy volunteers, primarily to test for safety (e.g., to identify any adverse effects), dosage tolerance, absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion and clinical pharmacology, and, if possible, to gain early evidence of effectiveness. In Phase 2, a slightly larger sample of patients who have the condition or disease for which the investigational product is being
17
studied receive the investigational product to assess the effectiveness of the investigational product, to determine dose tolerance and the optimal dose range, and to gather additional information relating to safety and potential adverse effects. If the data show the investigational product may be effective and has an acceptable safety profile in the targeted patient population, Phase 3 studies, also referred to as pivotal studies or enabling studies, are initiated to further establish clinical safety and provide substantial evidence of the effectiveness of the investigational product in a broader sample of the general patient population, to determine the overall risk benefit ratio of the investigational product, and provide an adequate basis for physician and patient labeling. During all clinical studies, Good Clinical Practice (“GCP”) standards and applicable human subject protection requirements must be followed. The results of the research and product development, manufacturing, preclinical studies, clinical studies, and related information are submitted in a NDA to the FDA.
The process of completing clinical testing and obtaining FDA approval for a new therapeutic product, such as a drug, biologic or cell-based product, is likely to take years and require the expenditure of substantial resources. If a NDA is submitted, there can be no assurance that the FDA will file, review, and approve it. Even after initial FDA approval has been obtained, post market studies could be required to provide additional data on safety or effectiveness. Additional pivotal studies would be required to support adding other indications to the labeling. Also, the FDA will require post market reporting and could require specific surveillance or risk mitigation programs to monitor for known and unknown side effects of the product. Results of post marketing programs could limit or expand the continued marketing of the product. Further, if there are any modifications to the product, including changes in indication, manufacturing process, labeling, or the location of the manufacturing facility, a NDA supplement would generally be required to be submitted to the FDA prior to or corresponding with that change, or for minor changes in the periodic safety update report that must be submitted annually to the FDA.
The rate of completion of any clinical trial depends upon, among other factors, sufficient patient enrollment and retention. Patient enrollment is a function of many factors, including the size of the patient population, the nature of the trial, the number of clinical sites, the availability of alternative therapies, the proximity of patients to clinical sites, and the eligibility and exclusion criteria for the trial. Delays in planned patient enrollment might result in increased costs and delays. Patient retention could be affected by patient noncompliance, adverse events, or any change in circumstances making the patient no longer eligible to remain in the trial.
Failure to adhere to regulatory requirements for the protection of human subjects, to ensure the integrity of data, other IND requirements, and GCP standards in conducting clinical trials could cause the FDA to place a “clinical hold” on one or more studies of a product candidate, which would stop the studies and delay or preclude further data collection necessary for product approval. Noncompliance with GCP standards would also have a negative impact on the FDA’s evaluation of a NDA. If at any time the FDA finds that a serious question regarding data integrity has been raised due to the appearance of a wrongful act, such as fraud, bribery or gross negligence, the FDA may invoke its Application Integrity Policy (“AIP”) under which it could immediately suspend review of any pending NDA or refuse to accept the submission of a NDA as filed, require the sponsor to validate data, require additional clinical studies, disapprove a pending NDA or withdraw approval of marketed products, as well as require corrective and preventive action to ensure data integrity in future submissions. Significant noncompliance with IND regulations could result in the FDA not only refusing to accept a NDA as filed but could also result in enforcement actions, including civil and administrative actions, civil money penalties, criminal prosecution, criminal fines and debarment. Whether or not FDA approval has been obtained, approval of a product by regulatory authorities in foreign countries must be obtained prior to the commencement of marketing the product in those countries.
The requirements governing the conduct of clinical trials and product approvals vary widely from country to country, and the time required for approval might be longer or shorter than that required for FDA approval. Although there are some procedures for unified filings for some European countries, in general, each country at this time has its own procedures and requirements.
In most cases, if the FDA has not approved a product candidate for sale in the United States, the unapproved product may be exported to any country in the world for clinical trial or sale if it meets U.S. export requirements and has marketing authorization in any listed country without submitting an export request to the FDA or receiving FDA approval to export the product, as long as the product meets the regulatory requirements of the country to which the product is being exported. Listed countries include each member nation in the European Union or the European Economic Area, Canada, Australia, New Zealand, Japan, Israel, Switzerland and South Africa. If an unapproved product is not approved in one of the listed countries, the unapproved product may be exported directly to an unlisted country if the product meets the requirements of the regulatory authority of that country, and the FDA determines that the foreign country has statutory or regulatory requirements similar or equivalent to the United States.
In addition to the regulatory framework for product approvals, we and our collaborative partners must comply with federal, state and local laws and regulations regarding occupational safety, laboratory practices, the use, handling and
18
disposition of radioactive materials, environmental protection and hazardous substance control, and other local, state, federal and foreign regulation. All facilities and manufacturing processes used by third parties to produce our product candidates for clinical use in the United States and our products for commercialization must be in compliance with cGMP requirements and are subject to periodic regulatory inspections. The failure of third-party manufacturers to comply with applicable regulations could extend, delay or cause the termination of clinical trials conducted for our product candidates or the withdrawal of our products from the market. The impact of government regulation upon us cannot be predicted and could be material and adverse. We cannot accurately predict the extent of government regulation that might result from future legislation or administrative action.
Patents, Proprietary Rights and Know‑How
Our success will depend in part on our ability to obtain patents and otherwise preserve the intellectual property rights relating to the design, operation, sale and distribution of our products. We intend to seek patents on our products when we deem it commercially appropriate. The process of seeking patent protection can be lengthy and expensive, and there can be no assurance that patents will be issued for currently pending or future applications or that our existing patents or any new patents issued will be of sufficient scope or strength or provide meaningful protection or any commercial advantage to us. We may be subject to, or may initiate, litigation or patent office interference proceedings, which may require significant financial and management resources. The failure to obtain necessary licenses or other rights or the advent of litigation arising out of any such intellectual property claims could have a material adverse effect on our operations.
We have relied to date on a combination of patent licenses, trademark rights, trade secret protection, distribution agreements, manufacturing agreements, manufacturing capability and other unpatented proprietary information to protect our intellectual property rights. While we do not currently own any issued patents directed to the treatment of sickle cell anemia, we do own patent applications in that area, as well as issued patents and patent applications directed to the treatment of diverticulosis, diabetes and hypertriglyceridemia. We furthermore have Orphan Drug market exclusivity for the treatment of sickle cell anemia with Endari® in the United States (through July 7, 2024) and in the EU (ten years from the approval date, if approved).
We also rely on employee agreements to protect the proprietary nature of our products. We require that our officers and key employees enter into confidentiality agreements that require these officers and employees to assign to us the rights to any inventions developed by them during their employment with us. All the confidentiality agreements include non-solicitation provisions that remain effective during the course of employment and for periods following termination of employment.
Patents
We have issued patents related to compositions including PGLG and methods involving administration of PGLG for the treatment of diverticulosis in the United States, Europe, Japan, Australia, India, Mexico, China, Indonesia, Korea and Russia. A patent application related to the same subject matter has been allowed in the United States, and associated patent applications are currently pending in the United States, the EU, Brazil, India, Korea and Russia.
Patent directed to compositions for decreasing HbA1C levels in individuals who are shown to have average blood sugar levels in the diabetic range has issued in Japan and Indonesia; a related Philippines patent application has been allowed. Associated applications are currently pending in the United States, Europe, Brazil, India, China and Indonesia.
The company has issued patents directed to the treatment of hypertriglyceridemia in Japan and the Philippines. A corresponding European patent application has been allowed. Associated applications are pending in the United States, Europe, Brazil, India, China and Indonesia.
A patent application directed to the treatment of sickle cell using a multi-component composition is pending in the United States and Europe. An international application directed to the same invention has been filed under the Patent Cooperation Treaty.
HbA1C levels are one of the best indicators of whether diabetics and prediabetics have blood sugar levels under control, through therapeutic application of L-glutamine. Diabetes is a chronic disease that occurs when the pancreas is no longer able to make insulin, or when the body cannot make good use of the insulin it produces. People with diabetes have an increased risk of developing a number of serious health problems including cardiovascular disease, kidney failure and blindness. Japan has more than 7 million diagnosed cases of diabetes, which represents about 7.6% of Japanese between the ages of 20 and 79. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there are an estimated 29 million
19
Americans living with diabetes and an estimated 86 million Americans with prediabetes, a serious health condition that can increase a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Licenses and Promotional Rights Agreements
In June 2016, we entered into a non‑exclusive agreement with CellSeed and Dr. Kohji Nishida for the development of CAOMECS technology. Under this agreement, upon commercialization we are required to pay royalties based upon net sales.
Trademarks
We currently own U.S. trademark registrations for “Emmaus Medical” and “Endari” and were recently granted a trademark registration for “Xyndari™” (as Endari® will be marketed if approved) in the EU. This Annual Report also contains trademarks, service marks, trade names and copyrights of other companies, which are the property of their respective owners. Solely for convenience, these trademarks, service marks, trade names and copyrights may appear without the® or TM symbols, but such references are not intended to indicate that we do not assert, to the fullest extent under applicable law, our rights or the rights of the applicable licensor to the same.
Employees
As of January 5, 2021, we had 55 employees, 53 of whom were full time. We have not experienced any work stoppages and we consider our relations with our employees to be good.
Corporate Information
We were incorporated in Delaware on March 20, 1987 under the name Age Research, Inc. Prior to January 16, 2007, our company (then called Strativation, Inc.) existed as a “shell company” with nominal assets and whose sole business was to identify, evaluate and investigate various companies to acquire or with which to merge. On January 16, 2007, we entered into an Agreement and Plan of Merger with CNS Response, Inc., and CNS Merger Corporation, our wholly owned subsidiary, pursuant to which CNS Merger Corporation merged with and into CNS Response, Inc., which survived the merger. On March 7, 2007, we changed our corporate name to CNS Response, Inc. On November 2, 2015, we changed our corporate name to MYnd Analytics, Inc. On July 17, 2019, after completion of our merger transaction with EMI described in the lead-in to this Item 1, we changed our name to “Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc.”
Our principal executive offices and corporate offices are located at 21250 Hawthorne Boulevard, Suite 800, Torrance, California, and our telephone number at that address is (310) 214‑0065. We maintain an Internet website at the following address: www.emmausmedical.com. The information on our website is not incorporated by reference in this Annual Report or in any other filings we make with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
An investment in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. If any of these risks occur, our business, financial condition, results of operations, or cash flow could be materially and adversely affected. This could cause the market price of our common stock to decline, resulting in a loss of all or part of your investment.
Risks Related to Our Business
We have operated at a loss and may continue to operate at a loss for the foreseeable future.
We have operated at a loss due to substantial expenditures related to commercialization of Endari®, pursuit of marketing authorization of Endari® outside the U.S., research and development of our other product candidates, interest on our outstanding indebtedness and general and administrative expenses. We incurred net losses of $54.8 million and $72.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively, and had an accumulated deficit of $226.2 million as of December 31, 2019. There is no assurance that we will be able to increase our Endari® sales or become profitable or that we will have sufficient capital resources to fund our operations until we are able to generate sufficient revenues to become profitable.
20
We are dependent on the commercial success of our only approved product, Endari®.
Our ability to become profitable will depend upon the commercial success of Endari®. In addition to the risks discussed elsewhere in this section, our ability to generate future revenues from Endari® sales will depend on a number of factors, including, but not limited to:
|
|
• |
achievement of broad market acceptance and coverage by third-party payors for Endari®; |
|
|
• |
the effectiveness of our in-house commercialization team and other efforts in marketing and selling Endari®; |
|
|
• |
our ability to compete effectively against competing products, including Oxbryta™ (voxelotor) and Adakveo® (crizanlizumab); |
|
|
• |
contract manufacturers’ ability to successfully manufacture commercial quantities of Endari® at acceptable cost levels and in compliance with regulatory requirements; |
|
|
• |
our ability to maintain a cost-efficient commercial organization and, to the extent we seek to do so, successfully partner with third parties; |
|
|
• |
our ability to effectively work with physicians to ensure that their patients have access to Endari® and fill and refill prescriptions to adhere to their twice-daily regimen; |
|
|
• |
the efficacy and safety of Endari®; and |
|
|
• |
our ability to comply with ongoing regulatory requirements. |
Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with our commercialization efforts, we are unable to predict the extent to which we will generate revenues from Endari® sales or the timing for when or the extent to which we will become profitable, if ever. Even if we do achieve increased revenues from Endari® sales and become profitable, we may not be able to sustain our revenues or maintain or increase our profitability on an ongoing basis.
We are dependent on financing to sustain our operations, and there is substantial doubt regarding our ability to continue as a going concern.
Unless and until we become profitable, we will continue to depend upon proceeds from sales of our debt or equity securities (including the exercise of options and warrants) or other financing arrangements, and to a lesser extent, upon payments from potential strategic partners and licensees, to generate funds needed to finance our business and operations. As of December 31, 2019, we had cash and cash equivalents of $1.8 million, and investments in marketable securities of $27.9 million, which consisted of common shares of Telecon RF Pharmaceutical, Inc., or Telcon, pledged by us to secure our obligations under our API Supply Agreement with Telcon. The API Supply Agreement was amended on December 23, 2019 to release the Telcon shares from the pledge and to permit us to sell the shares in exchange for our agreement to use a portion of the net sale proceeds to purchase a 10-year convertible bond of Telcon be pledged to Telcon pursuant to the API Supply Agreement in substitution of the pledge of the Telcon shares. On September 28, 2020, we entered into a convertible bond purchase agreement pursuant to which we purchased at face value a convertible bond of Telcon in the principal amount of KRW30 billion, or approximately $26.1 million, on the terms described in the convertible bond purchase agreement. We purchased the convertible bond with a portion of the net proceeds from the sale of Telcon common shares owned by us as reported in our October 14, 2020 press release. As contemplated by our December 23, 2019 agreement with Telcon, the convertible bond and any proceeds therefrom replace our former Telcon shares and proceeds therefrom as collateral security under the API Supply Agreement with Telcon.
Depending upon our future results of operations and other factors, we will need additional financing to fund our business and operations, including our commitment to provide funding to EJ Holdings, Inc. described below under “Risks Relating to Our Investment in EJ Holdings, Inc.,” and will continue to be dependent on future financing until such time, if ever, as we can generate sufficient revenues to become profitable. We have no current understandings or commitments to obtain any additional financing. Accordingly, we may not be able to obtain future financing on favorable terms, or at all. If we are unable to obtain needed future financing, we may have to curtail some of our business activities or modify our business plans and may be unable to meet our commitment to provide funding to EJ Holdings, Inc. Due to the uncertainty of our ability to meet our current and future operating and capital expenses, there is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
Because we were unable to timely file this Annual Report and other periodic reports under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”), we are ineligible to register securities on the short-form Registration Statement on Form S-3 until we have timely filed all required reports under the Exchange Act for the 12 months prior to filing a
21
Registration Statement on Form S-3. The inability to utilize Form S-3 may adversely impact our ability to raise capital in a timely manner and increase transaction costs.
In light of the foregoing, there is substantial doubt regarding our ability to continue as a going concern and the report of our independent public accounting firm on our financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2019 contains a going concern qualification.
The COVID-19 pandemic may adversely affect our revenues, results of operations and financial condition and impact our ability to obtain needed financing.
COVID-19 and the various precautionary measures taken by many governmental authorities around the world to limit its spread has had a severe effect on global markets and the global economy. The extent to which the coronavirus impacts our business and operations will depend on future developments, which are highly uncertain and cannot be predicted, including new information which may emerge concerning the severity of COVID-19 and the nature and extent of governmental actions taken to contain it or treat its impact and the availability, cost, effectiveness and public acceptance of any FDA-approved vaccines, among others. COVID-19 and official actions in response to it have caused a major slowdown in overall economic activity in the U.S. and elsewhere, curtailed consumer spending and made it more challenging to adequately staff and manage our business and operations, including our accounting and financial operations. Although COVID-19 and official responses have not had a material adverse effect on our Endari® sales to date, COVID-19 or future official responses may deter or prevent sickle cell disease, or SCD, patients from traveling to see their doctors or filling or refilling their prescriptions for Endari®, our one approved product, which could cause a temporary or prolonged decline in our revenues and have a material adverse effect on our results of operation and financial condition. COVID-19 or the governmental response may adversely affect the timing and conduct of clinical studies or the ability of regulatory bodies to consider or grant approvals with respect to Endari® or our prescription grade L-glutamine drug candidates or oversee the development of our drug candidates, may further divert the attention and efforts of the medical community to coping with COVID-19 and disrupt the marketplace in which we operate. For example, we experienced a temporary disruption earlier in 2020 in patient enrollment in our Pilot/Phase I study of our prescription grade L-glutamine oral powder in diverticulosis, but patient enrollment has resumed. Any outbreak of COVID-19 among our executives or key employees or their families and loved ones could disrupt our management and operations and adversely affect our Endari® sales, results of operations and financial condition. The foregoing factors could also have an adverse effect on the market price of our common stock or the value of our other outstanding securities.
We will continue to depend upon proceeds from loans, including loans from related parties, and sales of our debt or equity securities to generate funds needed to finance our business and operations. We have no commitment from third parties to provide us with any additional financing. Until the U.S. economy and capital markets stabilize, our ability to obtain future financing is likely to be challenging. We regularly explore possible financing alternatives and intend to consider emergency federal or state funding that may be available to companies affected by COVID-19. There is no assurance that we will qualify for any government funding or otherwise be able to obtain any needed financing.
We may expend our limited resources to pursue a product candidate or indication and fail to capitalize on product candidates or indications for which there is a greater likelihood of commercial success.
Because we have limited financial and management resources, we focus on a limited number of research programs and product candidates. As a result, we may forego or delay pursuit of opportunities with other product candidates or for other indications that later prove to have greater commercial potential. Our resource allocation decisions may cause us to fail to capitalize on viable product candidates or profitable market opportunities. Our spending on current and future research and development programs and product candidates for the specific indications we selected may not yield any commercially viable products. If we do not accurately evaluate the commercial potential or target market for a particular product candidate, we may relinquish valuable rights to that product candidate through collaboration, licensing or other arrangements in cases in which it would have been more advantageous for us to retain sole development and commercialization rights.
We face intense competition, and if our competitors are successful in marketing or develop alternative treatments our commercial opportunities may be reduced or eliminated.
The pharmaceutical industry is characterized by rapidly advancing technologies, intense competition and a strong emphasis on developing proprietary therapeutics. We face competition from a number of sources, some of which may target the same indication as Endari®, such as pharmaceutical companies, including generic drug companies, biotechnology companies, drug delivery companies and academic and research institutions, many of which have greater financial resources, marketing capabilities, including well-established sales forces, manufacturing capabilities, research and development capabilities, experience in obtaining regulatory approvals for product candidates than do we. For example, in late 2019 the FDA approved a
22
new drug application, or NDA, submitted by Novartis, permitting the marketing of ADAKVEO® (crizanlizumab-tmca) to reduce the frequency of vaso-occlusive crises in adults and pediatric patients aged 16 years and older with SCD. ADAKVEO®, which is administered by intravenous infusion every four weeks, is a selectin blocker humanized IgG2 kappa monoclonal antibody that binds to P-selectin. Also, in late 2019, Global Blood Therapeutics, Inc. (“GBT”) announced that the FDA approved its NDA for Oxbryta™ (voxelotor) tablets for the treatment of SCD in adults and children 12 years of age and older. Oxbryta™ is an oral, once-a-day therapy intended to treat SCD by targeting hemoglobin polymerization. Both Novartis and GBT have far greater financial, sales and marketing resources than our company and there is no assurance that we will be able to compete effectively with ADAKVEO® or Oxbryta™ as a stand-alone therapy or that Endari® will gain widespread use as an adjunct to the use of ADAKVEO® or Oxbryta™. If we are unable to compete effectively or successfully position Endari® as a complementary therapy, our Endari® sales and results of operation may suffer, which could have a material, adverse effect on our financial condition. We also face competition from non-prescription grade L-glutamine supplements. L-glutamine is manufactured in large quantities, primarily by a few large chemical companies, and processed and sold as a nutritional supplement. The sale of non-prescription grade L-glutamine nutritional supplements at prices lower than the price that we charge for Endari® could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
If we are unable to achieve and maintain adequate levels of coverage and reimbursement for Endari®, on reasonable pricing terms, its commercial success may be severely hindered.
Successful sales of Endari® depend on the availability of adequate coverage and reimbursement from third-party payors and governmental healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid. Patients who are prescribed medicine for the treatment of their conditions generally rely on third-party payors to reimburse all or part of the costs associated with their prescription drugs. Coverage decisions may depend upon clinical and economic standards that disfavor new drug products when more established or lower cost therapeutic alternatives are already available or subsequently become available. Assuming we obtain coverage for Endari®, the resulting reimbursement payment rates might not be adequate or may require co-payments that patients find unacceptably high. Patients are unlikely to use Endari® unless reimbursement is adequate to cover a significant portion of the cost of Endari®. Future coverage and reimbursement will likely be subject to increased restrictions in the U.S. Third-party coverage and reimbursement for Endari® may cease to be available or adequate in the U.S., which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
In addition, the market for Endari® will depend significantly on access to third-party payors’ drug formularies, which are lists of medications for which third-party payors provide coverage and reimbursement. The competition in the industry to be included in such formularies may lead to downward pricing pressures on us. Also, third-party payors may refuse to include Endari® in their formularies or otherwise restrict patient access to Endari® if a less costly generic equivalent or other alternative treatment is available.
The majority of Endari® sales are to a few customers and loss of a customer could adversely affect our results of operations.
The majority of Endari® sales are to specialty distributors and specialty pharmacies who, in turn, resell Endari® to pharmacies, hospitals and other customers. The loss of any of these specialty distributors and specialty pharmacies’ accounts or a material reduction in their Endari® purchases could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
In addition, the distribution network for pharmaceutical products in the U.S. has undergone, and may continue to undergo, significant consolidation marked by mergers and acquisitions. As a result, a smaller number of large distributors control a significant share of the market, which has increased, and may continue to increase, competitive and pricing pressures on pharmaceutical products. We cannot assure you that we can manage these pricing pressures or that specialty distributor and specialty pharmacy purchases will not fluctuate unexpectedly from period to period.
The market exclusivity for Endari® for SCD is limited, which could adversely affect our ability to compete in the market and adversely affect the commercial success of Endari®.
The exclusivity protections that protect Endari® for use for SCD are limited in ways that may affect our ability to effectively exclude third parties from competing against us. In particular:
|
|
• |
Orphan Drug market exclusivity protection for Endari® for SCD will expire July 7, 2024. |
|
|
• |
Orphan Drug designation will not preclude the FDA from granting Orphan Drug designation to another sponsor developing the same drug for the same indication, approving such other drug before our drug would receive FDA approval, granting Orphan Drug designation and approving such other drug after we would receive approval if such drug is considered clinically superior to our product, approving a product that is the same as our product for a different indication, or approving a different product intended to treat SCD; |
23
|
|
• |
there are many countries, including some key markets for Endari®, in which we do not have intellectual property coverage and where neither orphan drug nor data exclusivity is available. |
These limitations and any reductions in our expected protection, including other products that could be approved by FDA under the Orphan Drug Act, may subject Endari® to greater competition than we expect and could adversely affect our ability to generate revenue from Endari®, perhaps materially. These circumstances may also impair our ability to obtain license partners or other international commercialization opportunities on terms acceptable to us, if at all.
Many of our potential customers are in markets with underdeveloped health care systems.
Our only approved product, Endari®, is a prescription-grade L-glutamine oral powder treatment for sickle cell anemia and sickle ß0-thalassemia, two of the most common forms of SCD. SCD is a genetic blood disorder that affects 20 million - 25 million people worldwide and occurs primarily among those whose ancestors are from regions including sub-Saharan Africa, South America, the Caribbean, Central America, the Middle East, India and Mediterranean regions such as Turkey, Greece and Italy. Thus, while SCD affects people throughout the world, the prevalence of SCD is higher in certain geographies, such as central and sub-Saharan Africa and the Caribbean, that currently have underdeveloped health care systems or significantly lower rates of health insurance coverage and incidence of these conditions in the United States is relatively low. Furthermore, the majority of people in many of these geographies are low-income and may be unable to afford Endari®. These factors may ultimately limit our addressable market. Our ability to achieve profitability may be adversely impacted if we are unable to access markets with greater prevalence of SCD, or if there are insufficient SCD patients in geographies with more well-developed health care systems.
A variety of other risks associated with marketing any of our products internationally could hurt our business.
We are seeking regulatory approval for Endari® for SCD outside of the U.S. but may not be successful. For example, in January 2018, the European Medicines Agency, or EMA, provided their agreement on the pediatric investigation plan, or PIP, for our prescription grade L-glutamine oral powder in SCD and we filed with the EMA an application for marketing authorization, or MAA, in the EU. In May 2019, we announced that the EMA’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use, or CHMP, had adopted a negative opinion regarding our MAA based upon the CHMP’s position that our main clinical study did not conclusively support the efficacy of the treatment in SCD patients. In light of the CHMP’s opinion, we withdrew our MAA in September 2019 to consider pursuing alternative decentralized and centralized regulatory pathways for obtaining marketing authorization in the EU or one or more EU countries. There is no assurance that we will be successful in obtaining marketing authorization in the EU or other jurisdictions outside the U.S. If we obtain marketing authorization, we expect that we will be subject to additional risks related to operating in foreign countries including:
|
|
• |
business interruptions resulting from geopolitical actions, including war and terrorism or actual or potential public health emergencies, including the recent coronavirus (COVID-19) disease outbreak. |
|
|
• |
differing regulatory requirements in foreign countries; |
|
|
• |
the potential for parallel importing (i.e., when a local seller, faced with high or higher local prices, opts to import goods from a foreign market with low or lower prices rather than buying them locally); |
|
|
• |
unexpected changes in tariffs, trade barriers, price and exchange controls and other regulatory requirements; |
|
|
• |
economic weakness, including inflation or political instability in particular foreign markets; |
|
|
• |
compliance with tax, employment, immigration and labor laws for employees living or traveling abroad; |
|
|
• |
foreign taxes, including withholding of payroll taxes; |
|
|
• |
foreign currency fluctuations, which could result in increased operating expenses and reduced revenues, and other obligations related to doing business in another country; |
|
|
• |
difficulties staffing and managing foreign operations; |
|
|
• |
workforce uncertainty in countries where labor unrest is more common than in the U.S.; |
|
|
• |
potential liability under the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act or comparable foreign regulations; |
|
|
• |
challenges enforcing our contractual and intellectual property rights, especially in foreign countries that do not respect and protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as the U.S.; and |
24
|
|
• |
production shortages resulting from any events affecting raw material supply or manufacturing capabilities abroad. |
These and other risks associated with our potential international operations may compromise our ability to achieve or maintain profitability.
We may not be able to anticipate the demand for and appropriate supply of Endari®.
Our sales of Endari® can be greatly affected by the inventory levels our distributors carry. We monitor inventory of Endari® using a combination of methods. However, our estimates of specialty distributor inventories may differ significantly from actual inventory levels. Significant differences between actual and our estimated inventory levels may result in excessive production (requiring us to hold substantial quantities of unsold inventory), inadequate supplies of products in distribution channels, insufficient product available at the retail level, and unexpected increases or decreases in orders from our specialty distributors. These changes may cause our revenues to fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter, and in some cases may cause our operating results for a quarter to be below our expectations or the expectations of securities analysts or investors. In addition, at times we offerdiscounts to our customers in advance of Endari® price increases or as an incentive for bulk orders of Endari®, which discounts may result in specialty distributor purchases in excess of customer demand, resulting in reduced specialty distributor purchases in later periods and substantial fluctuations in our results of operations from period to period. If our financial results are below analysts’ or investors’ expectations, the market price of our common stock may be adversely affected.
If the L-glutamine manufacturers upon which we rely fail to produce in the volumes and quality that we require on a timely basis, or fail to comply with stringent regulations applicable to pharmaceutical manufacturers, we may face interruptions in the commercialization of, or be unable to meet demand for, our L- glutamine based products, and may lose any marketing exclusivity and potential revenues.
We do not currently have our own manufacturing capabilities and depend entirely upon third-party manufacturers for commercial supplies of Endari® and clinical supplies of prescription grade L‑glutamine used in our product candidates under development. Our third-party manufacturers and other key suppliers may experience manufacturing or production difficulties and may not be able to expand their capacity or to produce additional supplies for us in the event that demand for Endari® or our requirements for prescription grade L-glutamine were to increase substantially. If these manufacturers or key suppliers were to encounter any of these difficulties, or otherwise fail to comply with their regulatory and contractual obligations, our ability to expand our Endari® sales or timely launch any potential product candidate, if approved, would be jeopardized. If we are unable to ensure adequate supply of an orphan drug for which we have obtained marketing exclusivity, the FDA may approve another drug for marketing, which could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial condition.
We currently obtain substantially all our prescription grade L-glutamine from a single Japanese supplier, Ajinomoto Aminoscience LLC, or Ajinomoto. We intend to continue to rely on Ajinomoto to produce our pharmaceutical grade L-glutamine, but we have not entered into, and may not be able to establish, long-term supply agreements with this key supplier on acceptable terms. Furthermore, pursuant to a letter of intent with Ajinomoto, we have agreed to purchase from Ajinomoto substantially all L-glutamine that we will need for our commercial products. If Ajinomoto were to experience any manufacturing or production difficulties producing prescription grade L-glutamine, or we were unable to purchase sufficient quantities of prescription grade L‑glutamine on acceptable terms, it could interrupt sales of Endari® and have a material, adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, all manufacturers, packers, distributors and suppliers of pharmaceutical products must comply with applicable cGMP regulations for the manufacture of pharmaceutical products, which are enforced by the FDA through its facilities inspection program. If our manufacturers and key suppliers are not in compliance with cGMP requirements, it may result in a delay of approval for products undergoing regulatory review or the inability to meet market demands for any approved products, particularly if these sites are supplying single source ingredients required for the manufacture of any potential product. Furthermore, each manufacturing facility used to manufacture drug or biological products is subject to FDA inspection and must meet cGMP requirements. As a result, if one of the manufacturers that we rely on shifts production from one facility to another, the new facility must undergo a preapproval inspection and, for biological products, must be licensed by regulatory authorities prior to being used for commercial supply. A failure to comply with any applicable manufacturing requirements, including cGMP requirements, could delay or prevent the promotion, marketing or sale of our products. If the FDA or any other applicable regulatory authorities do not approve the facilities for the manufacture of Endari® or if they withdraw any such approval in the future, we may need to find alternative manufacturing facilities, which would significantly impact our ability to commercially supply Endari®.
25
If the safety of any quantities supplied is compromised due to a third-party manufacturer’s failure to comply with or adhere to applicable laws or for other reasons, we may be liable for injuries suffered by patients who have taken such products and we may not be able to obtain regulatory approval for or successfully commercialize our products.
We expect to rely on third parties to conduct future clinical trials of our product candidates and those third parties may not perform satisfactorily, including failing to meet deadlines for the conduct of such trials.
We engaged a third-party contract research organization (“CRO”) to conduct our clinical trials for Endari® and expect to engage a CRO to conduct any further required clinical trials of Endari® and any clinical trials with respect to any of our product candidates that may progress to clinical development. We expect to continue to rely on third parties, such as CROs, clinical data management organizations, medical institutions and clinical investigators, to conduct those clinical trials. Agreements with such third parties might terminate for a variety of reasons, including a failure to perform by the third parties. If we need to enter into alternative arrangements, it could delay our product development activities.
Our reliance on these third parties for research and development activities reduces our control over these activities but does not relieve us of our responsibilities. For example, we will remain responsible for ensuring that each of our clinical trials is conducted in accordance with the general investigational plan and protocols for the trial. Moreover, the FDA requires us to comply with standards, commonly referred to as GCPs for conducting, recording and reporting the results of clinical trials to ensure that data and reported results are credible and accurate and that the rights, integrity and confidentiality of trial participants are protected. We also are required to register ongoing clinical trials and post the results of completed clinical trials on a government-sponsored database, www.ClinicalTrials.gov, within specified timeframes. Failure to do so can result in the FDA refusing to accept a NDA for the product candidate under study, fines, adverse publicity and civil and criminal sanctions.
Furthermore, these third parties may also have relationships with other entities, some of which may be our competitors. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties, meet expected deadlines or conduct our clinical trials in accordance with regulatory requirements and our stated protocols, we will not be able to obtain, or may be delayed in obtaining, marketing approvals for our product candidates and will not be able to, or may be delayed in our efforts to, successfully commercialize them as products. We also expect to rely on other third parties to store and distribute supplies of our product candidates for clinical trials of them. Any performance failure on the part of our distributors could delay clinical development or marketing approval of our product candidates or commercialization of them as products, producing additional losses and depriving us of potential revenue.
Delays in the commencement, enrollment and completion of clinical trials could result in increased costs to us and delay in our ability to develop and obtain regulatory approval for product candidates. The commencement, enrollment and completion of clinical trials can be delayed for a variety of reasons, including delays or difficulties in enrolling patients due to unforeseen natural disasters, public health crises, political crises and other catastrophic events or other events outside of our control, such as the recent emergence and spread of COVID-19, which may cause participants to not want to participate in these trials or otherwise have any unnecessary contact with the medical community.
Endari® may cause undesirable side effects or have other unexpected properties that could result in post-approval regulatory action.
Although Endari® was found to be safe and generally well tolerated in clinical trials, the most common side effects seen with Endari® included constipation, nausea, headache, pain in the stomach area, cough, pain in the hands or feet, back pain, and chest pain. If we or others identify previously unknown undesirable side effects, or other previously unknown problems, caused by Endari® or other products with the same or related active ingredients, a number of potentially significant negative consequences could result, including:
|
|
• |
regulatory authorities may withdraw their approval of Endari®; |
|
|
• |
we may need to recall Endari®; |
|
|
• |
we may need to add warnings or narrow the indication in the product label or to create a Medication Guide outlining the risks of such side effects for distribution to patients; |
|
|
• |
we may be required to change the way Endari® is administered or modify Endari® in some other way; |
|
|
• |
the FDA may require us to conduct additional clinical trials or costly post-marketing testing and surveillance to monitor the safety or efficacy of the product; |
|
|
• |
we could be sued and held liable for harm caused to patients; and |
26
Any of the above events resulting from undesirable side effects or other previously unknown problems could prevent us from achieving or maintaining market acceptance of Endari® and could substantially increase the costs of commercializing Endari®.
We face potential product liability exposure relating to Endari® and, if successful claims are brought against us, we may incur substantial liability if our insurance coverage for those claims is inadequate.
The commercial use of Endari® will expose us to the risk of product liability claims despite the fact it is approved for commercial sale by the FDA and manufactured in facilities licensed and regulated by the FDA. Any side effects, manufacturing defects, misuse or abuse associated with Endari® could result in injury to a patient or even death and product liability claims against us. In addition, a liability claim may be brought against us even if Endari® merely appears to have caused an injury. Product liability claims may be brought against us by consumers, health care providers, pharmaceutical companies or others selling or otherwise coming into contact with Endari® and we could incur substantial liabilities.
In addition, regardless of merit or eventual outcome, product liability claims may result in:
|
|
• |
decreased demand for Endari®; |
|
|
• |
impairment of our business reputation; |
|
|
• |
recall or withdrawal of Endari® from the market; |
|
|
• |
costs related to litigation; |
|
|
• |
distraction of management’s attention from our business; |
|
|
• |
substantial monetary awards to patients or other claimants; or |
|
|
• |
loss of revenues. |
We maintain product liability insurance coverage and carry commercial excess and umbrella coverage, but our insurance coverage may not be sufficient to cover all of our product liability related expenses or losses and may not cover us for any consequential expenses or losses we may suffer. We may not be able to continue to maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost, in sufficient amounts or upon adequate terms to protect us against losses due to product liability. Large judgments have been awarded in class action or individual lawsuits based on drugs that had unanticipated side effects, including side effects that are less severe than those of Endari®. A successful product liability claim or series of claims brought against us could cause the value of our common stock to decline and, if judgments exceed our insurance coverage, could decrease our cash and have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
The use of any of our product candidates in clinical trials and in the market may expose us to liability claims.
We are exposed to potential liability risks inherent in the testing and manufacturing of our product candidates and marketing of any products. While in clinical stage testing, our product candidates could potentially harm people or allegedly harm people and we may be subject to costly and damaging product liability claims. Informed consent and contractual limitations on payments for subject injury or waivers we obtain may not be enforceable and may not protect us from liability or the costs of product liability litigation. Although we carry clinical product liability insurance, it may not be sufficient to cover future claims.
In addition, in some cases the contractors on which we rely for manufacturing our product candidates may indemnify us for third-party claims brought against us arising from matters for which these contractors are responsible. We could be materially and adversely affected if we were required to pay damages or incur defense costs in connection with a claim outside the scope of indemnity or insurance coverage, if the indemnity is not performed or enforced in accordance with its terms, or if our liability exceeds the amount of applicable insurance or indemnity. In addition, there can be no assurance that insurance will continue to be available in amounts and on terms acceptable to us, if at all, to cover any potential claims or liabilities.
We will need to increase the size and complexity of our organization in the future, and we may experience difficulties in managing our growth and executing our growth strategy.
Our management and personnel, systems and facilities currently in place may not be adequate to support our business plan and future growth. Continued operations and growth require that we manage our commercialization activities for Endari® and product development efforts effectively and in a cost-effective manner. We will also need to continue to improve our
27
operational, financial, management and regulatory compliance controls and reporting systems and procedures. We will need to expand our scientific, sales and marketing, managerial, operational, financial and other resources to support our planned commercialization activities.
We will need to attract and retain sufficient talented employees and scientific collaborators.
Historically we have utilized, and continue to utilize, part-time outside consultants to perform certain tasks, including tasks related to accounting and finance, compliance programs, clinical trial management, regulatory affairs, formulation development and other drug development functions. Our growth strategy related to Endari® may entail expanding our use of consultants to implement these and other tasks going forward. There can be no assurance that we will be able to manage our existing consultants or engage other competent consultants, as needed, on economically reasonable terms.
In addition, we have scientific and clinical advisors who assist us in our commercialization strategies for Endari® and our other product development efforts, including development of new medical indications for L-glutamine-based products. Although we have established research collaborations, we cannot assure you that our relationships with our research collaborators and scientific and clinical advisors will continue or that we will be able to attract additional research partners and advisors. Without such scientific relationships to assist in our research and development, we may not be able to successfully develop our product candidates or expand our product offerings.
We rely heavily on Yutaka Niihara, M.D., M.P.H., our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, and the loss of his services would have a material adverse effect upon our business and prospects.
Our success depends, to a significant extent, upon the continued services of Yutaka Niihara, M.D., M.P.H., our founder and our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer. Since inception, we have been dependent upon Dr. Niihara, who was one of the initial inventors on the patents for the method underlying Endari®. While Dr. Niihara and the rest of our executive officers are parties to confidentiality agreements that prevent them from soliciting our existing customers or disclosing information deemed confidential to us, we do not have any agreement with Dr. Niihara or any key members of management that would prohibit them from joining our competitors or forming competing companies. If Dr. Niihara or any key management personnel resign to join a competitor or form a competing company, the loss of such personnel, together with the loss of any customers or potential customers due to such executive’s departure, could materially and adversely affect our business and results of operations. In addition, we do not maintain key man life insurance policies on any of our executive officers.
Our business and operations may be adversely affected by information technology (“IT”) system failures or cybersecurity or data breaches.
We rely on IT networks and systems, including those of third-party service providers, to collect, process, store and transmit confidential information including, but not limited to, personal information and intellectual property for a variety of functions including, but not limited to, conducting clinical trials, financial reporting, data and inventory management. We also outsource certain services, including recruiting services, call center services, contract sales organization services and other ancillary services relating to the commercial marketing and sale of Endari® in the U.S., as well as significant elements of our IT security systems, as a result, our service providers have access to our confidential information.
Despite the implementation of security measures and recovery plans, our network and information systems and those of third party service providers may be vulnerable to damage from computer viruses, cyberattacks, physical or electronic break-ins, service disruptions, and security breaches from inadvertent or intentional actions by our employees or vendors, or from attacks by malicious third parties. While we have not experienced any such system failure or security breach to date, if such an event were to occur, our operations may be disrupted, and we may suffer from economic loss, reputational harm, regulatory actions or other legal proceedings. Further, such breaches and other inappropriate access can be difficult to detect, and any delay in identifying them may lead to increased risks of the actions described above. We expect that risks and exposures related to cybersecurity breaches will remain high for the foreseeable future due to the rapidly evolving nature and sophistication of these threats.
We have identified a material weakness in our internal controls over financial reporting.
In connection with the preparation and filing of this Annual Report, our management concluded that the material weaknesses in our internal controls over financial reporting originally identified in our Annual Report on Form 10‑K for the 2018 fiscal year had not been fully remediated and our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective. These matters are described in more detail in Part II – Item 9A “Controls and Procedures” in this Annual Report. We cannot guarantee when our disclosure controls and procedures will be fully effective or that we will not identify other material weaknesses in the future. Any material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting could result in errors in our consolidated financial
28
statements, which could erode market confidence in our company, adversely affect the market price of our common stock and, in egregious circumstances, result in possible claims based upon such financial information.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
We may not be able to obtain and enforce intellectual property rights that cover our commercial activities or are sufficient to prevent third parties from competing against us.
Our success with respect to Endari® will depend, in part, on our ability to preserve our trade secrets and to prevent third parties from infringing upon our proprietary rights because we do not have (and will do not expect to be able to obtain) composition of matter patents or methods of use patents that cover Endari®. As a result, competitors who obtain the requisite regulatory approval (subject to any regulatory exclusivity period, such as for Orphan Drug status) can offer products with the same active ingredients as Endari®.
In addition to licensing patent rights and seeking patents for our intellectual property, we also rely on trade secrets, including unpatented know-how, technology and other proprietary information, in our business. Our competitors may also use our methods, or acquire similar expertise, which could impair our ability to commercialize similar products.
We seek to protect our trade secrets, in part, by entering into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to them, such as our employees, corporate collaborators, outside scientific collaborators, contract manufacturers, consultants, advisors and other third parties. Despite these efforts, any of these parties may breach the agreements and disclose our proprietary information, including our trade secrets, and remedies thereunder may not be adequate. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive and time consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. Some courts inside and outside the U.S. are less willing or unwilling to protect trade secrets. In addition, if any of our trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a competitor, we would have no right to prevent them, or those to whom they communicate it, from using that technology or information to compete with us.
Although we expect all of our employees to assign their inventions to us, and all of our employees, consultants, advisors and any third parties who have access to our proprietary know-how, information or technology to enter into confidential information and invention agreements, we cannot provide any assurances that all such agreements have been duly executed or will be held enforceable.
We depend on licenses and sublicenses of certain patents. If any of these licenses, sublicenses, or the licenses under which we have been sublicensed terminates, or if any of the patents that have been licensed or sublicensed to us is challenged and we are limited in our ability to utilize any of those patents, we may be unable to develop, out-license, market and sell our products, which would cause a material adverse effect on our business, prospects, financial condition, and operating results.
Our ability to develop products depends on licenses and sublicenses we have obtained to patents that claim the use of L-glutamine to treat SCD, diverticulosis and diabetes and the use of CAOMECS for the treatment of corneal impairments.
These licenses and sublicenses could be terminated if we fail to satisfy our obligations under them. In addition, if the license under which we have been sublicensed terminates, our sublicense could also terminate. In the event any claims in the patents that we have been licensed or sublicensed are challenged, the court or patent authority could determine that such patent claims are invalid or unenforceable or not sufficiently broad in scope to protect our proprietary rights. As the licensee or sublicensee of such patents, our ability to participate in the defense or enforcement of such patents could be limited.
In particular, the patent for the use of L-glutamine to treat SCD expired in May 2016, and our license to the patent terminated with the expiration of the patent. This also means that our competitors are free to utilize processes, technologies and methods that were previously protected by the SCD patent to potentially develop competing products. Many of our competitors have greater resources than we do and may be able to develop competing products more quickly than we can. While we have an Orphan Drug designation for the use of L-glutamine for the treatment of SCD, Orphan Drug exclusivity may be lost if another L-glutamine product for the same indication demonstrates clinical superiority. If our competitors develop alternative L-glutamine products, it may have a material and adverse effect on our operations and our ability to commercialize our products.
If we are unable to protect proprietary technology that we invent and develop, we may not be able to compete effectively, and our business and financial prospects may be harmed.
Where appropriate, we seek patent protection for inventions we conceive and reduce to practice, however, patent protection may be limited or not available for all of these inventions. In addition, we may need to design around patents held by
29
others. If we must spend significant time and money protecting our patents, designing around patents held by others or in-licensing patent or other proprietary rights held by others, potentially for large fees, our business and financial prospects may be harmed.
The patent prosecution process is expensive and time consuming, and we may not be able to file and prosecute all necessary or desirable patent applications at a reasonable cost or in a timely manner. It is also possible that we will fail to identify patentable aspects of our research and development output before it is too late to obtain patent protection. We also may have to relinquish to strategic partners or other third parties to whom we license our technology the right to control the preparation, filing and prosecution of patent applications claiming our inventions and to maintain any resulting patents. Therefore, patent applications and patents claiming our inventions may not be prosecuted and enforced in a manner consistent with the best interests of our business.
Our pending and future patent applications may not result in patents being issued that protect our product candidates, in whole or in part, or which effectively prevent others from commercializing competitive product candidates. Changes in either the patent laws or interpretation of the patent laws in the U.S. and other countries may diminish the value of our patents or narrow the scope of our patent protection.
Even if our patent applications issue as patents, they may not issue in a form that will prevent competitors from competing with us or otherwise provide us with any competitive advantage. Our competitors may be able to circumvent our patents by developing similar or alternative treatments in a non-infringing manner.
In addition, the issuance of a patent is not conclusive as to its inventorship, scope, validity or enforceability, and our patents may be challenged in the courts or patent offices in the U.S. and abroad. Such challenges may result in loss of exclusivity, freedom to operate and/or in patent claims being narrowed, invalidated or held unenforceable, in whole or in part, which could limit our ability to prevent others from commercializing products similar or identical to our product candidates or products, or limit the duration of the patent protection of our product candidates or products. Given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new therapeutics, patents protecting our product candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized as products. Patent protection for Endari® expired in May 2016. As a result, our patent portfolio may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing products similar or identical to ours.
We will incur significant ongoing expenses in maintaining our patent portfolio. Should we lack the funds to maintain our patent portfolio or to enforce our rights against infringers, we could be adversely impacted.
Third parties may initiate legal proceedings alleging that we are infringing their intellectual property rights, the outcome of which would be uncertain and could have a material adverse effect on the success of our business.
Our commercial success depends upon our ability, and the ability of our collaborators, to develop, manufacture, market and sell our products without infringing the proprietary rights of third parties. There is considerable intellectual property litigation in the biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries. We may become party to, or be threatened with, future adversarial proceedings or litigation regarding intellectual property rights with respect to our product candidates and products which could impede our ability to make, use, sell, distribute or market our products in such jurisdiction. Even if claims of infringement are without merit, any such action could divert the time and attention of management and impair our ability to access additional capital and/or cost us significant funds to defend.
If we are found to infringe a third party’s intellectual property rights, we could be required to obtain a license from such third party to continue developing our product candidates and manufacturing and marketing any of our products. However, we may not be able to obtain any required license on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Alternatively, we could be ordered to cease commercializing any of our products that is found to infringe a third party’s intellectual property right. In addition, we could be found liable for monetary damages, including treble damages and attorneys’ fees if we are found to have willfully infringed a third party’s patent. A finding of infringement could prevent us from developing our product candidates and commercializing our products or force us to cease some of our business operations. Claims that we have misappropriated the confidential information or trade secrets of third parties could have a similar negative impact on our business.
We may be subject to claims by third parties asserting that we or our employees have misappropriated their intellectual property or claiming ownership of what we regard as our own intellectual property.
Although we try to ensure that our employees do not use the proprietary information or know-how of others in their work for us, we may be subject to claims that these employees or we have used or disclosed intellectual property, including
30
trade secrets or other proprietary information, of any such employee’s former employer. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims.
Moreover, we may be subject to a third-party pre-issuance submission of prior art to the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office, or become involved in opposition, derivation, reexamination, inter partes review, post-grant review or interference proceedings challenging our patent rights or the patent rights of others. An adverse determination in any such submission, proceeding or litigation could reduce the scope of or invalidate our patent rights, allow third parties to commercialize products similar or identical to our product candidates or products and compete directly with us, without payment to us, or result in our inability to manufacture or commercialize products without infringing third-party patent rights. In addition, if the breadth or strength of protection provided by our patents and patent applications is threatened, it could dissuade companies from collaborating with us to license, develop or commercialize current or future product candidates.
We may become involved in lawsuits to protect or enforce any patents or other intellectual property, which could be expensive, time consuming and unsuccessful.
Competitors may infringe our issued patents, trade secrets, know-how or other intellectual property. To counter infringement or unauthorized use or to determine the scope and validity of our intellectual property rights, we may be required to file infringement claims or pursue other proceedings, which can be expensive and time consuming. Any claims we assert against perceived infringers could provoke these parties to assert counterclaims against us alleging that we infringe their patents. In addition, in a patent infringement proceeding, a court may decide that our patent is invalid or unenforceable, in whole or in part, construe the patent’s claims narrowly or refuse to stop the other party from using the technology at issue on the grounds that our patents do not cover the technology. An adverse result in any litigation or other proceeding could put one or more of our patents at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly, subject us to significant liabilities, require us to cease using the subject technology or require us to license the subject technology from the third party, any or all of which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Intellectual property litigation could cause us to spend substantial resources and distract our personnel from their normal responsibilities.
Even if resolved in our favor, litigation or other legal proceedings relating to intellectual property claims may cause us to incur significant expenses and could distract our technical and management personnel from their normal responsibilities. In addition, there could be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments, and if securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, it could have a substantial adverse effect on the trading price of our common stock. Such litigation or proceedings could substantially increase our operating losses and reduce the resources available for development activities or future sales, marketing or distribution activities. We may not have sufficient financial or other resources to conduct such litigation or proceedings adequately. Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of such litigation or proceedings more effectively than we can because of their greater financial resources. Uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of patent litigation or other proceedings could compromise our ability to compete in the marketplace.
We may not be able to protect our intellectual property rights throughout the world.
Filing, prosecuting and defending patents in all countries throughout the world would be prohibitively expensive, and our intellectual property rights in some countries outside the U.S. can be less extensive than those in the U.S. In addition, the laws of some foreign countries do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as federal and state laws in the U.S. Consequently, we may not be able to prevent third parties from practicing our inventions in countries outside the U.S., or from selling or importing products made using our inventions in and into the U.S. or other jurisdictions. Competitors may use our technologies in jurisdictions where we have not obtained patent protection to develop their own products or export otherwise infringing products to territories where we have patent protection, but enforcement is not as strong as in the U.S. These products may compete with our products and our patents or other intellectual property rights may not be effective or sufficient to prevent them from competing. Our efforts to enforce our intellectual property rights around the world may be inadequate to obtain a significant commercial advantage from the intellectual property that we develop or license.
Risks Related to Regulatory Oversight of Our Business and Compliance with Law
Endari® is subject to ongoing and continued regulatory review, compliance with which may result in significant expense and limit our ability to commercialize Endari®.
We are subject to ongoing FDA obligations and continued regulatory review with respect to the manufacturing, processing, labeling, packaging, distribution, adverse event reporting, storage, advertising, promotion and recordkeeping for
31
Endari®. These requirements include submissions of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, registration, as well as continued compliance with good clinical practices and good laboratory practices or cGMPs. In addition, our product labeling, advertising and promotion are subject to regulatory requirements and continuing regulatory review. The FDA strictly regulates the promotional claims that may be made about prescription drug products. In particular, a drug product may not be promoted for uses that are not approved by the FDA as reflected in the product’s approved labeling, although the FDA does not regulate the prescribing practices of physicians.
Manufacturers of drug products and their facilities are subject to continual review and periodic inspections by the FDA and other regulatory authorities for compliance with cGMP regulations. If we or a regulatory agency discovers previously unknown problems with a product, such as adverse events of unanticipated severity or frequency, or problems with the facility where, or processes by which, the product is manufactured, a regulatory agency may impose restrictions on that product, the manufacturer or us, including requiring product recall, notice to physicians, withdrawal of the product from the market or suspension of manufacturing.
The FDA’s regulations, policies or guidance may change, and new or additional statutes or government regulations may be enacted that could further restrict or regulate post-approval activities relating to our commercialization of Endari®. We cannot predict the likelihood, nature or extent of adverse government regulation that may arise from future legislation or administrative action. If we are not able to achieve and maintain regulatory compliance, we may not be permitted to market Endari®, which would adversely affect our ability to generate revenue and achieve or maintain profitability.
We may not be able to receive regulatory approval for our prescription grade L-glutamine treatment for diverticulosis or other indications, which would adversely affect our financial and operating condition.
All our other product candidates are still in preclinical development. Regulatory approval is required to market our prescription grade L-glutamine treatment for diverticulosis or other indications and for any other product candidates we may develop. Even if the FDA and other regulatory authorities approve our prescription grade L-glutamine treatment for diverticulosis, or any of our other product candidates, the manufacture, packaging, labeling, distribution, marketing and sale of such products will be subject to strict and ongoing post-approval regulations. Compliance with such regulations will be expensive and consume substantial financial and management resources.
The FDA has the authority to regulate the claims we make in marketing our prescription products to ensure that such claims are true, not misleading, supported by scientific evidence, and consistent with the approved labeling of those products. The FDA and the Federal Trade Commission (“FTC”) also have the authority to regulate the claims we make in marketing our dietary supplement AminoPure. Failure to comply with FDA or FTC requirements in this regard could result in, among other things, warning letters, withdrawal of approvals, seizures, recalls, injunctions prohibiting a product’s manufacture and distribution, restricting promotional activities, requiring corrective actions regarding sales and marketing activities, other operating restrictions, civil money penalties, disgorgement, and criminal prosecution. In addition, if we make any marketing claims that are related to a health care provider’s unlawful submission for reimbursement from government programs, we could be subject to potential liability for violations of the False Claims Act, which may lead to disqualification from government programs or criminal prosecution, or both. Any of these government enforcement actions, if taken against us, could negatively impact our product sales and profitability.
Additionally, regulatory approval of any of our prescription products may be conditioned on our agreement to conduct costly post-marketing follow-up studies to monitor the safety or effectiveness of such products or to implement specific risk mitigation strategies. In addition, as clinical experience with any of our products following such approval, if any, expands after approval because the product is used by a greater number and more diverse group of patients than during clinical trials, unknown side effects or other problems may be observed that were not observed or anticipated during pre-approval clinical trials. In any such case, one or more regulatory authorities could require additional risk information be added to the labeling of the product, restrict the indications for which the product may be sold, restrict the distribution channels, or revoke the product’s regulatory approval, which could hinder our ability to generate revenues from that product. If we fail to develop and commercialize our product candidates as planned, our financial results and financial condition will be adversely affected, we will have to delay or terminate some or all of our research product development programs, and we may be forced to cease operations.
The development process to obtain FDA approval for new drugs therapies is very costly and time consuming and if we cannot complete our clinical trials in a cost-effective manner, our operations may be adversely affected.
Before obtaining marketing approval from regulatory authorities for the sale of any product candidate, we or a collaborator must complete preclinical development and then complete one or more extensive clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of the product candidate in humans. Clinical testing is expensive, difficult to design and implement,
32
can take many years to complete and is uncertain as to outcome. Costs of clinical trials may vary significantly over the life of a development project owing, but not limited to, the following:
|
|
• |
the number of patients that participate in the trials; |
|
|
• |
the per patient trial costs; |
|
|
• |
the number of sites and clinical investigators involved in the trials; |
|
|
• |
the number and types of trials and studies that may need to be performed; |
|
|
• |
the length of time required to recruit, screen, and enroll eligible patients; |
|
|
• |
the duration of the clinical trials; |
|
|
• |
the countries in which the trials are conducted; |
|
|
• |
the number of doses that patients receive; |
|
|
• |
adverse events experienced by trial participants; |
|
|
• |
the drop out or discontinuation rates of patients; |
|
|
• |
potential additional safety monitoring or other studies requested by regulatory agencies; |
|
|
• |
the extent and duration of patient follow up; |
|
|
• |
difficulties that could arise in analyzing and reporting to regulators the results of clinical trials; and |
|
|
• |
the efficacy and safety profile of the product candidate. |
If we are unable to control the timing and costs of our clinical trials and conduct our trials and apply for regulatory approvals in a timely and cost-effective manner, our operations may be adversely affected.
Our product development costs will also increase if any regulatory agencies impose a clinical hold on any of our clinical studies or we experience delays in obtaining marketing approvals, particularly if we are required to conduct additional clinical studies beyond those that we submit in any NDA. We do not know whether any of our preclinical studies or clinical trials will begin as planned, will need to be restructured or will be completed on schedule, or at all. Significant preclinical study or clinical trial delays also could shorten any periods during which we may have the exclusive right to commercialize our approved product candidates or allow our competitors to bring products to market before we do, and thereby impair our ability to successfully commercialize our product candidates.
We may not be able to complete clinical trial programs for any of our product candidates successfully within any specific time period or at all, and if such clinical trials take longer to complete than we project, our ability to execute our current business strategy will be adversely affected.
Clinical testing is expensive, difficult to design and implement, can take many years to complete, and is uncertain as to outcome. A failure of one or more clinical trials can occur at any stage of development. The outcome of preclinical testing and early clinical trials may not be predictive of the success of later clinical trials, and interim results of a clinical trial do not necessarily predict final results. Moreover, clinical data are often susceptible to varying interpretations and analyses, and many companies that have believed their product candidates performed satisfactorily in preclinical studies and clinical trials have nonetheless failed to obtain marketing approval of them.
Generally speaking, whether we complete our clinical trials in a timely manner, or at all, for any product candidate is dependent in part upon: (i) the date the applicable investigational new drug, or IND, becomes effective enabling us to commence the applicable clinical studies (which, under U.S. law, occurs no more than 30 days after the FDA receives the IND, unless the FDA places the IND on clinical hold, in which case the FDA may request us to provide additional data from completed preclinical studies or undertake additional preclinical studies, the latter of which could materially delay the clinical and regulatory development of the applicable product candidate); (ii) the engagement of clinical trial sites and clinical investigators; (iii) reaching an agreement with clinical investigators on acceptable clinical trial agreement terms, clinical trial protocols or informed consent forms; (iv) obtaining approval from the institutional review boards used by the clinical trial sites we seek to engage; (v) the rate of patient enrollment and retention; and (vi) the rate to collect, clean, lock and analyze the clinical trial database.
Clinical trials required for demonstration of substantial evidence of effectiveness and safety often require the enrollment of large numbers of patients, and suitable patients may be difficult to identify and recruit. Our ability to enroll
33
sufficient numbers of patients in our clinical trials, especially when the disease or condition being studied is rare, depends on many factors, including the size of the relevant patient population, the nature and design of the protocol, the proximity of patients to clinical sites, the eligibility and exclusion criteria applicable for the trial, existence of competing clinical trials and the availability of already approved therapeutics for the indications being studied (whether or not such therapeutics are less safe or less effective than our product candidate under trial). If we fail to enroll and maintain the number of patients for which the clinical trial was designed, the statistical significance and/or statistical power of that clinical trial may be reduced which would make it harder to demonstrate that the product candidate being tested in such clinical trial is safe and effective for its intended use.
We may be required to suspend, repeat or terminate our clinical trials if they do not meet regulatory requirements, the results are negative or inconclusive, human subject protections are inadequate, the trials are not well designed, or clinical investigators fail to comply with all requirements for the conduct of trials under the applicable IND, any of which may result in significant negative repercussions on our business and financial condition.
We cannot market a pharmaceutical product in any jurisdiction until we have completed rigorous preclinical testing and clinical trials for that product, demonstrated the product’s safety and substantial evidence of effectiveness for its intended use, obtained the approval of the applicable regulatory authority for our proposed labeling of the product, and met the other requirements of such jurisdiction’s extensive regulatory approval process. Preclinical testing and the conduct of clinical trials are long and expensive. Data obtained from preclinical and clinical tests can be interpreted in different ways and could ultimately be deemed by regulatory authorities to be insufficient with respect to providing substantial evidence of effectiveness and safety required for regulatory approval, which could delay, limit or prevent regulatory approval. It may take us many years to complete the required testing of our product candidates to support an application for marketing approval and failure can occur at any stage during this process.
We cannot provide assurance that our preclinical testing and clinical trials will be completed successfully within any time period specified by us, or without significant additional resources or expertise provided by third parties to conduct such testing. We cannot provide assurance that any such testing will demonstrate that our product candidates meet regulatory approval requirements for safety and effectiveness or that any such product will be approved for a specific indication. Results from early clinical trials may not be indicative of the results that will be obtained in later-stage clinical trials or in the population of patients for whom the applicable product is prescribed following any approval. In addition, negative or inconclusive results from the clinical trials we conduct, or adverse events experienced by the patients in such clinical trials, could cause us to have to suspend, repeat or terminate the clinical trials. Clinical trials are subject to continuing oversight by governmental regulatory authorities and institutional review boards and must meet the requirements of these authorities including but not limited to requirements for informed consent, human subject protection and good clinical practices; and we cannot guarantee that we will be able to comply, or that a regulatory authority will agree that we have complied, with such requirements.
We rely on third parties, such as CROs, contract laboratories, regulatory consultants and data management companies to assist us in overseeing and monitoring clinical trials as well as to process the clinical data and manage test requests, which may result in delays or failure to complete trials, if the third parties fail to perform or meet applicable regulatory requirements and standards. A failure by us or any such third parties to comply with the terms and conditions of the protocol for any clinical study or the regulatory requirements for any particular product candidate or to complete the clinical trials for a product candidate in the projected time frame could have a significant negative effect on our business and financial condition.
There are significant requirements imposed on us and on clinical investigators who conduct clinical trials under an IND. Although we are responsible for selecting qualified clinical investigators, providing them with the information they need to conduct an investigation properly, ensuring proper monitoring of the investigations, and ensuring that the investigations are conducted in accordance with the general investigational plan and protocols contained in the IND, we cannot ensure the clinical investigators will maintain compliance with all regulatory requirements at all times. The pharmaceutical industry has experienced cases where clinical investigators have been found to incorrectly record data, omit data, or even falsify data. We cannot ensure that the clinical investigators in our trial will not make mistakes or otherwise compromise the integrity or validity of data, any of which would have a significant negative effect on our ability to obtain marketing approval, our business, and our financial condition.
Changes in regulatory requirements and guidance or unanticipated events during our clinical trials may occur, which may result in necessary changes to clinical trial protocols, informed consents and clinical trial budgets, any of which changes could result in increased costs to us, delay our development timeline or reduce the likelihood of successful completion of the clinical trial.
Changes in regulatory requirements or the FDA’s interpretation of those requirements, which may be provided through guidance documents, or the occurrence of unanticipated events during our clinical trials could require us to amend
34
clinical trial protocols, informed consent forms and trial budgets. If we experience delays in initiation, conduct or completion of any of our clinical trials, or if we terminate any of our clinical trials due to changes in regulatory requirements or guidance documents, unexpected and serious adverse events, or other unanticipated events, we may incur additional costs and have difficulty enrolling subjects or achieving clinical investigator or institutional review board acceptance of the changes and successfully completing the trial. Any such additional costs and difficulties could potentially materially harm the commercial prospects for our product candidates and delay our ability to generate product revenue.
There are various uncertainties related to the research, development and commercialization of the cell sheet engineering regenerative medicine products we are developing in collaboration with a strategic partner which could negatively affect our ability to commercialize such products.
We have historically focused on the research and development of our prescription grade L-glutamine treatment for SCD and have limited experience in the research, development or commercialization of cell sheet regenerative medicine products or any other biological product. No clinical trials of cell sheet regenerative products have been conducted in the U.S. and no biological products based on cell sheet engineering have been approved by regulatory authorities in any jurisdiction. Such products must be manufactured in conformance with current cGMP requirements as well as Good Tissue Practice (“GTP”) requirements and demonstrate that they are safe, pure and potent to be effective for their intended uses to obtain FDA approval. The GTP requirements, which are specifically applicable to all cellular-based products, are intended to prevent communicable disease transmission. It is uncertain what type and quantity of scientific data would be required to support initiation of clinical studies or to sufficiently demonstrate the safety, purity and potency of cell sheet regenerative medicine products for their intended uses. Such uncertainties could delay our ability to obtain FDA approval for and to commercialize such products. In addition, the research and commercialization of cell sheet regenerative medicine products could be hindered if third-party manufacturers of such products are not compliant with cGMP, GTP, and any other applicable regulations. Any delay in the development of, obtaining FDA approval for, or the occurrence of any problems with third-party manufacturers of cell sheet regenerative medicine products would negatively affect our ability to commercialize such products.
We are subject to numerous complex regulations and failure to comply with these regulations, or the cost of compliance with these regulations, may harm our business.
The research, testing, development, manufacturing, quality control, approval, labeling, packaging, storage, recordkeeping, promotion, advertising, marketing, distribution, possession and use of Endari® are subject to regulation by numerous governmental authorities in the U.S. The FDA regulates drugs under the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act (the “FDC&A”) and implementing regulations. Noncompliance with any applicable regulatory requirements can result in refusal to approve products for marketing, warning letters, product recalls or seizure of products, total or partial suspension of production, prohibitions or limitations on the commercial sale of products or refusal to allow the entering into of federal and state supply contracts, fines, civil penalties and/or criminal prosecution. Additionally, the FDA and comparable governmental authorities have the authority to withdraw product approvals that have been previously granted. Moreover, the regulatory requirements relating to Endari® may change from time to time, and it is impossible to predict what the impact of any such changes may be.
Health care reform measures and changes in policies, funding, staffing and leadership at the FDA and other agencies could hinder or prevent the commercial success of Endari®.
In the U.S., legislative and regulatory changes to the healthcare system could affect our future results of operations and the future results of operations of our potential customers. For example, the Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act of 2003 established a Part D prescription drug benefit, under which Medicare beneficiaries can obtain prescription drug coverage from private sector plans that are permitted to limit the number of prescription drugs that are covered in each therapeutic category and class on their formularies. If Endari® is not widely included on the formularies of these plans, our ability to market Endari® may be adversely affected.
Furthermore, there have been and continue to be initiatives at the federal and state levels that seek to reduce healthcare costs. In March 2010, President Obama signed into law the Patient Protection and Affordable Health Care Act of 2010, as amended by the Health Care and Education Affordability Reconciliation Act of 2010 (jointly, the “PPACA”), which includes measures to significantly change the way health care is financed by both governmental and private insurers. Among the provisions of the PPACA of importance to the pharmaceutical industry are the following:
|
|
• |
an annual, nondeductible fee on any entity that manufactures or imports certain branded prescription drugs and biologic agents, apportioned among these entities according to their market share in certain government healthcare programs; |
35
|
|
• |
a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 50% point-of-sale discounts off negotiated prices of applicable brand drugs to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period, as a condition for the manufacturer’s outpatient drugs to be covered under Medicare Part D; |
|
|
• |
extension of manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability to covered drugs dispensed to individuals who are enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations; |
|
|
• |
expansion of eligibility criteria for Medicaid programs by, among other things, allowing states to offer Medicaid coverage to additional individuals and by adding new mandatory eligibility categories for certain individuals with income at or below 133% of the Federal Poverty Level, thereby potentially increasing both the volume of sales and manufacturers’ Medicaid rebate liability; |
|
|
• |
expansion of the entities eligible for discounts under the Public Health Service pharmaceutical pricing program; |
|
|
• |
new requirements to report certain financial arrangements with physicians and teaching hospitals, as defined in the PPACA and its implementing regulations, including reporting any “transfer of value” made or distributed to teaching hospitals, prescribers, and other healthcare providers and reporting any ownership and investment interests held by physicians and their immediate family members and applicable group purchasing organizations during the preceding calendar year, with data collection required and reporting to the CMS required by the 90th day of each calendar year; |
|
|
• |
a new requirement to annually report drug samples that manufacturers and distributors provide to physicians; |
|
|
• |
expansion of health care fraud and abuse laws, including the False Claims Act and the Anti-Kickback Statute, new government investigative powers, and enhanced penalties for noncompliance; |
|
|
• |
a licensure framework for follow-on biologic products; |
|
|
• |
a new Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research; |
|
|
• |
creation of the Independent Payment Advisory Board which, beginning in 2014, will have authority to recommend certain changes to the Medicare program that could result in reduced payments for prescription drugs and those recommendations could have the effect of law even if Congress does not act on the recommendations; and |
|
|
• |
establishment of a Center for Medicare Innovation at the CMS to test innovative payment and service delivery models to lower Medicare and Medicaid spending, potentially including prescription drug spending. |
Additionally, individual states have become increasingly aggressive in passing legislation and implementing regulations designed to control pharmaceutical product pricing, including price or patient reimbursement constraints, discounts, restrictions on certain product access, and marketing cost disclosure and transparency measures, and encourage importation from other countries and bulk purchasing. Legally mandated price controls on payment amounts by third-party payors or other restrictions could harm out business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
In addition, regional healthcare authorities and individual hospitals are increasingly using bidding procedures to determine what pharmaceutical products and which suppliers will be included in their prescription drug and other healthcare programs. This may reduce demand for Endari® or put pressure on our product pricing, which could negatively affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects.
The commercial success of Endari® will depend, in part, upon the availability of coverage and reimbursement from third-party payors at the federal, state and private levels. Third-party payors include governmental programs such as Medicare or Medicaid, private insurance plans and managed care plans. These third-party payors may deny coverage or reimbursement for a product or therapy in whole or in part if they determine that the product or therapy was not medically appropriate or necessary. Also, third-party payors have attempted to control costs by limiting coverage through the use of formularies and other cost-containment mechanisms and the amount of reimbursement for particular procedures or drug treatments.
36
Additionally, given recent federal and state government initiatives directed at lowering the total cost of healthcare, Congress and state legislatures will likely continue to focus on healthcare reform, the cost of prescription drugs and the reform of the Medicare and Medicaid programs. While we cannot predict the full outcome of any such legislation, it may result in decreased reimbursement for prescription drugs, which may further exacerbate industry-wide pressure to reduce prescription drug prices. This could harm our ability to market Endari® and generate revenues. In addition, legislation has been introduced in Congress (the Affordable and Safe Prescription Drug Importation Act) that, if enacted, would permit more widespread importation or re-importation of pharmaceutical products from foreign countries into the U.S., including from countries where the products are sold at lower prices than in the U.S. Such legislation, or similar regulatory changes, could lead to a decision to decrease our prices to better compete, which, in turn, could adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects. It is also possible that other legislative proposals having similar effects will be adopted.
Furthermore, regulatory authorities’ assessment of the data and results required to demonstrate safety and efficacy can change over time and can be affected by many factors, such as the emergence of new information, including on other products, changing policies and agency funding, staffing and leadership. We cannot be sure whether future changes to the regulatory environment will be favorable or unfavorable to our business prospects.
If we fail to comply with federal and state healthcare laws, including fraud and abuse and health information privacy and security laws, we could face substantial penalties and our business, results of operations, financial condition and prospects could be adversely affected.
As a pharmaceutical company, even though we do not and will not control referrals of healthcare services or bill directly to Medicare, Medicaid or other third-party payors, certain federal and state healthcare laws and regulations pertaining to fraud and abuse and patients’ rights are and will be applicable to our business. We could be subject to healthcare fraud and abuse and patient privacy regulation by both the federal government and the states in which we conduct our business. The laws that may affect our ability to operate include:
|
|
• |
the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, which constrains out marketing practices, educational programs, pricing policies, and relationships with healthcare providers or other entities, by prohibiting, among other things, soliciting, receiving, offering or paying remuneration, directly or indirectly, to induce, or in return for, either the referral of an individual or the purchase or recommendation of an item or service reimbursable under a federal healthcare program, such as the Medicare and Medicaid programs; |
|
|
• |
federal civil and criminal false claims laws and civil monetary penalty laws, which prohibit, among other things, individuals or entities from knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, false or fraudulent claims for payment from Medicare, Medicaid, or other third-party payors; |
|
|
• |
the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (“HIPAA”), which created new federal criminal statutes that prohibit executing a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or making false statements relating to healthcare matters; |
|
|
• |
HIPAA, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act of 2009 (“HITECH”), and its implementing regulations, which imposes certain requirements relating to the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information; and |
|
|
• |
state law equivalents of each of the above federal laws, such as anti-kickback and false claims laws which may apply to items or services reimbursed by any third-party payor, including commercial insurers, and state laws governing the privacy and security of health information in certain circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways and often are not preempted by HIPAA, thus complicating compliance efforts. |
Because of the breadth of these laws and the narrowness of the statutory exceptions and safe harbors available under the U.S. federal Anti-Kickback Statute, it is possible that some of our business activities could be subject to challenge under one or more of such laws. If we or our operations are found to be in violation of any of the laws described above or any other governmental regulations that apply to us, we may be subject to penalties, including civil and criminal penalties, damages, fines, exclusion from participation in U.S. federal or state health care programs, and the curtailment or restructuring of our operations. Any penalties, damages, fines, curtailment or restructuring of our operations could materially adversely affect our ability to operate our business and our financial results.
The FDA provides guidelines with respect to appropriate promotion and continuing medical and health education activities. Although we endeavor to follow these guidelines, the FDA or the Office of the Inspector General: U.S. Department of Health and Human Services may disagree, and we may be subject to significant liability, including civil and administrative
37
remedies as well as criminal sanctions. In addition, management’s attention could be diverted, and our reputation could be damaged.
Although compliance programs can mitigate the risk of investigation and prosecution for violations of these laws, the risks cannot be eliminated entirely. Any action against us for violation of these laws, even if we successfully defend against it, could cause us to incur significant legal expenses and divert our management’s attention from the operation of our business. Moreover, achieving and sustaining compliance with applicable federal and state privacy, security and fraud laws may prove costly.
Our business is subject to extensive government regulation, which could cause delays in the development of our product candidates and commercialization of any resulting products, impose significant costs on us or provide advantages to our larger competitors.
The FDA and similar regulatory authorities in foreign countries impose substantial requirements upon the development, manufacture and marketing of therapeutic products, such as drugs, biologics, and cell-based therapies. Failure to obtain marketing approval for any of our product candidates in any jurisdiction will prevent us from commercializing it as a product in that jurisdiction. The FDA and most other regulatory authorities impose requirements for laboratory and clinical testing, manufacturing, labeling, registration, marketing, storage, distribution, recordkeeping, reporting, and advertising and promotion, and other costly and time-consuming processes and procedures applicable to therapeutic products. In some cases, as a condition for approval to market any of our product candidates, the FDA or other regulatory authorities may impose commitments that we must satisfy following any such approval. These post-approval commitments could vary substantially from country to country depending upon the type, complexity and novelty of the applicable therapeutic product. Satisfaction of any such post-approval commitments (including the requirement to conduct additional clinical studies), if imposed by the FDA or other regulatory authorities, could take several years or more. In addition, post-approval requirements regarding safety surveillance, cGMP compliance, advertising and promotion, adverse event reporting, and recordkeeping must be met.
The effect of government regulation may be to delay marketing approval of our product candidates for a considerable or indefinite period of time, to impose costly processes and procedures upon our activities and to furnish a competitive advantage to companies that compete with us. There can be no assurance that marketing approval for any of our product candidates would be granted by the FDA or other regulatory authority on a timely basis, if at all, or, once granted, that the marketing authorization would not be withdrawn or other regulatory actions taken which might limit our ability to market our proposed products. Any such delay in obtaining or failing to obtain such approvals or imposition of regulatory actions would adversely affect us, the manufacturing and marketing of the products resulting from marketing approval of any of our product candidates, and our ability to generate product revenue.
Even though we have obtained Orphan Drug designation for Endari®, we may not be able to maintain Orphan Drug marketing exclusivity for this product candidate or any of our other product candidates.
Regulatory authorities in some jurisdictions, including the U.S. and the European Union, may designate therapeutic products under development for relatively small patient populations as “orphan drugs”. Under the Orphan Drug Act, the FDA may designate a therapeutic product as an Orphan Drug if it is intended to treat a rare disease or condition, which is generally defined as a patient population of fewer than 200,000 individuals in the U.S. We have obtained Orphan Drug designation from the FDA and Orphan Medicinal designation from the EC for L-glutamine treatment for SCD, and we may seek Orphan Drug designation for our other product candidates. Generally, if a product candidate with an Orphan Drug designation subsequently receives the first marketing approval for the indication for which it has been granted such designation, the drug is entitled to a period of marketing exclusivity, which precludes the FDA or EC, as applicable, from approving another marketing application for the same product candidate prior to the expiration of that time period. The applicable period is seven years in the U.S. and ten years in the EU. The exclusivity period in the EU can be reduced to six years if the product no longer meets the criteria for Orphan Medicinal designation or if its commercialization is sufficiently profitable so that market exclusivity is no longer justified. Orphan Drug and Orphan Medicinal exclusivity may be lost if the FDA or EMA determines that the request for designation was materially defective or if the manufacturer is unable to ensure sufficient quantity of the product to meet the needs of patients with the rare disease or condition. In the U.S., Orphan Drug exclusivity may be lost if another L-glutamine product for the same indication demonstrates clinical superiority, such as a better safety or efficacy profile, in which case the FDA would be permitted to approve the third-party product. Orphan Drug exclusivity does not bar the FDA from approving another L-glutamine product for any other indication. Nor does Orphan Drug designation bar the FDA from granting Orphan Drug designation and approving another product for the same orphan disease or condition.
38
Any product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval would be subject to post-marketing regulatory requirements and limitations and could be subject to recall or withdrawal from the market, and we may be subject to penalties if we fail to comply with such regulatory requirements or if we experience unanticipated problems in commercializing any of our product candidates, when and if any of them are approved by regulators.
Any product candidate for which we obtain marketing approval, along with the collection and reporting of post-approval clinical data, manufacturing processes, labeling, advertising and promotional activities for the resulting product, will be subject to continual requirements of and review by the FDA and other regulatory authorities. These requirements include submissions of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, establishment registration and product listing requirements, cGMP requirements relating to manufacturing, quality control, quality assurance and corresponding maintenance of records and documents, requirements regarding the distribution of samples to physicians and recordkeeping. Even if the FDA or other regulators outside the U.S. grant marketing approval to any of our product candidates, the approval may be subject to limitations on the indicated uses for which it may be marketed as a product or to the conditions of approval, including the requirement to implement a risk evaluation and mitigation strategy (“REMS”). If any of our product candidates receives marketing approval, the labeling (including the package insert) that must accompany its distribution as a product may limit its approved use, which could limit the total number of prescriptions written for such products.
In consultation with the FDA, Emmaus is designing clinical studies to generate data in stages to fulfill the post-marketing commitment for the current SCD indication of Endari®. These studies will require additional funding and are designed to include dosing and safety, particularly in those populations not yet given Endari®. On any future products, the FDA may also require additional costly post-marketing studies or clinical trials or surveillance to monitor the safety or effectiveness of any other approved product. The FDA closely regulates the post-approval marketing and promotion of therapeutic products to ensure they are marketed for the approved indications and in accordance with the provisions of the approved labeling, and that any marketing claims or communications by a person or company responsible for the manufacture and distribution of the product regarding off-label use are truthful and not misleading. If we market any of our products for indications that have not been approved in a manner that is considered misleading or not truthful, we may be subject to enforcement action for misbranding the product. Violations of the FDC&A relating to the promotion of prescription products may lead to investigations alleging violations of federal and state healthcare fraud and abuse laws, as well as state consumer protection laws. In recent years, several pharmaceutical companies have been or settled lawsuits for fined significant amounts for such violations.
In addition, later discovery of previously unknown adverse events or other problems with any of our product candidates that are approved for marketing as products, the contract manufacturers from which we obtain supplies of these products, the manufacturing processes they use to manufacture these products, or our or their failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may have negative consequences, including:
|
|
• |
restrictions on the manufacturers or manufacturing processes for such products; |
|
|
• |
restrictions on the labeling or marketing of such products; |
|
|
• |
restrictions on distribution or use of such products; |
|
|
• |
requirements to conduct post marketing studies or clinical trials; |
|
|
• |
warning letters; |
|
|
• |
recall or withdrawal of such products from the market; |
|
|
• |
refusal to approve pending applications or supplements to approved marketing applications that we submit; |
|
|
• |
clinical holds on clinical studies of such products; |
|
|
• |
fines, restitution or disgorgement of revenue or profit generated by sales of such products; |
|
|
• |
suspension or withdrawal of the marketing approvals of such products; |
|
|
• |
refusal to permit the import or export of such products; |
|
|
• |
seizure of such products; |
|
|
• |
injunctions prohibiting the manufacture, marketing, sale, distribution, or related action in respect of such products; |
|
|
• |
the imposition of civil or criminal penalties; or |
39
|
|
• |
debarment of our company and any of our officers or other employees responsible for such problems from future dealings with the FDA. |
Noncompliance with applicable regulatory requirements regarding safety monitoring, also called pharmacovigilance, and with requirements related to the development of therapeutics for the pediatric population, can also result in significant financial penalties. Similarly, failure to comply with applicable regulatory requirements regarding the protection of personal information can also lead to significant penalties and sanctions.
Our current and future relationships with customers and third-party payors in the U.S. and elsewhere may be subject, directly or indirectly, to applicable anti-kickback, fraud and abuse, false claims, transparency, health information privacy and security and other healthcare laws and regulations, which could expose us to criminal sanctions, civil penalties, contractual damages, reputational harm, administrative burdens and diminished profits and future earnings.
Our industry is highly regulated and changes in law may adversely impact our business, operations or financial results. Any present or future arrangements with third-party payors, healthcare providers and professionals and customers may expose us to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations that may restrict certain marketing and contracting practices. We are subject to various federal and state laws pertaining to healthcare fraud and abuse, including inducing, facilitating or encouraging submission of false claims to government programs and prohibitions on the offer or payment or acceptance of kickbacks or other remuneration for the purchase of our products. Healthcare providers, physicians and third-party payors in the U.S. and elsewhere will play a primary role in the recommendation and prescription of any product candidates for which we obtain marketing approval. Our future arrangements with customers and third-party payors may expose us to broadly applicable fraud and abuse and other healthcare laws and regulations, which may constrain the business or financial arrangements and relationships through which we sell, market and distribute any products. In addition, we may be subject to transparency laws aimed at controlling healthcare costs and patient privacy regulation by the U.S. federal and state governments and by governments in foreign jurisdictions in which we conduct our business. The applicable federal, state and foreign healthcare laws and regulations that may affect our ability to operate include (but are not limited to):
|
|
• |
the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, which prohibits, among other things, persons from knowingly and willfully soliciting, offering, receiving or providing remuneration, directly or indirectly, in cash or in kind, to induce or reward, or in return for, either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, order or recommendation of, any good or service, for which payment may be made under federal and state healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid; |
|
|
• |
federal civil and criminal false claims laws and civil monetary penalty laws, including the federal False Claims Act, which impose criminal and civil penalties, including civil qui tam actions (commonly referred to as “whistleblower actions”), against individuals or entities for knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, to the federal government, including the Medicare and Medicaid programs, claims for payment that are false or fraudulent or making a false statement to avoid, decrease or conceal an obligation to pay money to the federal government; |
|
|
• |
provisions under the federal Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (“HIPAA”) that impose criminal and civil liability for executing a scheme to defraud any healthcare benefit program or making false statements relating to healthcare matters; |
|
|
• |
provisions under HIPAA, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act of 2009 (“HITECH”) and their respective implementing regulations, that impose obligations on covered healthcare providers, health plans, and healthcare clearinghouses, as well as their business associates that create, receive, maintain or transmit individually identifiable health information for or on behalf of a covered entity, with respect to safeguarding the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information; |
|
|
• |
the federal Open Payments program under the federal Physician Payments Sunshine Act, which requires manufacturers of drugs, biologics, cell based therapies, medical devices and medical supplies for which payment is available under Medicare, Medicaid or the Children’s Health Insurance Program, with specific exceptions, to report annually to the CMS, information related to “payments or other transfers of value” made to physicians, which is defined to include doctors, dentists, optometrists, podiatrists and chiropractors, and teaching hospitals and applicable manufacturers and applicable group purchasing organizations to report annually to CMS ownership and investment interests held by the physicians and their immediate family members; |
40
|
|
• |
state and foreign laws that require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the pharmaceutical industry’s voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government or otherwise restrict payments that may be made to healthcare providers; |
|
|
• |
state and foreign laws that require pharmaceutical and biopharmaceutical manufacturers to report information related to payments and other transfers of value to physicians and other healthcare providers or marketing expenditures; and |
|
|
• |
state and foreign laws governing the privacy and security of health information in certain circumstances, many of which differ from each other in significant ways and often are not preempted by HIPAA, thus complicating compliance efforts. |
Because of the sweeping language of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute, many potentially beneficial business arrangements would be prohibited if the statute were strictly applied. To avoid this outcome, the Department of Health and Human Services has published regulations, known as “safe harbors,” that identify exceptions to or exemptions from the statute’s prohibitions. Arrangements that do not fit within the safe harbors are not automatically deemed to be illegal but must be evaluated on a case by case basis for compliance with the statute and may be subject to scrutiny (and ultimately prosecution) by enforcement agencies. We seek to comply with the Anti-Kickback Statute and, if necessary, to fit within one of the defined safe harbors. We may be less willing than some of our competitors to take actions or enter into business arrangements that do not clearly satisfy the safe harbors. As a result, this unwillingness may put us at a competitive disadvantage. However, due to the breadth of the statutory provisions and the absence of uniform guidance in the form of regulations or court decisions, there can be no assurance that our practices fit within the safe harbors or that they will not be challenged under anti-kickback or similar laws. Further, liability may be established without a person or entity having actual knowledge of the federal Anti-Kickback Statute or specific intent to violate it. Violations of such restrictions may be punishable by civil or criminal sanctions, including fines and civil monetary penalties, as well as the possibility of exclusion from U.S. federal healthcare programs (including Medicaid and Medicare). Any such violations could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition, results or operations and cash flows.
Under the False Claims Act, drug manufacturers have been held responsible for claims filed by physicians for reimbursement of the cost of medical services related to uses of a pharmaceutical product that are not on the approved labeling, known as “off-label use,” if the manufacturer promoted the product for such off-label use. If the FDA or other government agencies determine that our promotional materials, trainings or other activities constitute off-label promotion of any of our products, it could request that we modify our training or promotional materials or other activities or subject us to regulatory enforcement actions, including the issuance of a warning letter, injunction, seizure, civil fine, and criminal penalties. Violations of the False Claims Act may result in treble damages based on the amount of overpayment and additional civil fines of $5,000 to $10,000 for each false claim. Drug manufacturers could also be held responsible for reimbursement claims submitted by any physician for pharmaceutical products that were knowingly not manufactured in compliance with cGMP regulations.
In addition to the state laws previously described, we also are subject to other state fraud and abuse statutes and regulations. Many of the states in which we operate or plan to expand to have adopted a form of anti-kickback law, self-referral prohibition, and false claims and insurance fraud prohibition. The scope of these laws and the interpretations of them vary from state to state and are enforced by state courts and regulatory authorities, each with broad discretion. Generally, state laws reach to all healthcare services and not just those covered under a governmental healthcare program. A determination of liability under any of these laws could result in fines and penalties and restrictions on our ability to operate in these states. There is no assurance that our arrangements or business practices will not be subject to government scrutiny or be found to violate applicable fraud and abuse laws.
Efforts to ensure that our business arrangements with third parties will comply with applicable healthcare laws and regulations may involve substantial costs. Further, we cannot guarantee that our arrangements or business practices will not be subject to government investigations and prosecutions which, even if we are ultimately found to be without fault, can be costly and disruptive to our business. It is possible that governmental authorities will conclude that our business practices may not comply with current or future statutes, regulations or case law involving applicable fraud and abuse or other healthcare laws and regulations. If our operations are found to be in violation of any of these laws or any other governmental regulations that may apply to us, we and our employees, officers, or directors may be subject to significant civil, criminal and administrative penalties, including, without limitation, damages, fines, imprisonment, exclusion from participation in government healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, and the curtailment or restructuring of our operations, which could have a material adverse effect on our business. If any of the physicians or other healthcare providers or entities with whom we expect to do
41
business, including our collaborators, is found not to be in compliance with applicable laws, such person or entity may be subject to criminal, civil or administrative sanctions, including exclusions from participation in government healthcare programs, which could also materially affect our business.
Recently enacted and future legislation may increase the difficulty and cost for us to obtain marketing approval of our product candidates and then commercialize them as products and affect the prices we may obtain.
In the U.S. and some foreign jurisdictions, there have been a number of legislative and regulatory changes and proposed changes regarding the healthcare system that could prevent or delay marketing approval of our product candidates, restrict or regulate post-approval activities and affect our ability to profitably sell any product candidates for which we obtain marketing approval.
Among policy makers and payors in the U.S. and elsewhere, there is significant interest in promoting changes in healthcare systems with the stated goals of containing healthcare costs, improving quality and expanding access. In the U.S., the pharmaceutical industry has been a particular focus of these efforts and has been significantly affected by major legislative initiatives. In March 2010, President Obama signed into law the PPACA, which intended to broaden access to health insurance, reduce or constrain the growth of healthcare spending, enhance remedies against fraud and abuse, add new transparency requirements for the healthcare and health insurance industries, impose new taxes and fees on the health industry and impose additional health policy reforms.
Among the provisions of the PPACA of importance to our potential product candidates are:
|
|
• |
an annual, nondeductible fee on any entity that manufactures or imports specified branded prescription drugs and biologic agents, apportioned among these entities according to their market share in certain government healthcare programs; |
|
|
• |
an increase in the statutory minimum rebates a manufacturer must pay under the Medicaid Drug Rebate Program to 23.1% and 13.0% of the average manufacturer price for branded and generic drugs, respectively; |
|
|
• |
expansion of healthcare fraud and abuse laws, including the False Claims Act and the Anti-Kickback Statute, new government investigative powers and enhanced penalties for noncompliance; |
|
|
• |
a new Medicare Part D coverage gap discount program, in which manufacturers must agree to offer 50% point of sale discounts off negotiated prices of applicable brand medicines to eligible beneficiaries during their coverage gap period, as a condition for a manufacturer’s medicines purchased outside a hospital setting to be covered under Medicare Part D; |
|
|
• |
extension of a manufacturer’s Medicaid rebate liability to covered medicines dispensed to individuals who are enrolled in Medicaid managed care organizations; |
|
|
• |
expansion of eligibility criteria for Medicaid programs by, among other things, allowing states to offer Medicaid coverage to additional individuals and by adding a new eligibility category for certain individuals with income at or below 133% of the federal poverty level beginning in 2014, thereby potentially increasing a manufacturer’s Medicaid rebate liability; |
|
|
• |
expansion of the entities eligible for discounts under the 340B Public Health Service pharmaceutical pricing program; |
|
|
• |
the new requirements under the federal Open Payments program and its implementing regulations; |
|
|
• |
a new requirement to annually report samples of medicines that manufacturers and distributors provide to physicians; and |
|
|
• |
a new Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute to oversee, identify priorities in, and conduct comparative clinical effectiveness research, along with funding for such research. |
In addition, other legislative changes have been proposed and adopted since the PPACA was enacted. These changes include aggregate reductions to Medicare payments to providers of up to 2% per fiscal year, starting in 2013. On March 1, 2013, the President signed an executive order implementing the 2% Medicare payment reductions, and on April 1, 2013, these reductions went into effect. In January 2013, President Obama signed into law the American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012, which, among other things, reduced Medicare payments to several providers and increased the statute of limitations period for the government to recover overpayments to providers from three to five years. These new laws may result in additional reductions in Medicare and other healthcare funding, which could have a material adverse effect on customers for any of our products, and, accordingly, our financial operations. Further, there have been multiple attempts through legislative action and
42
legal challenge to repeal or amend the PPACA, and we cannot predict the impact that such a repeal or amendment would have on our business and operations.
On November 20, 2020, the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services published a Final Rule entitled “Removal of Safe Harbor Protection for Rebates to Plans or PBMs Involving Prescription Pharmaceuticals and Creation of New Safe Harbor Protection,” referred to as the Rebate Rule, which amends the discount safe harbor by eliminating protection for price concessions, including rebates, that are offered by pharmaceutical manufacturers to plan sponsors, or pharmacy benefit managers under contract with them, under the Medicare Part D program and Medicare Advantage Plans, unless the price reduction is one required by law. Effective January 1, 2022, in advance of the calendar year 2022 Part D plan year, safe harbor protection will be eliminated for manufacturer rebates paid directly (or indirectly through a pharmacy benefit manager) to Part D prescription drug plans and Medicare Advantage prescription drug plans. Effective December 30, 2020, the Rebate Rule will establish two new safe harbors. The first new safe harbor will protect price reductions paid by manufacturers to prescription drug plans (including prescription drug plans offered by Medicare Advantage organizations) and Medicaid managed care organizations, which are fully reflected at the point-of-sale. The second new safe harbor will protect fair-market-value service fees paid to pharmacy benefit managers by manufacturers. This new rule could result in a change in incentives for health plans and PBMs in negotiating rebates and discounts with manufactures for preferred formulary placement. Because the rule is not yet in effect, at this time we cannot predict how these changes would impact our business and operations.
We expect that the PPACA, as well as other healthcare reform measures that may be adopted in the future, may result in more rigorous coverage criteria and in additional downward pressure on the price that we receive for any of our products. Any reduction in reimbursement from Medicare or other government-funded programs may result in a similar reduction in payments from private payors. The implementation of cost containment measures or other healthcare reforms may prevent us from being able to generate revenue, attain profitability or commercialize any of our products.
Legislative and regulatory proposals have been made to expand post-approval requirements and restrict sales and promotional activities for prescription medicines. We cannot be sure whether additional legislative changes will be enacted, or whether the FDA regulations, guidance or interpretations will be changed, or what the impact of such changes on the marketing approvals of our product candidates, if any, may be. In addition, increased scrutiny by the U.S. Congress of the FDA’s approval process may significantly delay or prevent marketing approval, as well as subject us to more stringent product labeling and post-marketing testing and other requirements.
If we fail to comply with environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, we could become subject to fines or penalties or incur costs that could harm our business.
We are subject to numerous environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, including those governing laboratory procedures and the handling, use, storage, treatment and disposal of hazardous materials and wastes. Our operations involve the use of hazardous and flammable materials, including chemicals and biological materials. Our operations also produce hazardous waste products. We generally contract with third parties for the disposal of these materials and wastes. We cannot eliminate the risk of contamination or injury from these materials. In the event of contamination or injury resulting from our use of hazardous materials, we could be held liable for any resulting damages, and any liability could exceed our resources. We also could incur significant costs associated with civil or criminal fines and penalties for failure to comply with such laws and regulations.
Although we maintain workers’ compensation insurance for costs we may incur due to injuries to our employees resulting from the use of hazardous materials, the insurance may not provide adequate coverage against potential liabilities. We do not maintain insurance for environmental liability or toxic tort claims that may be asserted against us in connection with our storage or disposal of biological, hazardous or radioactive materials.
In addition, we may incur substantial costs to comply with current or future environmental, health and safety laws and regulations. These current or future laws and regulations may impair our research and, development or production efforts. Our failure to comply with these laws and regulations also may result in substantial fines, penalties or other sanctions.
Risks Related to Our Investment in EJ Holdings, Inc.
EJ Holdings has no revenues and is dependent on us to fund its business and operations, and there is no assurance that we can continue to provide needed funding or that EJ Holdings will be able to continue its activities.
EJ Holdings, Inc., or EJ Holdings, a Japanese corporation 40% owned by us, is engaged in phasing in its amino acid manufacturing plant in Ube, Japan and obtaining regulatory clearances from the FDA and other regulatory agencies for the
43
manufacture of PGLG in accordance with cGMP. EJ Holdings has had no revenues since its inception, has depended on loans from us to acquire the Ube plant and fund its operations and will continue to be dependent on loans from us or other financing unless and until its plant is activated and it can secure customers, including us, for its products. There is no assurance that we can continue to provide needed funding to EJ Holdings, or that needed funding will be available from other sources. EJ Holdings has no commitments or understandings regarding any additional funding. If EJ Holdings fails to obtain needed funding, it may need to suspend activities at the Ube plant. Under the asset purchase agreement by which EJ Holdings purchased the Ube plant, the seller has the right to repurchase the plant at the purchase price, plus certain taxes, paid by EJ Holdings if the plant does not become operational within a reasonable period of time (not to exceed five years). In that event, it is likely that we would lose some or all of our investment in EJ Holdings.
EJ Holdings may not be able to obtain needed financing or repay our loans, and our ownership interest in EJ Holdings may be diluted by additional financing.
As of December 31, 2020, we had loaned EJ Holdings a total of $17.8 million, including $4.0 million of loans made pursuant to our written commitment dated October 28, 2020 to loan EJ Holdings a total of up to $6.5 million through the period ending March 31, 2021. Management of EJ Holdings believes such loans will be sufficient to fund its planned activities at the Ube plant through the first quarter of 2021. It is possible, however, that EJ Holdings will need to secure additional debt financing or issue capital stock to fund such activities. We also anticipate that EJ Holdings will need to incur substantial debt or equity financing to fund the plant’s operations once phase in is completed, including, but not limited to, maintaining the physical plant and maintaining regulatory approvals for the manufacture of its products. To the extent EJ Holdings raises additional debt or equity financing, its ability to repay our loans may be adversely affected or our ownership interest may be diluted.
If EJ Holdings fails to reactivate its plant and obtain customers, it may not be able to sell its plant and property and we may lose our investment.
If EJ Holdings fails to reactivate the Ube plant or to secure customers for its products, it may need to sell its plant and property. There is no assurance that it will be able to do so at an attractive price or at all. Our loans to EJ Holdings are general unsecured obligations of EJ Holdings and we have no mortgage or other security interest in the plant or other property of EJ Holdings. Depending on the price at which the plant and property can be sold if it becomes necessary, EJ Holdings may be unable to repay our loans and its other secured or unsecured obligations and we may lose some or all of our investment in EJ Holdings.
EJ Holdings is subject to risks inherent in a new business and may not be successful.
EJ Holdings was formed in February 2017 for the purpose of acquiring, owning and operating Kyowa’s phased-out amino acid manufacturing plant in Ube, Japan. EJ Holdings is engaged in phasing in the plant and obtaining regulatory clearances to reactivate the plant, including FDA and other regulatory approvals for the manufacture of PGLG in accordance with cGMP. EJ Holdings has no operating history, and there is no assurance that it will be successful in bringing the plant online on a timely basis, or at all, or if it does so that it will be able to secure customers for its products or successfully implement its business plan.
We do not control EJ Holdings, and EJ Holdings may engage in activities contrary to our best interests.
JIP owns 60% of EJ Holdings and is entitled to designate a majority of EJ Holdings’ board of directors, its Chief Executive Officer and outside auditors, and, as such, controls the management, business and operations of EJ Holdings. It is possible that EJ Holdings will engage in actions or business activities that we believe are inconsistent with the MOU and not in our best interests and that may have an adverse effect on the economic or strategic value of our ownership interest in EJ Holdings.
EJ Holdings retains discretion over its use of any funds that we provide to it.
We do not control EJ Holdings’ day-to-day operations. Accordingly, funds provided by us to EJ Holdings may be used by it in any manner its management deems appropriate, including making capital expenditures and paying of salaries and other compensation of its officers and other employees. There is no assurance that EJ Holdings will use our funds in a manner that will enhance the value of our ownership interest in EJ Holdings.
44
Risks Related to Our Securities
We have experienced, and may continue to experience, significant volatility in our stock price that is uncorrelated to our results of operations or prospects.
The trading price for our common stock has historically been volatile and traded at higher or lower prices that are seemingly uncorrelated with our results of operations, financial condition or prospects. Between July 18, 2019 and December 31, 2020, the closing sale price of our common stock as reported on the OTC Markets Group, Inc. ranged from a low of $0.72 to a high of $6.86 and may continue to exhibit volatility. Factors such as the following may affect the volatility in our stock price:
|
|
● |
our quarterly operating results; |
|
|
● |
marketing approvals or other developments regarding Endari® or competing products; |
|
|
● |
announcements of regulatory developments or technological innovations by us or our competitors; |
|
|
● |
changes in our relationship with our vendors, distributors or other strategic partners; |
|
|
● |
government regulation of drug pricing; and |
|
|
● |
developments in patent or other technology ownership rights; |
Other factors which may affect our stock price include general economic conditions or changes in the economy, the financial markets or the pharmaceutical or biotechnology industries driven by extraordinary events such as the COVID-19 pandemic. We may be particularly vulnerable to volatility caused by these conditions or events, as we have only a single approved product and have relatively thin trading volume in our stock.
Stockholders may experience future dilution as a result of future equity offerings.
In order to raise additional capital in the future we may sell and issue additional shares of our common stock or securities convertible into or exchangeable for our common stock, which sales would have a dilutive effect on our stockholders.
The outstanding convertible debentures and warrants may result in further dilution to our stockholders.
Our outstanding Second Amended and Restated 10% Senior Secured Convertible Debentures in the aggregate principal amount of $7.2 million as of December 31, 2020 and related warrantsto purchase a total of up to 1,537,200 shares of our common stock include so-called full-ratchet anti-dilution adjustments in the event we sell or issue shares of common stock or common stock equivalents at an effective price less than the then conversion price of the debentures and exercise price of such warrants, subject to certain exceptions. These anti-dilution adjustments resulted in a reduction in the conversion price of the debentures and the exercise price of such warrants to $2.00 per share based upon our issuance and sale of 100,000 shares of our common stock at a price of $2.00 per share in March 2020. Since March 2020, we have issued additional warrants to purchase a total of 2,070,000 shares of our common stock with identical anti-dilution adjustments. These anti-dilution adjustments also would be triggered by future issuances by us of shares of our common stock or common stock equivalents at an effective price per share below the then-conversion and exercise prices of the debentures and such warrants, which adjustments would have a further dilutive effect on our stockholders.
A substantial number of shares of common stock may be sold in the market, which may depress the market price for our common stock.
Sales of a substantial number of shares of our common stock in the public market could cause the market price of our common stock to decline. A substantial majority of the outstanding shares of our common stock are, and the shares of common stock which may be sold in future offerings by us will be, freely tradable without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act.
We may issue preferred stock in the future, and the terms of the preferred stock may reduce the value of our common stock.
We are authorized to issue up to 15,000,000 shares of preferred stock in one or more series. Our board of directors may determine the terms of future preferred stock offerings without further action by our stockholders. If we issue preferred stock, it could affect your rights or reduce the value of our outstanding common stock. In particular, specific rights granted to future
45
holders of preferred stock may include voting rights, preferences as to dividends and liquidation, conversion and redemption rights, sinking fund provisions, and restrictions on our ability to merge with or sell our assets to a third party.
Trading on the OTC Markets is volatile and sporadic, which could depress the market price of our common stock and make it difficult for our security holders to resell their common stock.
Until July 31, 2020 our common stock was quoted on the OTCQB tier of the OTC Markets Group, Inc. On August 3, 2020, our common stock was relegated to the OTC Pink tier of the OTC Markets Group, Inc. pending the filing of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and our Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q for the quarters ended March 31, 2020, June 30, 2020 and September 30, 2020 and posting of our OTCQB Certification and verification of the company profile through OTCIQ.com. Trading in securities quoted on the OTC Markets is often thin and characterized by wide fluctuations in trading prices due to many factors, some of which may have little to do with our operations or business prospects. This volatility could depress the market price of our common stock for reasons unrelated to our business or operating performance. Moreover, the OTC Markets is not a stock exchange, and trading of securities on the OTC Markets is often more sporadic than the trading of securities listed on a quotation system such as The Nasdaq Capital Market or a stock exchange like the NYSE American. These factors may result in investors having difficulty purchasing and reselling shares of our common stock.
Out common stock is not traded on a national securities exchange, which may adversely affect our ability to raise needed financing.
The OTC Markets Group, Inc. is not a national securities exchange within the meaning of federal and state securities laws, so our common stock is not eligible for the exemption from state securities, or “blue sky,” laws for “covered securities” within the meaning of the National Securities Markets Improvement Act of 1996, which may adversely affect our ability to sell our securities to raise needed financing and increase transactions costs of such financing.
As long as our common stock is quoted on the OTC Markets, our stockholders may face significant restrictions on the resale of our common stock due to state “blue sky” laws.
Each state has its own securities laws, often called “blue sky” laws, which limit sales of securities to a state’s residents, unless the securities are registered in that state or qualify for an exemption from registration, and govern the reporting requirements for broker-dealers doing business directly or indirectly in the state. Before a security is sold in a state, there must be a registration in place to cover the transaction, or the transaction must be exempt from registration. The applicable broker must also be registered in that state. As long as our common stock is quoted on the OTC Pink tier or the OTCQB tier, a determination regarding registration will be made by those broker-dealers, if any, who agree to serve as market-makers for our common stock. There may be significant state blue sky law restrictions on the ability of investors to sell, and on purchasers to buy, our common stock. You should therefore consider the resale market for our common stock warrants to be limited, as you may be unable to resell your common stock without the significant expense of state registration or qualification.
Not applicable.
We lease office space under operating leases from unrelated entities. The rent expense during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 was approximately $926,000 and $669,000 respectively.
We lease 21,293 square feet of office space for our headquarters in Torrance, California, at a base rental of $78,908 per month, which the lease will expire on September 30, 2026. We also leased an additional 1,850 square feet office space in New York, New York, at a base rent of $8,479 per month, which the lease will expire on December 31, 2022.
In addition, we lease 1,322 square feet of office space in Tokyo, Japan, 465 square feet of office space in Seoul, Korea, and 1,163 square feet of office space in Dubai, UAE, which leases will expire on September 30, 2020, November 29, 2020, and June 19, 2023, respectively.
We believe our existing facilities are adequate for our current and planned future operations, and we expect to be able to renew the leases on commercially reasonable terms.
46
Not applicable.
Not applicable.
47
|
ITEM 5. |
MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON STOCK, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES |
Market Information
Our common stock was listed for trading on The Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol “MYND” until July 17, 2019 and the symbol “EMMA” from then until the opening of the market on September 11, 2019, after which it became eligible for quotation on the OTCQB market. On August 3, 2020, our common stock was relegated to trading on the OTC Pink tier of the OTC Markets Group, Inc. The following table sets forth the high and low sales price for our common stock as reported on The Nasdaq Capital Market and high and low bid information for our common stock as reported on OTCQB or OTC Pink tier for the periods indicated. The information reported on the OTCQB and OTC Pink tier reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, mark-down or commission and may not necessarily represent actual transactions.
|
|
|
High |
|
|
|
Low |
|
||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2019 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First Quarter |
|
$ |
12.91 |
|
|
|
$ |
3.90 |
|
|
Second Quarter |
|
$ |
9.30 |
|
|
|
$ |
6.00 |
|
|
Third Quarter |
|
$ |
11.76 |
|
|
|
$ |
1.33 |
|
|
Fourth Quarter |
|
$ |
3.25 |
|
|
|
$ |
1.69 |
|
|
Year Ended December 31, 2020 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First Quarter |
|
$ |
2.14 |
|
|
|
$ |
0.85 |
|
|
Second Quarter |
|
$ |
1.99 |
|
|
|
$ |
1.08 |
|
|
Third Quarter |
|
$ |
2.16 |
|
|
|
$ |
0.85 |
|
|
Fourth Quarter |
|
$ |
1.36 |
|
|
|
$ |
0.72 |
|
|
Year Ended December 31, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
First Quarter (through January 5, 2021) |
|
$ |
1.45 |
|
|
|
$ |
1.31 |
|
Holders
As of January 5, 2021, we had approximately 394 stockholders of record.
Dividends
We did not pay cash dividends on our common stock in either of the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, and do not expect to do so in the foreseeable future. The decision whether to pay cash dividends on our common stock will be made by our board of directors in its discretion and will depend on our financial condition, operating results, capital requirements and other factors that the board of directors considers relevant.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
None.
Additional Information
Copies of our annual reports, quarterly reports, current reports, and any amendments to those reports are available free of charge on the Internet at www.sec.gov and on our website at www.emmausmedical.com. Such reports are not part of this Annual Report or incorporated by reference herein. All statements made in any of our reports, including all forward‑looking statements, are made as of the date of such reports and we do not assume or undertake any obligation to update any of those statements or documents, except as required by law.
Not required for a smaller reporting company
48
The following discussion of our financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and the related notes, and the other financial information included in this Annual Report. This discussion contains forward‑looking statements based upon current expectations that involve risks and uncertainties. Our actual results may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward‑looking statements as a result of various factors, including those set forth under “Risk Factors” or in other parts of this Annual Report.
Overview of Restatement
As previously disclosed in the company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 8, 2020, the board of directors of the company, based on the recommendation of the audit committee and in consultation with management and the company’s predecessor independent public accounting firm, concluded that, because of errors identified in the previously issued financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2018 and the quarterly periods ended June 30, 2019 and September 30, 2019, the company would restate the previously issued financial statements.
The restated financial statements correct the following errors:
|
|
1. |
Warrants issued by EMI in October 2018 and accounted for as equity should have been treated as derivative liabilities and accounted for at fair value with changes in fair value recorded in earnings. This error resulted in $7.8 million, $8.6 million, and $7.5 million understatements of the fair value of warrant derivative liabilities as of June 30, 2019, March 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, respectively. It also resulted in understatements of stockholder’s deficit of $5.6 million as of September 30, 2019 and $9.7 million as of June 30, 2019, March 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018. This error also resulted in $0.2 million and $1.0 million understatements of net loss for the six months and three months ended June 30, and March 31, 2019, respectively, and in a $2.4 million overstatement of net loss for the year ended December 31, 2018. In connection with the completion of our merger transaction with EMI on July 17, 2019, the exercise price of the warrants was adjusted and the warrants were reclassified to equity. |
|
|
2. |
EMI’s interest in EJ Holdings, which was consolidated as a Variable Interest Entity, should have been accounted for based upon the equity method. This error is resulted in $13.2 million and $0.2 million overstatements of cash and other current assets, respectively, and a $13.6 million understatement of the equity method investment as of December 31, 2018. The error also resulted in a $0.2 million overstatement of loss from operations and a $0.1 million overstatement of loss before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2018. |
|
|
3. |
Fair value of cashless warrants exercised in September 2018 upon expiration of warrants should have been recorded in additional paid-in capital. The error resulted in $18.3 million of an overstatement of change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities and an understatement of additional paid-in cash for the year ended December 31, 2018. |
|
|
4. |
Other adjustments consist of the following: |
Period adjustments of variable considerations resulted in $1,4 million and $436,000 understatements of revenue and accounts receivable and $945,000 overstatement of accounts payable as of December 31, 2018 and $1.3 million overstatement of revenue as of September 30, 2019.
An error in accounting for on the financing of insurance premium resulted in $141,000 and $598,000 understatements of prepaid expenses and current liabilities as of December 31, 2018 and September 30, 2019, respectively.
Adjustments of the stock modification accounting resulted in $52,000 understatements of additional paid-in capital and general and administrative expense for the year ended December 31, 2018 and an overstatement of general and administrative expenses for the nine months ended September 30, 2019.
An error in the accounting for conversion feature of securities resulted in $172,000 and $249,000 understatements of additional paid-in capital and interest expenses, respectively and $543,000 and $466,000 overstatements of loss on debt extinguishment and change in fair value of embedded conversion option, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2018.
49
An error in the classification of shipping cost and royalty expenses resulted in a $229,000 understatement of cost of sales and $80,000 and $141,000 overstatements of selling cost and general and administrative expense, respectively for the year ended December 31, 2019. The error also resulted in a $71,000 understatement of cost of sales and $11,000 and $60,000 overstatements of selling cost and general and administrative expense.
An error in the debt modification accounting resulted in a $1.1 million understatement of additional paid-in capital as of September 30, 2019. The error also resulted in $320,000 overstatements of loss on debt extinguishment for the three months and nine months ended September 30, 2019 and a $1.3 million understatement of interest expense for nine months ended September 30, 2019.
An error in the GPB warrant liability classification resulted in a $91,000 understatement of warrant derivative liabilities and a $776,000 overstatement of additional paid-in capital as of December 31, 2019. The error also resulted in a $685,000 understatement of change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities for the three months and the nine months ended September 30, 2019.
Company Overview
We are a commercial-stage biopharmaceutical company engaged in the discovery, development, marketing and sale of innovative treatments and therapies, primarily for rare and orphan diseases. On July 7, 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, approved our lead product, Endari® (prescription-grade L-glutamine oral powder), to reduce the severe complications of sickle cell disease (“SCD”) in adult and pediatric patients five years of age and older. Endari® has received Orphan Drug designation from the FDA and Orphan Medical designation from the European Commission, which designations afford marketing exclusivity for Endari® for a seven-year period in the U.S. and ten-year period in the European Union, respectively, following marketing approval.
We commenced commercialization of Endari® in the U.S. in January 2018 in collaboration with a contract sales organization. Effective January 2020, we have relied upon our in-house commercial sales team. Endari® is reimbursable by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and every state provides coverage for Endari® for outpatient prescriptions to all eligible Medicaid enrollees within their state Medicaid programs. We have distribution agreements in place with the nation’s leading distributors as well as physician group purchasing organizations and pharmacy benefits managers, making Endari® available at selected pharmacies nationwide.
Until we began marketing and selling Endari® in the U.S. in early 2018, we had minimal revenues and relied upon funding from sales of equity securities and debt financings and loans, including loans from related parties to fund our business and operations. As of December 31, 2019, our accumulated deficit was $226.2 million and we had cash and cash equivalents of $1.8 million. We expect net revenues to increase as we expand our commercialization of Endari® in the U.S. and expand or commence early access programs and eventual marketing and commercialization abroad.
Until we can generate sufficient net revenues, our future cash requirements are expected to be financed through public or private equity or debt financings, loans or corporate collaboration and licensing arrangements. We are unable to predict if or when we will become profitable.
As reported in more detail in our Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 22, 2019, as amended by our Form 8-K/A filed on August 14, 2019, on July 17, 2019, we completed our merger transaction with EMI Holding, Inc., formerly known as Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. (“EMI”), in accordance with the terms of the Agreement and Plan of Merger and Reorganization, dated as of January 4, 2019, among us, Athena Merger Subsidiary, Inc., and EMI, as amended by Amendment No. 1 thereto, dated as of May 10, 2019, which we refer to as the merger agreement. Pursuant to the merger agreement, Athena Merger Subsidiary, Inc. merged into EMI, with EMI surviving as our wholly owned subsidiary. On July 17, 2019, immediately after completion of the merger, we changed our name to “Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc.”
The merger was treated as a reverse recapitalization transaction under the acquisition method of accounting in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. For accounting purposes, EMI is considered to have acquired us. The merger is intended to qualify as a tax-free reorganization for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
50
Management’s discussion and analysis of financial condition and results of operations is based on our financial statements, which have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States (“GAAP”). The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities and expenses. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate these estimates and judgments, including those described below. We base our estimates on our historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the present circumstances. These estimates and assumptions form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ materially from these estimates.
While our significant accounting policies are more fully described in Note 2 of the Notes to Financial Statements included in this Annual Report, we believe that the following accounting policies are the most critical to assist you in fully understanding and evaluating our reported financial results and affect the more significant judgments and estimates that we use in the preparation of our financial statements.
Financial Overview
Revenues, net
Since January 2018, we have generated net revenues primarily through the sale of Endari® as a treatment for SCD.
Net revenues from Endari® sales are recognized upon transfer to our distributors and specialty pharmacy providers. Distributors resell our products to other pharmacy and specialty pharmacy providers, health care providers, hospitals, and clinics. In addition to agreements with these distributors, we enter into contractual arrangements with specialty pharmacy providers, in-office dispensing providers, physician group purchasing organizations, pharmacy benefits managers and government entities that provide for government-mandated or privately negotiated rebates, chargebacks and discounts with respect to the purchase of our products. These various discounts, rebates, and chargebacks are referred to as “variable consideration.” Revenue from product sales is recorded net of variable consideration.
Under the Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 606, the Company recognizes revenue when its customers obtain control of the Company's product, which typically occurs on delivery. Revenue is recognized in an amount that reflects the consideration that the Company expects to receive in exchange for the product, or transaction price. To determine revenue recognition for contracts with customers within the scope of ASC 606, the Company performs the following 5 steps: (i) identify the contract(s) with a customer; (ii) identify the performance obligations in the contract; (iii) determine the transaction price; (iv) allocate the transaction price to the Company’s performance obligations in the contract; and (v) recognize revenue when (or as) the Company satisfies the relevant performance obligations.
Revenue from product sales is recorded at the transaction price, net of estimates for variable consideration consisting of sales discounts, returns, government rebates, chargebacks and commercial discounts. Variable consideration is estimated using the expected-value amount method, which is the sum of probability-weighted amounts in a range of possible transaction prices. Actual variable consideration may differ from the Company's estimates. If actual results vary from the Company's estimates, the Company adjusts the variable consideration in the period such variances becomes known, which would affect net revenues in that period. The following are our significant categories of variable consideration:
Sales Discounts: We provide our customers prompt payment and large order discounts and from time to time offer additional discounts that are recorded as a reduction of revenue in the period the revenue is recognized. Sales attributable to one-time discounts offered by us increased in 2019 and may adversely affect sales in subsequent periods.
Product Returns: We offer our distributors a right to return product principally based upon (i) overstocks, (ii) inactive product or non-moving product due to market conditions, and (iii) expired product. Product return allowances are estimated and recorded at the time of sale.
Government Rebates: We are subject to discount obligations under state Medicaid programs and the Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage gap program. We estimate Medicaid and Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage gap rebates based upon a range of possible outcomes that are probability-weighted for the estimated payor mix. These reserves are recorded in the same period the related revenues are recognized, resulting in a reduction of product revenues and the establishment of a current liability that is included as accounts payable and accrued expenses on our balance sheet. Our liability for these rebates consists primarily of estimates of claims expected to be received in future periods related to recognized revenues.
51
Chargebacks and Discounts: Chargebacks for fees and discounts represent the estimated obligations resulting from contractual commitments to sell products to certain specialty pharmacy providers, in-office dispensing providers, group purchasing organizations, and government entities at prices lower than the list prices charged to distributors. The distributors charge us for the difference between what they pay for the products and our contracted selling price to these specialty pharmacy providers, in-office dispensing providers, group purchasing organizations, and government entities. In addition, we have contractual agreements with pharmacy benefit managers who charge us for rebates and administrative fee in connection with the utilization of product. These reserves are established in the same period that the related revenues are recognized, resulting in a reduction of revenues. Chargeback amounts are generally determined at the time of resale of product by our distributors.
Cost of goods sold consists primarily of raw materials, packaging, shipping and distribution of Endari®.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development costs consist of expenditures for new products and technologies consisting primarily of fees paid to contract research organizations (“CRO”) that conduct clinical trials of our product candidates, payroll‑related expenses, study site payments, consultant fees and activities related to regulatory filings, manufacturing development costs and other related supplies. The costs of later stage clinical studies such as Phase 2 and 3 trials are generally higher than those of earlier studies. This is primarily due to the larger size, expanded scope, patient related healthcare and regulatory compliance costs, and generally longer duration of later stage clinical studies.
Our contracts with CROs are generally based on time and materials expended, whereas study site agreements are generally based on costs per patient as well as other pass-through costs, including start-up costs and institutional review board fees. The financial terms of these agreements are subject to negotiation and vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payment flows. Payments under some of these contracts depend on factors such as the successful enrollment of patients and the completion of clinical trial milestones.
Future research and development expenses will depend on any new product candidates or technologies that we may introduce into our research and development pipeline. In addition, we cannot predict which product candidates may be subject to future collaborations, when such arrangements will be secured, if at all, and to what degree, if any, such arrangements would affect our development plans and capital requirements.
Due to the inherently unpredictable nature of the drug approval process and the interpretation of the regulatory requirements, we are unable to estimate the amount of costs of obtaining regulatory approval of Endari® outside of the U.S. or the development of our other preclinical and clinical programs. Clinical development timelines, the probability of success and development costs can differ materially from expectations and can vary widely. These and other risks and uncertainties relating to product development are described in this Annual Report under the headings “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business” and “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Regulatory Oversight of our Business and Compliance with Law.”
General and Administrative Expense
General and administrative expense consists principally of salaries and related costs, including share‑based compensation for our directors and executive officers, of our employees, including our in-house commercialization team. Other general and administrative expense includes facility costs, patent filing costs, and professional fees and expenses for legal, consulting, auditing and tax services. Inflation has not had a material impact on our general and administrative expense over the past two years.
Selling Expenses
Selling expenses consist principally of salaries and related costs for personnel involved in the launch, promotion, sales and marketing of our products. Other selling cost include advertising, third party consulting costs, the cost of contracted and in-house sales personnel and travel-related costs. We expect selling expenses to increase as we acquire additional sales and administrative personnel to support the commercialization of Endari® in the U.S. and abroad.
Environmental Expenses
The cost of compliance with environmental laws has not been material over the past two years and any such costs are included in general and administrative costs.
52
Inventories consist of raw material, finished goods and work-in-process and are valued on a first‑in, first‑out basis and at the lower of cost or net realizable value. Substantially all raw materials purchased during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 were supplied by one vendor.
Notes Payable, Convertible Notes Payable and Warrants
From time to time, we obtain financing in the form of notes payable and/or notes with detachable warrants, some of which are convertible into shares of our common stock and some of which are issued to related parties. We analyze all of the terms of our convertible debentures and promissory notes and debentures and promissory notes issued with warrants to determine the appropriate accounting treatment, including determining whether conversion features are required to be bifurcated and treated as a discount, allocation of fair value of the issuance to the debt instrument, detachable stock purchase warrant, and any beneficial conversion features, and the applicable classification of the convertible debentures and promissory and warrants as debt, derivative liabilities, equity or temporary equity (i.e., mezzanine capital).
We allocate the proceeds from the issuance of debt instruments with detachable stock purchase warrants to the two elements based on the relative fair values of the debt instruments without the warrants and of the warrants themselves at the time of issuance. We account for the portion of the proceeds allocated to warrants in additional paid‑in capital and the remaining proceeds are allocated to the debt instruments. The allocation to warrants results in a discount to notes payable which is amortized using the effective interest method to interest expense over the expected term of the note. We also include the intrinsic value of the embedded conversion feature of convertible debentures and promissory notes in the discount to notes payable, which is amortized and charged to interest expense over the expected term of the debentures and promissory notes.
We also estimate the total value of any beneficial conversion feature and accompanying warrants in allocating debt proceeds. The proceeds allocated to the beneficial conversion feature are determined by taking the estimated fair value of shares issuable under the convertible debentures and promissory notes less the fair value of the number of shares that would be issued if the conversion rate equaled the fair value of our common stock as of the date of issuance. In situations where the debt includes both a beneficial conversion feature and a warrant, the proceeds are allocated to the warrants and beneficial conversion feature based on the pro‑rata fair value. We used the Binomial Monte‑Carlo Cliquet (aka Ratchet) Option Pricing Model option pricing model to determine the fair value of our warrants prior to the Merger and Black-Scholes after the Merger.
Notes payable to related parties, interest expense and accrued interest to related parties are separately identified in our consolidated financial statements. We also disclose significant terms of all transactions with related parties.
Share‑based Compensation
We recognize compensation expense for share‑based compensation awards during the service term of the recipients of the awards. The fair value of share‑based awards is calculated using the Black‑Scholes‑Merton pricing model. The Black‑Scholes‑Merton model requires subjective assumptions regarding future stock price volatility and expected time to exercise, which greatly affect the calculated values. The expected term of awards granted is calculated using the simplified method allowed under the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) Staff Accounting Bulletin Nos. 107 and 110. The risk‑free rate used to value an award is based on the U.S. Treasury rate as of the date of the award that corresponds to the vesting period of the award. Until July 2019, our common stock was not publicly traded and we lacked company specific historical and implied volatility information for our common stock. Therefore, the expected volatility was based on the historical volatility of the common stock of comparable publicly traded companies.
53
We define fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. We measure fair value under a framework that provides a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1 measurements) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3 measurements). The three levels of the fair value hierarchy are described as follows:
Level 1: Inputs to the valuation methodology are unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
Level 2: Inputs to the valuation methodology include:
|
|
• |
Quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets; |
|
|
• |
Quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in inactive markets; |
|
|
• |
Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability; and |
|
|
• |
Inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means. |
If the asset or liability has a specified (contractual) term, the Level 2 input must be observable for substantially the full term of the asset or liability.
Level 3: Inputs to the valuation methodology that are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement.
The asset’s or liability’s fair value measurement level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement. Valuation techniques used need to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The fair value of marketable securities is determined based upon quoted prices on nationally recognized securities exchanges and are classified as Level 1 investments at December 31, 2019 and 2018. The fair value of our debt instruments is not materially different from their carrying values as presented. The fair value of our convertible debt instruments was determined based on Level 2 inputs. The carrying value of the debt was discounted based on allocating proceeds to other financial instruments within the arrangement as discussed in Note 8 to our consolidated financial statements.
Certain of our outstanding warrants contain net cash settlement provision and, consequently, are accounted for as liabilities that are remeasured at fair value on a recurring basis using Level 3 inputs. The Level 3 inputs in the valuation of warrants include expected term and expected volatility.
Marketable Securities
Marketable securities are recorded at fair value using the quoted market prices and changes in fair value are recorded as net realized gains or losses in comprehensive income. We monitor these investments for impairment and make appropriate reductions in carrying values as necessary.
54
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 (As Restated) |
|
||
|
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS ($ in thousands) |
|
||||||||
|
REVENUES, NET |
|
|
$ |
22,752 |
|
|
$ |
16,459 |
|
|
COST OF GOODS SOLD |
|
|
|
1,094 |
|
|
|
993 |
|
|
GROSS PROFIT |
|
|
|
21,658 |
|
|
|
15,466 |
|
|
OPERATING EXPENSES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
|
2,183 |
|
|
|
1,723 |
|
|
Selling |
|
|
|
6,975 |
|
|
|
4,733 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
|
17,012 |
|
|
|
17,464 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
|
26,170 |
|
|
|
23,920 |
|
|
LOSS FROM OPERATIONS |
|
|
|
(4,512 |
) |
|
|
(8,454 |
) |
|
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss on debt extinguishment |
|
|
|
(438 |
) |
|
|
(2,702 |
) |
|
Change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities |
|
|
|
3,545 |
|
|
|
4,476 |
|
|
Change in fair value of embedded conversion option |
|
|
|
131 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Net losses on investment in marketable securities and long-term investment |
|
|
|
(21,947 |
) |
|
|
(43,977 |
) |
|
Net losses on equity method investment |
|
|
|
(414 |
) |
|
|
(97 |
) |
|
Miscellaneous reverse merger costs |
|
|
|
(309 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Notes conversion costs |
|
|
|
(3,341 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Interest and other income |
|
|
|
232 |
|
|
|
1,002 |
|
|
Interest expense |
|
|
|
(27,625 |
) |
|
|
(22,796 |
) |
|
Total other expense |
|
|
|
(50,166 |
) |
|
|
(64,094 |
) |
|
LOSS BEFORE INCOME TAXES |
|
|
|
(54,678 |
) |
|
|
(72,548 |
) |
|
INCOME TAXES |
|
|
|
164 |
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
NET LOSS |
|
|
|
(54,842 |
) |
|
|
(72,587 |
) |
|
NET LOSS PER COMMON SHARE |
|
|
$ |
(1.30 |
) |
|
$ |
(1.97 |
) |
|
WEIGHTED-AVERAGE COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING |
|
|
|
42,259,460 |
|
|
|
36,857,995 |
|
Years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018
Net Loss. Net loss was $54.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to $72.6 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, representing a decrease of $17.7 million, or 24.4%. The decrease in net loss was primarily a result of a $6.3 million increase in net revenue and a $13.9 million decrease in other expenses partially offset by a $2.3 million increase in operating expenses, as discussed below. As of December 31, 2019, we had an accumulated deficit of approximately $226.2 million. We anticipate that our net loss will narrow in the foreseeable future.
Revenues, Net. Net revenues increased by $6.3 million, or 38% to $22.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to 2018. Substantially all net revenues were attributable to Endari® sales. We afforded customers a higher level of price discounts related to large volume orders in 2019 than in 2018. This resulted in an offset to the growth in net revenues compared to the higher growth in gross sales and boxes of Endari® sold in 2019. We expect Endari® revenues to increase as we expand our commercialization efforts in the U.S. and abroad.
Cost of Goods Sold. Cost of goods sold increased by $0.1 million, or 10% to $1.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to 2018 as net revenues increased. Cost of goods sold consist primarily of costs for raw materials, packaging, shipping and distribution of Endari®.
Research and Development Expenses. Research and development expenses increased by $0.5 million, or 27%, to $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to 2018. This increase was primarily due to an increase in expenses related to our Pilot/Phase 1 diverticulosis study. We expect our research and development costs to increase as the study progresses and as we undertake additional studies.
55
Selling Expenses. Selling expenses increased $2.2 million, or 45%, to $7.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to 2018. The increase was primarily due to an increase of $1.5 million in contract sales organization (CSO) fees for Endari® and $0.7 million in salaries and other marketing activities including public relations, sales meetings and sponsorships. We anticipate that our selling expenses will continue to increase as we expand Endari® marketing and sales activities both in the U.S. and outside the U.S. In January 2020, we terminated the relationship with our CSO and established our in-house sales force.
General and Administrative Expense. General and administrative expense decreased $0.5 million, or 3%, to $17.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to 2018. General and administrative expense includes share-based compensation expenses, professional fees, office rent and payroll expenses. Of the $17.0 million in total general and administrative expenses in 2019, $2.4 million were one-time expenses attributable to stock option and warrant modifications relating to the merger transaction. We expect on-going general and administrative expenses to remain substantially the same for the foreseeable future.
Other Income and Expense. Total other expense decreased by $13.9 million, or 21.7%, to $50.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 compared to 2018. The decrease was primarily due to by a reduction in net loss on investment in marketable securities of $22.5 million and a decrease in loss on debt extinguishment of $2.3 million, which were partially offset by an increase in interest expense of $4.8 million and $3.3 million in note conversion expense related to the convertible notes converted in connection with the Merger.
Seasonality
There may be seasonal variations in our Endari® sales due to factors such as year-end holidays, severe winter weather conditions in certain regions of the U.S., seasonal conditions that may affect medical practices and provider activity, including influenza or the recent Covid-19 outbreaks that may inhibit patients from seeking treatment for their SCD or filling or refilling prescriptions for Endari® and possibly other factors relating to the timing of patient deductibles and co-insurance limits.
Inflation
We do not believe that inflation and changing prices have had a significant impact on our results of operations.
COVID-19
We do not believe that the COVID-19 pandemic and related governmental response have had a significant impact on our financial condition or results of operations.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Based on our losses to date, anticipated future net revenues and operating expenses, debt repayment obligations, funding commitment to EJ Holdings and cash and cash equivalents balance of $1.8 million as of December 31, 2019, we do not have sufficient operating capital for our business without raising additional capital. While we look to expand our commercialization of Endari® in the U.S. and expand or commence early access programs and eventual marketing and commercialization abroad, there is no assurance that our net revenues will increase in the future.
We continue to incur expenses for the expanded commercialization of Endari®, research costs for our pilot study of our prescription grade L-glutamine oral powder in the treatment of diverticulosis and CAOMECS technology and expenses relating to EJ Holdings’ startup and operation of its Ube, Japan manufacturing facility. We have previously relied on private equity offerings, debt financings, and loans, including loans from related parties and other investors as discussed below. As of December 31, 2019, we had outstanding consolidated notes payable in an aggregate principal amount of $17.1 million, consisting of $3.9 million of non‑convertible promissory notes and $13.2 million of senior secured convertible debentures and convertible notes. All $17.1 million aggregate principal amount of notes payable outstanding as of December 31, 2019 was either due on demand or was to become due and payable within the next twelve months. Subsequent to December 31, 2019, our outstanding senior secured convertible debentures were amended and restated to extend the maturity date to August 31, 2021 subject to monthly redemption payments under the convertible debentures, and the maturity date of an outstanding convertible promissory note in the principal amount of $3.0 million as of December 31, 2019 was extended to June 15, 2023. The notes payable bear interest at annual rates ranging from 10% to 12%. The net proceeds of the notes were used for working capital purposes.
Until we can generate sufficient revenue, our future cash requirements are expected to be financed through public or private equity or debt offerings, loans or corporate collaboration and licensing arrangements or other financing arrangements. We have no current understanding or arrangements with respect to future financings, and there can be no assurance that we can
56
raise needed capital on terms acceptable to us (or at all). Due to the uncertainty of our ability to meet our current and future operating and capital expenses, there is substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern.
Subsequent to the year ended December 31, 2019, the company issued shares of common stock as follows:
|
Common Shares Issued after December 31, 2019 |
|
Dollar Amount |
|
|
Number of Shares Issued |
|
||
|
Common shares |
|
$ |
200,000 |
|
|
|
100,000 |
|
Cash Flows
Net cash used in operating activities
Net cash used in operating activities of $4.5 million in 2019 related to net loss of $54.8 million adjusted for non-cash items of $50.0 million primarily related to the amortization of discount on notes payable and convertible notes payable, net losses on investment in marketable securities, loss on debt settlement, shared-based compensation and fair value of replacement equity award, and notes conversion expenses.
Net cash used in investing activities
Net cash used in investing activities decreased by $5.9 million, or 80%, to $1.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from $7.4 million for the years ended December 31, 2018. The decrease was primarily due to $13.3 million used to fund the purchase by EJ Holdings, Inc. of the manufacturing plant in Ube, Japan in 2018, which was partially offset by $6.2 million decrease of cash proceeds from sales of marketable securities and $1.6 million of transaction costs relating to the merger transaction.
Net cash from financing activities
Net cash from financing activities increased by $9.6 million, or 168%, to a positive $3.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2019 from a negative $5.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2018, primarily as a result of a $7.3 million increase in cash proceeds from the issuance of common stock and a $14.7 million decrease in repayment of convertible notes partially offset by a $17.6 million decrease of cash proceeds from the issuance of convertible debentures and convertible note.
Off‑Balance‑Sheet Arrangements
We had no off-balance sheet arrangements in the periods presented.
57
Not required for a smaller reporting company.
The information required by this Item 8 is incorporated by reference to the information that begins on Page F‑1 of this Annual Report.
On September 10, 2020, our Audit Committee determined to engage Squar Milner LLP (“Squar Milner”) as our independent registered public accounting firm and to dismiss BDO USA, LLP (“BDO”) as our independent registered public accounting firm. Effective as of November 1, 2020, Squar Milner became part of Baker Tilly US, LLP (“Baker Tilly”).
BDO was engaged by us on January 8, 2020 to audit our annual financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2019 (the “2019 Annual Financials”) and to review our unaudited quarterly financial statements for 2020, but as of September 10, 2020 had not completed its audit for 2019 or issued any audit or review reports on our financial statements. At the time of BDO’s dismissal, there were no (1) disagreements (as that term is defined in Item 304(a)(1)(iv) of Regulation S-K under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (“Regulation S-K”) and related instructions), between management of the company and BDO on any matter of accounting principles or practices, financial statement disclosure or auditing scope or procedures which disagreements, if not resolved to the satisfaction of BDO, would have caused BDO to refer to the disagreements in its reports on the financial statements for 2019, or (2) reportable events as set forth in Item 304(a)(1)(v) of Regulation S-K, except as described below:
We reported in a Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC, on July 8, 2020 (the “July 2020 8-K”) that the previously filed audited consolidated financial statements of our EMI Holding, Inc. subsidiary, or EMI, for the year ended December 31, 2018 (the “2018 Annual Financials”), as well as EMI’s unaudited consolidated financial statements for the three months ended March 31, 2019 and the three and six months ended June 30, 2019 and our previously filed unaudited consolidated financial statements for the three and nine months ended September 30, 2019 (together with the 2018 Annual Financials, the “Affected Financials”), can no longer be relied upon as the result of accounting errors identified in the course of the preparation of the company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2019 related to (1) the misclassification as equity of warrants issued in October 2018 and (2) the erroneous consolidation as a Variable Interest Entity of our interest in EJ Holdings, Inc., a 40%-owned Japanese corporation (the “Reported Errors”). BDO advised management that BDO concluded that the Reported Errors materially impact the fairness and reliability of the 2018 Annual Financials and other Affected Financials and that, unless resolved to BDO’s satisfaction, would prevent BDO from rendering an audit report on our 2019 Annual Financials. As reported in the July 2020 8-K, management agreed with BDO’s conclusion regarding the Reported Errors. BDO also advised management that information had come to BDO’s attention regarding (1) the accounting for two revenue adjustments recorded in 2019 that should have been recorded in 2018,(2) the accounting for certain debt and related warrants issued in 2018 that also impacted 2019, and (3) the accounting for certain debt modifications in 2019 which BDO concluded impacted the Affected Financials in immaterial ways and which, unless resolved to BDO’s satisfaction, would prevent BDO from rendering an audit report on our 2019 Annual Financials. BDO advised management that it would be necessary to re-audit the 2018 Annual Financials to make all adjustments regarding these errors, as well as the Reported Errors, to BDO’s satisfaction. Management disagreed with BDO’s advice regarding the need to re-audit the 2018 Annual Financials for immaterial errors but agreed to consult with SingerLewak, LLP (“SingerLewak”), EMI’s predecessor auditor, and to consider engaging SingerLewak to re-audit the 2018 Annual Financials if the parties could agree upon on the appropriate scope of the re-audit. After considering the matter further and discussing it with management and BDO, SingerLewak advised management that, in accordance with its practices, any re-audit of the 2018 Financials by SingerLewak would include accounts affected by the Reported Errors only and that accounts affected by immaterial errors affecting the 2019 Annual Financials should be audited by BDO as the successor auditor. Since the parties were unable to agree on the scope of a re-audit of the 2018 Financials, the Audit Committee determined to dismiss BDO and to retain Squar Milner to audit both the 2019 Annual Financials and the 2018 Financials and to review our quarterly financial statements for 2020 and adjustments to our unaudited quarterly financial statements for 2019. Accordingly, the disagreement was not resolved prior to BDO’s dismissal. BDO also advised management that the Reported Errors necessarily meant that we did not maintain effective controls over certain aspects of the financial reporting process, which we previously reported in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2018.
58
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We are responsible for establishing and maintaining disclosure controls and procedures (“DCP”) that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports filed by us under the Exchange Act is: (a) recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms; and (b) accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive and principal financial officers, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosures. In designing and evaluating our DCP, we recognize that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and implemented, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving the desired control objectives.
We conducted an evaluation pursuant to Rule 13a‑15 of the Exchange Act of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our DCP as of December 31, 2019. This evaluation was conducted under the supervision (and with the participation) of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Interim Chief Financial Officer. Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Interim Chief Financial Officer concluded that our DCP were not effective as of December 31, 2019, because of the continuance of a material weakness (the “Material Weakness”) in our internal control over financial reporting due to inadequate application of generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) in the United States of America on certain complex transactions, inadequate financial closing process, segregation of duties including access control of information technology especially financial information, inadequate documentation of policies and procedures over risk assessments, internal control and significant account process and insufficient entity risk assessment process. Notwithstanding the Material Weakness, our management concluded that our consolidated financial statements for the periods covered by and included in this Annual Report are fairly stated in all material respects in accordance with GAAP for each of the periods presented in this Annual Report.
We committed to remediating the control deficiencies that constituted the Material Weakness by implementing changes to our internal control over financial reporting. In 2018, we began to implement measures designed to remediate the underlying causes of the control deficiencies that gave rise to the Material Weakness, including, without limitation:
|
|
• |
engaging third‑party accounting consulting firms to assist us in the review of our application of GAAP on complex debt financing transactions and revenue recognition under ASC 606; |
|
|
• |
using of GAAP Disclosure and SEC Reporting Checklists; |
|
|
• |
increasing the continuing professional training and academic education on accounting subjects for accounting staff; |
|
|
• |
enhancing the level of the precision of review controls related to our financial close and reporting; and |
|
|
• |
engaging other supplemental internal and external resources. |
59
Our management concluded that, as of December 31, 2019, we had not completed all the corrective measures that are necessary to remediate entirely the Material Weakness.
Management’s Plan for Remediation
Our management and board of directors are committed to the remediation of the Material Weakness, as well as the continued improvement of our overall system of internal control over financial reporting. We are in the process of implementing measures to remediate the underlying causes of the control deficiency that gave rise to the Material Weakness, which primarily include engaging additional and supplemental internal and external resources with the technical expertise in GAAP to ensure the appropriate accounting treatment for complex and unusual transactions involving options, convertible securities and other financial instruments and intend to seek to hire a permanent Chief Financial Officer with expertise and experience in GAAP to support our financial department, as well as to implement new policies and procedures to provide more effective controls to track, process, analyze, and consolidate the financial data and reports. We also intend to consider upgrading our financial accounting systems and software as our finances permit. Further, we are in the process of reviewing plans to establish a Disclosure Committee to ensure more effective internal communication of significant transactions.
We believe these measures will remediate the control deficiencies that gave rise to a Material Weakness. As we continue to evaluate and work to remediate these control deficiencies, we may determine that additional measures may be required.
We are committed to maintaining a strong internal control environment and believe that these remediation actions will represent improvements in our internal control over financial reporting when they are fully implemented. The Material Weakness will not be considered fully remediated until controls have been designed and implemented for a sufficient period of time for our management to conclude that the control environment is operating effectively. Additional remediation measures may be required, which may require additional implementation time. We will continue to assess the effectiveness of our remediation efforts in connection with our evaluation of our internal control over financial reporting and DCP.
As we continue to evaluate and work to remediate the Material Weakness and enhance our internal control over financial reporting and DCP, we may determine that we need to modify or otherwise adjust the remediation measures described above. As a result, we cannot assure you that our remediation efforts will be successful or that our internal control over financial reporting or DCP will be effective.
Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a‑15(f) under the Exchange Act. Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States of America. Our internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect our transactions and our dispositions of the assets; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that our receipts and expenditures are being made only in accordance with authorizations of our management and directors; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of our assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risks that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Interim Chief Financial Officer, we conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting based on the criteria set forth in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this evaluation, our management concluded that our internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of December 31, 2019.
A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of a company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. In conducting our review of our internal control over financial reporting, we identified the continuing Material Weakness described above.
60
This Annual Report does not include an attestation report of our independent registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. We are not subject to the attestation requirement because we are a non-accelerated filer and a smaller reporting company.
Changes in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Except as described above, based on the evaluation of our management as required by paragraph (d) of Rule 13a‑15 of the Exchange Act, we believe that there were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2019 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
None.
61
Directors and Executive Officers
The following individuals constitute our board of directors and executive officers:
|
Name |
|
Age |
|
|
Position |
|
|
Yutaka Niihara, M.D., M.P.H. |
|
|
61 |
|
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
|
Willis C. Lee |
|
|
60 |
|
|
Vice-Chairman and Chief Operating Officer |
|
Yasushi Nagasaki, C.P.A. |
|
|
53 |
|
|
Interim Chief Financial Officer |
|
Lan T. Tran, M.P.H. |
|
|
45 |
|
|
Chief Administrative Officer |
|
Ian Zwicker |
|
|
73 |
|
|
Director |
|
Masaharu Osato, M.D. |
|
|
66 |
|
|
Director |
|
Wei Peu Zen |
|
|
68 |
|
|
Director |
|
Robert Dickey IV |
|
|
65 |
|
|
Director |
|
Jane Pine Wood |
|
|
58 |
|
|
Director |
Background of Officers and Directors
The following is a summary of the background of each of our directors and executive officers. Except as noted in their respective biographies below, each of our directors and officers became a director or officer as of the completion of our merger transaction with EMI Holding, Inc., or EMI Holding, on July 17, 2019. All directors serve until the next annual meeting of stockholders at which their successor is elected or their earlier resignation or removal as a director. One or more of our directors or officers also serve as directors or officers of one or more of our wholly owned subsidiaries.
Yutaka Niihara, M.D., M.P.H. served as Chairman and Chief Executive Officer since January 2016, as Chief Scientific Officer from April 2015 until December 2015, as President and Chief Executive Officer from April 2011 to April 2015 and as a director since April 2011 of EMI Holding, and as a director of EMI Holding’s predecessor, Emmaus Medical, from 2003 to April 2011. Since May 2005, Dr. Niihara has also served as the President, Chief Executive Officer and Medical Director of Hope International Hospice, Inc., or Hope Hospice, a Medicare-certified hospice program. From June 1992 to October 2009, Dr. Niihara served as a physician specialist for Los Angeles County. Dr. Niihara is the principal inventor of the patented L-glutamine treatment for SCD. Dr. Niihara has been involved in patient care and research for sickle cell disease during most of his career and is a widely published author in the area of sickle cell disease. Dr. Niihara is board-certified by the American Board of Internal Medicine/Medical Oncology and by the American Board of Internal Medicine/Hematology. He is licensed to practice medicine in both the United States and Japan. Dr. Niihara is a Professor of Medicine at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA. Dr. Niihara a holds B.A. degree in Religion from Loma Linda University, a M.D. degree from the Loma Linda University School of Medicine and a M.P.H. degree from Harvard School of Public Health. We believe Dr. Niihara is qualified to serve as a director due to his critical involvement in the research and development of Endari® and extensive knowledge and experience in treating sickle cell disease in the primary care setting.
Willis C. Lee, M.S. served as Chief Operating Officer since May 2011, as a director since December 2015, as Vice-Chairman of the board of directors since January 2016 and as Chief Financial Officer from October 2016 to July 2018 of EMI Holding. Mr. Lee also previously served as a director of EMI Holding from May 2011 to May 2014 and again from to December 2015 to January 2016. Mr. Lee served as the Co-Chief Operating Officer and Chief Financial Officer and as a director of Emmaus Medical from March 2010 to May 2011. Prior to that time, he was the Controller at Emmaus Medical from February 2009 to February 2010. From 2004 to 2010, Mr. Lee led worldwide sales and business development of Yield Dynamics product group at MKS Instruments, Inc., a provider of instruments, subsystems, and process control solutions for the semiconductor, flat panel display, solar cell, data storage media, medical equipment, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and energy generation and environmental monitoring industries. Prior to that time, Mr. Lee held various managerial and senior positions at various public and private companies in the semiconductor and other industries. Mr. Lee received his B.S. degree and a M.S. degree in Physics from University of Hawaii and University of South Carolina, respectively. We believe Mr. Lee is qualified to serve as a director due to his extensive knowledge and experience, as well as his intimate knowledge of the company through his service as an executive officer of the company and Emmaus Medical.
62
Lan T. Tran, M.P.H. served as Chief Administrative Officer since May 2011 and as President from January 2018 until July 2019 of EMI Holding. She previously served as EMI Holding’s Corporate Secretary from May 2011 until September 2018 and Co-President from January 2016 until being named President. Prior to April 2011, she held various senior executive management positions with Emmaus Medical. Prior to joining Emmaus Medical, Ms. Tran was with for many years part of the executive management team at LA BioMed, a non-profit medical research and education company. Ms. Tran holds a B.S. degree in Psychobiology and a Master of Public Health degree from UCLA.
Yasushi Nagasaki, C.P.A. served as Interim Chief Financial Officer since September 1, 2020 and as Senior Vice President Finance from July 2019 to August 2020. Mr. Nagasaki also served as Senior Vice President Finance from April 2012 to July 2019 and as Chief Financial Officer from May 2011 to April 2012 of EMI Holding. From September 2005 until joining EMI Holding, Mr. Nagasaki was the Chief Financial Officer of Hexadyne Corporation, an aerospace and defense supplier. Mr. Nagasaki also served on the board of directors at Hexadyne Corporation from September 2005 to April 2011. From May 2003 to August 2005, Mr. Nagasaki was the Controller at Upsilon Intertech Corporation, an international distributor of defense and aerospace parts and sub systems. Mr. Nagasaki is a Certified Public Accountant and received a B.A. in Commerce from Waseda University and a M.A. in International Policy Studies from the Monterey Institute of International Studies, a graduate school of Middlebury College.
Ian Zwicker is the founder of Zwicker Advisory Group and has been its Chief Executive Officer since 2014. From 1981 to 1990, Mr. Zwicker served as Managing Director and held a variety of management positions at the investment banking firms of SG Cowen and Hambrecht & Quist. From 1990 to 1999, Mr. Zwicker served as Managing Director and head of worldwide technology investment banking for Donaldson, Lufkin & Jenrette Securities Corporation, and from 2000 to 2001 as the President of WR Hambrecht + Co (WRH). He was a member of the board of directors of Stirling Energy Systems, Inc. from 2006 to 2012. Mr. Zwicker was a Partner at WRH and was also Head of Capital Markets from 2013 to 2014. We believe Mr. Zwicker is qualified to serve as a director due to his executive experience and business expertise in the investment banking industry and as a former director of a public company.
Masaharu Osato, M.D. has been practicing gastroenterology and internal medicine (“GI”) at his private practice, the Osato Medical Clinic, Inc. in Torrance, CA, since 2001. Between 1998 and 2001 he completed a GI Fellowship at the Harbor-UCLA Medical Center. Between 1993 and 1997 and 1988 and 1993, respectively, Dr. Osato served as General Internist and Director of Health Screening Center at the Tokyo Adventist Hospital in Tokyo, Japan, and at the Kobe Adventist Hospital in Kobe, Japan. He attended the Loma Linda University School of Medicine in California between 1979 and 1983 and completed an internal medicine residency at the Kettering Memorial Medical Center at Wright State University between 1983 and 1986. Between 1986 and 1988 he completed a pediatric residency at the Loma Linda University Medical Center. We believe Dr. Osato is qualified to serve as a director due to his extensive knowledge of and experience in the
GI sector.
Wei Peu Zen is Vice Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Wai Kee Holdings Limited, a Hong Kong-based construction and infrastructure company whose shares are listed on the Main Board of Hong Kong Stock Exchange. He is also the Chairman, Chief Executive Officer and Managing Director of Build King Holdings Limited, a subsidiary of Wai Kee Holdings Limited. In addition, he is the Co-Chairman of Road King Infrastructure Limited, an associated corporation of Wai Kee Holdings Limited. The shares of both Build King Holdings Limited and Road King Infrastructure Limited are listed on the Main Board of Hong Kong Stock Exchange. Mr. Zen has over 40 years of experience in civil engineering and is responsible for the overall management of Wai Kee Group and oversees the operations of Wai Kee Group. Mr. Zen holds a B.Sc. degree in Engineering from The University of Hong Kong and a M.B.A. degree from The Chinese University of Hong Kong and is a member of both the Institution of Civil Engineers and the Hong Kong Institution of Engineers and a fellow member of the Institute of Quarrying, UK. He is a past Honorary Treasurer of Hong Kong Construction Association and a member of HKTDC Infrastructure Development Advisory Committee. He is also the President of Hong Kong Contract Bridge Association. We believe Mr. Zen is qualified to serve as a director due to his executive experience and business expertise. Mr. Zen also brings to the board of directors his diverse experience as a foreign national and board member and executive officer of Hong Kong-based publicly traded companies.
Robert Dickey IV has served as Managing Director at Foresite Advisors since March 2020 and was previously a Managing Director at Danforth Advisors from August 2018 to March 2020. Foresite Advisors provides finance support and strategy for life science companies, including CFO advisory, financial analysis, capital raising, and transactional support/execution for public offerings and M&A. Mr. Dickey served as a member on the board of directors at Sanuthera, Inc., a privately held medical device company, from 2013 to 2017, and was employed as Chief Financial Officer of Motif Bio Plc., a NASDAQ and London AIM exchange-listed antibiotics company, from January 2017 to February 2018. He also previously was employed with several other biotechnology companies, including as the Chief Financial Officer of Tyme Technologies, Inc. from May 2015 to January 2017, the Chief Financial Officer of NeoStem, Inc. from August 2013 to January 2015 and
63
the Senior Vice President of Hemispherx Biopharma, Inc. from November 2008 to August 2013. Prior to that time, among other things, Mr. Dickey served as a Managing Director at Legg Mason Wood Walker, Inc. and as a Senior Vice President at Lehman Brothers. He received his undergraduate degree from Princeton University and an M.B.A. from The Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania. We believe Mr. Dickey is qualified to serve as a director due to his experience as Chief Financial Officer of stock exchange listed life sciences company and other experiences in the life sciences industry, including as a former investment banker.
Jane Pine Wood was appointed as a director on March 25, 2020. She has served since October 3, 2016 as Chief Legal Counsel of BioReference Laboratories, Inc., Elmwood Park, New Jersey, a wholly owned subsidiary of OPKO Health, Inc. (NASDAQ: OPK), a diversified healthcare company. BioReference Laboratories, Inc. is the nation’s third-largest clinical laboratory with a core genetic testing business and 400-person sales and marketing team. Ms. Wood has over 30 years of experience representing clinical and anatomic laboratories, physicians, imaging centers, home health agencies, mental health providers, hospitals, other healthcare providers, and professional societies in corporate, regulatory, reimbursement, contractual, and other matters. She holds a B.A. degree, summa cum laude, from Texas A&M University and a J.D. degree from Vanderbilt University School of Law and is a member of the State Bars of New Jersey, Massachusetts, Ohio, and Tennessee. Ms. Wood is well suited to serve as a director in light of her extensive education and experiences in legal and regulatory affairs in the life science industry, including in advising a broad range of physicians and other healthcare providers and commercial healthcare companies. She adds her unique perspective as an expert in federal and state regulatory affairs and the only female director of the company.
Family and Other Relationships
There are no family relationships among any of the officers and directors.
Mr. Zen was originally appointed to the board of directors of EMI Holding on June 18, 2018 pursuant to the terms of outstanding convertible promissory notes dated November 6, 2017 and January 15, 2018 held by Mr. Zen and Wealth Threshold Limited, respectively, which entitled the note holders to designate one director if the aggregate investment in EMI Holding by the note holders and related note holders exceeded $20 million.
Board of Directors and Committees and Director Independence
Our board of directors currently consists of seven members. Our board of directors has determined that each of Ian Zwicker, Masaharu Osato, Wei Peu Zen, Robert Dickey IV and Jane Pine Wood is an “independent” director as defined by The NASDAQ Marketplace Rules currently in effect and all applicable rules and regulations of the SEC. All members of the Audit, Compensation, and Governance and Nominations Committees satisfy the “independence” standards of The NASDAQ Marketplace Rules applicable to members of such committees. The board of directors made this affirmative determination regarding these directors’ independence based on discussions with the directors and its review of the directors’ responses to a standard questionnaire regarding employment and compensation history, affiliations, family and other relationships and transactions between each director or any member of his or her immediate family and the Company or its subsidiaries or affiliates.
Audit Committee
Our Audit Committee consists of Mr. Dickey, Mr. Zwicker, Dr. Osato and Ms. Wood, each of whom is an independent director as defined by The NASDAQ Marketplace Rules. Mr. Dickey serves as Chairman of the Audit Committee and qualifies as an “audit committee financial expert” as defined under Item 407(d) of Regulation S‑K. The purpose of the Audit Committee is to represent and assist our board of directors in its general oversight of our accounting and financial reporting processes, audits of the financial statements and internal control and audit functions. The Audit Committee’s primary responsibilities and duties are to:
|
|
• |
Serve as an independent and objective party to monitor the Company’s financial reporting process, internal control system and disclosure control system. |
|
|
• |
Review and appraise the audit efforts of the company’s independent accountants. |
|
|
• |
Assume direct responsibility for the appointment, compensation, retention and oversight of the work of the outside auditors and for the resolution of disputes between the outside auditors and the company’s management regarding financial reporting issues, |
64
|
|
• |
Provide an open avenue of communication among the independent accountants, financial and senior management and the board of directors. |
The board of directors has adopted a written charter for the Audit Committee. A copy of the Audit Committee Charter is available on our website at www.emmausmedical.com.
Governance and Nominations Committee
The purpose of the Governance and Nominations Committee is to:
|
|
• |
Assist the board of directors by identifying qualified candidates for director, and to recommend to the board the director nominees for the next annual meeting of shareholders |
|
|
• |
To lead the board in its annual review of the board’s performance. |
|
|
• |
To recommend to the board nominees for each board Committee. |
|
|
• |
To develop and recommend to the board corporate governance guidelines applicable to the company. |
The Governance and Nominations Committee also currently consists of Mr. Dickey, Mr. Zwicker, Dr. Osato and Ms. Wood. Mr. Zwicker serves as Chairman of the Governance and Nominations Committee. A copy of the Governance and Nominations Committee Charter is available on our website at www.emmausmedical.com.
Compensation Committee
The purpose of the Compensation Committee is to review and approve of the company’s compensation and benefit programs. The Compensation Committee also currently consists of Mr. Dickey, Mr. Zwicker, Dr. Osato and Ms. Wood. Mr. Zwicker serves as Chairman of the Compensation Committee. A copy of the Compensation Committee Charter is available on our website at www.emmausmedical.com.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Our common stock is currently registered under Section 12 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. As a result, and pursuant to Rule 16a‑2, our directors and officers and beneficial owners of 10% or more of our common stock are currently required to file statements of beneficial ownership with respect to their ownership of our equity securities under Sections 13 or 16 of the Exchange Act. Based on a review of written representations from our executive officers and directors and a review of Forms 3, 4 and 5 furnished to us, we believe that during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2019 the directors, officers and owners of more than 10% of our common stock filed, on a timely basis, all reports required by Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, except that late reports on Form 3 were filed on July 29, 2019 on behalf of Dr. Niihara, Ms. Tran and Mr. Dickey due to delays in signing the reports or administrative errors by the Company’s personnel assisting with the filing. A late report on Form 3 also was filed on September 11, 2019 on behalf of Dr. Osato after company personnel discovered the Form 3 had previously been signed but not filed on his behalf. Late reports on Form 4 were filed on behalf of Mr. Zen on September 3, 2019 and on September 9, 2019 due to delays in signing the report resulting from the difference in time zones between Hong Kong, where he resides, and California, where our offices are located.
Code of Conduct and Ethics
Our board of directors has approved a Code of Conduct and Ethics, which we refer to as the Code of Ethics, which applies to all our directors, officers and employees. The Code of Ethics addresses, among other things, honesty and ethical conduct, conflicts of interest, compliance with laws, regulations and policies, including disclosure requirements under the federal securities laws, confidentiality, trading on inside information, and reporting of violations of the code. A copy of the Code of Ethics is available on our website at www.emmausmedical.com. Requests for copies of the Code of Ethics should be sent in writing to Emmaus License Sciences, Inc., Attention: Secretary, 21250 Hawthorne Boulevard, Suite 800, Torrance, California 90503.
Summary Compensation Table
On July 17, 2019 we completed our merger transaction with EMI Holding. On September 25, 2019, our board of directors approved a change in our fiscal year end from September 30 to December 31. Since the merger transaction occurred
65
prior to our former fiscal year end of September 30, 2019, in accordance with SEC rules, the following table sets forth information regarding all compensation paid for services to us in all capacities for our former fiscal years ended September 30, 2019 and 2018 by (i) each person who served as our principal executive officer during our former fiscal year ended September 30, 2019 and (ii) up to two additional individuals who were our two most highly compensated executive officers other than our principal executive officer during our former fiscal year ended September 30, 2019 and whose total compensation exceeded $100,000 (collectively referred to as our "former named executive officers"). The employment of each of our former named executive officers who were then employed by us was terminated in conjunction with the completion of the merger transaction.
|
Name and Position |
|
Twelve Months Ended September 30, |
|
Salary |
|
|
Bonus |
|
|
Stock Awards |
|
|
Option Awards |
|
|
All Other Compensation |
|
|
Total |
|
||||||
|
Patrick Herguth |
|
2019 |
|
$ |
190,359 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
246,000 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
436,359 |
|
|
Chief Executive Officer |
|
2018 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||||
|
George C. Carpenter IV |
|
2019 |
|
|
163,281 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
216,594 |
|
|
|
134,758 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
514,633 |
|
||
|
President and Chief Executive Officer |
|
2018 |
|
|
238,125 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
127,300 |
|
|
|
102,900 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
468,325 |
|
||
|
Donald D'Ambrosio |
|
2019 |
|
|
170,208 |
|
|
|
25,000 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
82,965 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
278,173 |
|
||
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
2018 |
|
|
215,015 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
29,700 |
|
|
|
27,200 |
|
|
|
16,835 |
|
|
|
288,750 |
|
|
The following table sets forth information concerning the compensation earned by our Chief Executive Officer, and our two other most highly compensated executive officers for the twelve months ended September 30, 2018 and 2019:
|
Name and Position |
|
Twelve Months Ended September 30, |
|
Salary |
|
|
Bonus |
|
|
Stock Awards |
|
|
Option Awards |
|
|
All Other Compensation |
|
|
Total |
|
||||||
|
Yutaka Niihara, M.D., MPH |
|
2019 |
|
$ |
80,208 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
80,208 |
|
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
|
2018 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
||||||
|
Joseph (Jay) C. Sherwood III |
|
2019 |
|
|
52,083 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
52,083 |
|
||||
|
Chief Financial Officer |
|
2018 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
||||||
|
Willis C. Lee |
|
2019 |
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
||||
|
Vice-Chairman and Chief Operating Officer |
|
2018 |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
||||||
The following table sets forth information concerning the compensation earned by our Chief Executive Office and our next two most highly compensated executive officers, whom we refer to as our “named executive officers,” for the three months ended December 31, 2019:
|
Name and Position |
|
Year ended December 31 |
|
Salary |
|
|
Bonus |
|
|
Stock Awards |
|
Option Awards |
|
|
All Other Compensation |
|
Total |
|
||||
|
Yutaka Niihara, M.D., MPH |
|
2019 |
|
$ |
96,250 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
— |
|
$ |
96,250 |
|
|
Joseph (Jay) C. Sherwood III |
|
2019 |
|
|
62,500 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
62,500 |
|
||
|
Willis C. Lee |
|
2019 |
|
|
60,000 |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
60,000 |
|
||
The compensation of Dr. Niihara and Mr. Lee does not reflect annual performance bonuses provided for in their respective employment agreements. We did not grant such performance bonuses in 2019, in part, to preserve available capital to fund operating expenses. Additionally, no specific performance criteria were established for our executive officers for 2019. As of this date, the Compensation Committee also has made no determination regarding any discretionary cash bonuses for 2019.
66
Outstanding Equity Awards at 2019 Fiscal Year End
The table below sets forth information regarding outstanding options held by the former named executive officers as of September 30, 2019:
|
|
|
Option Awards |
|
Stock Awards |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options (#) |
|
|
Equity Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Unearned |
|
|
Option Exercise |
|
|
Option Expiration |
|
Number of Shares of Stock That Have Not |
|
|
Market Value of Shares of Stock That Have Not |
|
||||||||||||
|
NAME |
|
Exercisable |
|
|
Non-Exercisable |
|
|
Options (#) |
|
|
Price |
|
|
Date |
|
Vested (#) |
|
|
Vested ($) |
|
|||||||||
|
Patrick Herguth |
|
|
33,332 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
7.68 |
|
|
12/12/2028 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
George Carpenter |
|
|
5,333 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
36.00 |
|
|
09/22/2026 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
362 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
300.00 |
|
|
10/08/2023 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
1,020 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
56.64 |
|
|
12/10/2022 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
11,330 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
9.30 |
|
|
04/04/2028 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
6,831 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
8.28 |
|
|
10/08/2028 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
4,998 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
8.76 |
|
|
12/03/2028 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
4,861 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
7.68 |
|
|
12/12/2028 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
Donald D’Ambrosio |
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
35.40 |
|
|
03/31/2027 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
9.30 |
|
|
04/04/2028 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
4,165 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
8.28 |
|
|
10/8/2028 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
4,416 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
8.76 |
|
|
12/03/2028 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
1,666 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
7.08 |
|
|
06/25/2029 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|||
The following table sets forth information regarding outstanding equity awards held by our named executive officers as of December 31, 2019:
|
Name |
|
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options Exercisable |
|
|
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options Unexercisable |
|
|
Option Exercise Price |
|
|
Option Expiration Date |
|||
|
Yutaka Niihara, M.D., MPH |
|
|
262,536 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
3.42 |
|
|
4/1/2022 |
|
|
|
|
525,072 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
3.42 |
|
|
2/28/2023 |
|
|
|
|
315,043 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
4.76 |
|
|
5/10/2026 |
|
Joseph (Jay) C. Sherwood III |
|
|
20,420 |
|
|
|
32,087 |
|
|
$ |
9.80 |
|
|
6/19/2029 |
|
Willis C. Lee |
|
|
262,536 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
3.42 |
|
|
4/1/2022 |
|
|
|
|
525,072 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
3.42 |
|
|
2/28/2023 |
|
|
|
|
315,043 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
4.76 |
|
|
5/10/2026 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
67
On April 5, 2011, we entered into employment agreements with Dr. Niihara and Mr. Lee. Each of the Employment Agreements had an initial two-year term, which renews automatically for consecutive one-year periods unless we or the officer provides notice of non-renewal at least 60 days prior to the expiration of the then current term.
Base Salary, Bonus and Other Compensation. Dr. Niihara’s, and Mr. Lee’s current base salaries are $385,000 and $240,000 per year, respectively, which will be reviewed at least annually. In addition to the base salary, each officer may be entitled to receive an annual performance bonus based on the officer’s performance. The Employment Agreements provide that the respective officer’s performance will be measured against a set of targets and goals as mutually established by us and the officer. Historically, our board of directors and the Compensation Committee of the board have evaluated each officer’s performance on an overall basis related to our progress on major milestones, without reliance on specific position by position pre-established targets and goals. The officers are also eligible to receive paid vacation and to participate in health and other benefit plans and to be reimbursed for reasonable and necessary business expenses on the same basis as our other employees.
Equity Compensation. The Employment Agreements provide that on December 31 of each calendar year, or as soon as reasonably practicable after such date (each a “Grant Date”), we will grant non-qualified 10-year stock options with a Black-Scholes-Merton value of $100,000 to Dr. Niihara, and $50,000 to Mr. Lee in each case with an exercise price per share equal to the “Fair Market Value” (as such term is defined in our 2011 Stock Incentive Plan) on the applicable Grant Date. The options are to vest as to one-third of the option shares on each of the first three anniversaries of the Grant Date. Any unvested options are to vest immediately upon a change in control (as defined below), termination of the officer’s employment other than a voluntary termination by the officer or our termination of the officer for cause. In the event that the officer is terminated for any reason other than cause, death or disability or retirement, each option, to the extent that it is exercisable at the time of such termination, shall remain exercisable for the 90-day period following such termination, but in no event following the expiration of its term. In the event that the officer’s employment terminates on account of death, disability or, with respect to any non-qualified stock option, retirement, each option granted that is outstanding and vested as of the date of such termination shall remain exercisable by such officer (or the officer’s legal representatives, heirs or legatees) for the one-year period following such termination, but in no event following the expiration of its term. No such stock option grants were made for either of the years ended December 31, 2018 or 2019.
Severance Compensation. If Dr. Niihara’s or Mr. Lee’s employment is terminated for any reason during the term of his Employment Agreement, other than for cause or without good reason, he will be entitled to receive his or her base salary prorated through the termination date, any expense reimbursement due and owing for reasonable and necessary business expenses, and unpaid vacation benefits (the “Voluntary Termination Benefits”). If Dr. Niihara’s or Mr. Lee’s employment is terminated due to his death or disability during the term of his employment agreement, he will also receive an amount equal to his target annual performance bonus, if any, and in the case of a termination due to disability, six additional months of his base salary to be paid out over a six-month period and payment of COBRA benefits for six months following the termination. If Dr. Niihara’s employment is terminated without cause or he resigns with good reason (but not within two years following a change in control), he will receive the Voluntary Termination Benefits and, subject to his signing a Release of all claims relating to his employment, a severance package equal to one year’s base salary to be paid out over a 12-month period, a pro rata amount of the annual performance bonus for the calendar year in which the termination date occurs based on the achievement of any applicable performance terms or goals for the year, and payment of COBRA benefits for 12 months following the termination. If Mr. Lee’s employment is terminated without cause or he resigns with good reason (but not within two years following a change in control) during the term of his employment agreement, he will receive the Voluntary Termination Benefits and, subject to his signing a Release if all claims relating to his employment, a severance package equal to six months’ base salary to be paid out over a six-month period, an amount equal to half of the targeted annual performance bonus, if any, and payment of COBRA benefits for six months following the termination.
Termination with cause includes a proven act of dishonesty, fraud, embezzlement or misappropriation of company proprietary information; a conviction of, or plea of nolo contendere to, a felony or a crime involving moral turpitude; willful misconduct which cannot be cured on reasonable notice to the officer; or the officer’s habitual failure or refusal to perform his duties if such failure or refusal is not cured within 20 days after receiving written notice thereof from the board of directors. Good reason includes a reduction of more than 10% to the officer’s base salary or other compensation (except as part of a general reduction for all executive employees); a material diminution of the officer’s authority, responsibilities, reporting or job duties (except for any reduction for cause); the company’s material breach of the Employment Agreement; or a relocation of the business requiring the officer to move or drive to work more than 40 miles from the location of our former offices. The officer may terminate the Employment Agreement for good reason if he provides written notice to the Company within 90 days of the event constituting good reason and the Company fails to cure the good reason within 30 days after receiving such notice.
68
Change of Control. The Employment Agreements will not be terminated upon a “change of control,” which means any merger or reorganization where the holders of the company’s capital stock prior the transaction own fewer than 50% of the shares of capital stock after the transaction, an acquisition of 50% of the voting power of the company’s outstanding securities by another entity, or a transfer of at least 50% of the fair market value of the company’s assets. Upon Dr. Niihara’s termination without cause or good reason that occurs within two years after a change of control, he will be entitled to receive the Voluntary Termination Benefits and, subject to his signing a Release of all claims relating to his employment, a severance package equal to two years’ base salary to be paid out over a 12-month period, an amount equal to double his targeted annual performance bonus, if any, payment of COBRA benefits for 18 months following the termination, and a one-time cash payment of $3.0 million. Upon Mr. Lee’s termination without cause or good reason that occurs within two years after a change of control, he will be entitle to receive the Voluntary Termination Benefits and, subject to his signing a Release of all claims relating to his employment, a severance package equal to one year’s base salary to be paid out over a 12-month period, an amount equal to the full-year targeted annual performance bonus, payment of COBRA benefits for 12 months following the termination, and a one-time cash payment of $200,000. In addition, each officer’s unvested equity awards shall vest upon such termination and the officer will have 36 months in which to sell or exercise such awards (subject to expiration of the term of such options). The officer will also be free from all lock-up or other contractual restrictions upon the free sale of shares that are subject to waiver by the company upon such termination.
Director Compensation
During our former fiscal year ended September 30, 2019, our former non-employee directors received cash compensation, as well as grants of common stock, restricted stock and stock options for their service on our Board of Directors or Board committees. The values of the option and restricted share grants were determined using the Black-Scholes Model and the closing price of the stock on the day of grant. All our former non-employee directors resigned as directors in conjunction with the completion of our merger transaction with EMI Holding in July 2019, with the exception of Dr. Smith, who resigned as a director effective September 30, 2019.
The following table sets forth information regarding our former non-employee director compensation for the former fiscal year ended September 30, 2019:
|
Name |
|
Fees Earned or Paid in Cash |
|
|
Option |
|
|
Stock Awards |
|
|
All Other Compensation |
|
|
Total |
|
|||||
|
Robin Smith. M.D.(1) |
|
$ |
195,000 |
|
|
$ |
59,500 |
|
|
$ |
178,240 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
432,740 |
|
|
John Pappajohn |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
18,919 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
18,919 |
|
|
Geoffrey Harris |
|
|
18,750 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
28,378 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
47,128 |
|
|
Michal Votruba |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
198,720 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
198,720 |
|
|
Peter Unanue |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
18,919 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
18,919 |
|
|
|
(1) |
On July 14, 2017, the Board approved a Chairman Services Agreement with Robin L. Smith, M.D. pursuant to which Dr. Smith provided non-exclusive advisory and management services to the Company, which may include advice and assistance concerning: strategic vision and planning; identification of growth and expansion opportunities; financial planning; and corporate partnering and business development (collectively, the "Services"). Under the Agreement, Dr. Smith was entitled to an annual cash fee of $300,000, payable in equal monthly installments, which reduced to $250,000 for calendar year 2018. In conjunction with the merger transaction, the Chairman Services Agreement terminated in accordance with its terms and Ms. Smith ceased to serve as Chairman of the Board. In conjunction with the termination, the Company paid Ms. Smith a $150,000 bonus as called for in the Chairman Services Agreement. |
The following is a summary of the current compensation of our non-employee directors:
|
|
• |
$100,000 per year cash compensation, payable in quarterly installments; |
|
|
• |
$1,000 per ad hoc board meeting attended in person or telephonically; and |
|
|
• |
possible awards of stock options to be determined by the Compensation Committee. |
The following table sets forth information regarding the compensation earned by our non-employee directors during the period July 17, 2019 when our non-employee directors other than Ms. Wood became directors in conjunction the
69
completion of the merger transaction with EMI Holding, and December 31, 2019. Ms. Wood became a director on March 25, 2020. Our employee directors, Dr. Niihara, and Mr. Lee, are not compensated for their services as directors.
|
Name |
|
Fees Earned or Paid in Cash |
|
|
Option Awards |
|
|
Total |
|
|||
|
Ian Zwicker |
|
$ |
50,000 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
50,000 |
|
|
Masaharu Osato, M.D. |
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
Wei Peu Zen |
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
Robert Dickey IV |
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
200,000 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
200,000 |
|
|
_____________ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ITEM 12. |
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS |
The following table sets forth certain information as of December 31, 2020 with respect to beneficial ownership of our common stock based on issued and outstanding shares of common stock owned by:
|
|
• |
Each person known to be the beneficial owner of 5% or more of our outstanding common stock; |
|
|
• |
Each named executive officer; |
|
|
• |
Each director; and |
|
|
• |
All our executive officers and directors as a group. |
Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with the rules of the SEC. In computing the number of shares beneficially owned by a person and the percentage of ownership of that person, shares of common stock subject to options, warrants and convertible notes held by that person that are currently exercisable or become exercisable within 60 days of December 31, 2020 are deemed outstanding even if they have not actually been exercised. Those shares, however, are not deemed outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage ownership of any other person.
Unless otherwise indicated, the persons and entities named in the table have sole voting and sole investment power with respect to the shares set forth opposite the stockholder’s name, subject to community property laws, where applicable.
Unless otherwise indicated in the table or footnotes, the address of each 5% or more owner is c/o Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc., 21250 Hawthorne Boulevard, Suite 800, Torrance, California 90503.
70
|
|
Title |
|
Amount and Nature of Beneficial Ownership of Shares of Common Stock |
|
|
Percent of Class (1) |
|
|||
|
Directors and Executive Officers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Yutaka Niihara, M.D., M.P.H. |
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
|
|
13,332,380 |
|
(2) |
|
25.9 |
% |
|
Willis C. Lee |
|
Vice-Chairman and Chief Operating Officer |
|
|
1,434,636 |
|
(3) |
|
2.9 |
% |
|
Yasushi Nagasaki |
|
Interim Chief Financial Officer |
|
|
1,169,753 |
|
(4) |
|
2.3 |
% |
|
Lan T. Tran, M.P.H. |
|
Chief Administrative Officer |
|
|
1,129,213 |
|
(5) |
|
2.3 |
% |
|
Masaharu Osato, M.D. |
|
Director |
|
|
735,396 |
|
(6) |
|
1.5 |
% |
|
Wei Peu Zen |
|
Director |
|
|
2,278,048 |
|
(7) |
|
4.7 |
% |
|
Ian Zwicker. |
|
Director |
|
|
217,029 |
|
|
* |
|
|
|
Robert Dickey IV |
|
Director |
|
|
— |
|
|
* |
|
|
|
Jane Pine Wood |
|
Director |
|
|
— |
|
|
* |
|
|
|
Officers and Directors as a Group (9 persons) |
|
|
|
|
20,296,455 |
|
(8) |
|
39.6 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5% or More Owners |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Telcon RF Pharmaceutical, Inc. |
|
|
|
|
4,147,491 |
|
(9) |
|
8.5 |
% |
|
__________ |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Represents beneficial ownership of less than one percent (1%). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
(1) Based on 48,987,189 shares of common stock issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2020. |
|
|||||||||
|
(2) Includes 10,864,540 shares of common that are held jointly by Dr. Niihara and Soomi Niihara, his wife. Also includes 63,000 shares held by Soomi Niihara and 92,794 shares owned by Hope International Hospice, Inc., or Hope Hospice. Dr. Niihara is the chief executive officer and a co-director of Hope Hospice and shares voting and investment power over such shares. Also includes 1,102,651 shares underlying stock options and 1,365,189 shares underlying warrants." |
|
|||||||||
|
(3) Includes 1,102,651 shares underlying stock options. |
|
|||||||||
|
(4) Includes 1,102,651 shares underlying stock options. |
|
|||||||||
|
(5) Includes 1,102,651 shares underlying stock options. |
|
|||||||||
|
(6) Includes 516,152 shares held by Osato Medical Clinic and its pension plan. Also includes 217,029 shares underlying stock options. |
|
|||||||||
|
(7) Includes 1,270,214 shares owned by Profit Preview International Group Limited, a Hong Kong limited company wholly owned by Mr. Zen. Excludes 375,308 shares owned by Smart Start investments Limited, a Hong Kong corporation, of which the Mr. Zen is a director and 9.93% shareholder, and 350,048 shares owned by Wealth Threshold Limited, a British Virgin Islands limited company and wholly owned subsidiary of Wai Kee Holdings Limited, a Hong Kong stock exchange listed company of which Mr. Zen is a director and 24.71% shareholder, as to which shares Mr. Zen disclaims beneficial ownership. |
|
|||||||||
|
(8) Includes 4,844,662 shares underlying stock options and 1,365,189 shares underlying warrants. |
|
|||||||||
|
(9) The information regarding Telcon RF Pharmaceutical, Inc. is based solely on its Schedule 13/G filed with the SEC on August 26, 2019. The address for the stockholder is S-Tower 14th Floor 439 Bongunsa-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul, South Korea. |
|
|||||||||
Securities Authorized for Issuance under Equity Compensation Plans
The following table provides information as of December 31, 2019 regarding compensation plans, including any individual compensation arrangements, under which our equity securities are authorized for issuance:
|
Plan Category |
|
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights |
|
|
Weighted-average exercise price of outstanding options, warrants and rights |
|
|
Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans |
|
|||
|
Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
|
|
7,245,350 |
|
|
$ |
4.68 |
|
|
|
2,167,150 |
|
71
Except as follows in the below items, since the beginning of our last fiscal year, there has not been, nor is there currently proposed, any transaction or series of similar transactions to which we are or will be a party:
|
|
● |
in which the amount involved exceeds the lesser of $120,000 or 1% of the average of our total assets at year-end for the last two completed fiscal years; and |
|
|
● |
in which any director, executive officer, or other stockholder of more than 5% of our common stock or any member of their immediate family had or will have a direct or indirect material interest. |
Loans by Related Persons
In January 2020, we entered into revolving line of credit agreement with Dr. Yutaka Niihara. Under the agreement, at our request from time to time, Dr. Niihara may, but is not obligated to, lend or re-lend to us up to $1,000,000, including $600,000 loaned to us in December 2019. Outstanding amounts under the agreement are due and payable upon demand and bear interest, payable monthly, at a variable annual rate equal to the Prime Rate in effect from time to time plus 3%. In addition to the payment of interest, we agreed to pay Dr. Niihara an amount, which we refer to as a “tax gross-up,” intended to make him whole for federal and state income taxes payable by him with respect to interest paid to him the previous year. As of December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance under the revolving line of credit agreement of $600,000 was reflected on our consolidated balance sheet. With the tax-gross up, the effective interest rate on the outstanding balance as of December 31, 2019 was 10.4%. The revolving line of credit agreement will expire on November 22, 2022.
The following table sets forth information relating to our promissory notes payable and convertible notes payable from related persons outstanding at any time during the years ended December 31, 2018 and 2019 (amounts in thousands).
|
Class |
Lender |
|
Interest Rate |
|
|
Date of Loan |
|
Term of Loan |
|
Principal Amount Outstanding at December 31, 2019 |
|
|
Highest Principal Outstanding |
|
|
Amount of Principal Repaid or Converted into Stock |
|
|
Amount of Interest Paid |
|
|
Conversion Rate |
|
|
Shares Underlying Notes December 31, 2019 |
|
|||||||
|
Current, Promissory notes payable to related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Hope International Hospice, Inc. (1) |
|
10% |
|
|
6/3/2016 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
78 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Yutaka Niihara (2)(3) |
|
10% |
|
|
9/14/2017 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
904 |
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Lan T. Tran (2) |
|
11% |
|
|
2/10/2018 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
43 |
|
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subtotal |
|
$ |
43 |
|
|
$ |
1,313 |
|
|
$ |
277 |
|
|
$ |
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Current, Convertible notes payable to related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Yasushi Nagasaki (2) |
|
10% |
|
|
6/29/2012 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
200 |
|
|
$ |
200 |
|
|
$ |
56 |
|
|
$ |
3.30 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Yutaka & Soomi Niihara (2)(3) |
|
10% |
|
|
11/16/2015 |
|
2 years |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
73 |
|
|
$ |
4.50 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Wei Peu Zen (3) |
|
10% |
|
|
11/6/2017 |
|
2 years |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
597 |
|
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Profit Preview International Group, Ltd. (4) |
|
10% |
|
|
2/1/2018 |
|
2 years |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,037 |
|
|
|
4,037 |
|
|
|
385 |
|
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Profit Preview International Group, Ltd. (4) |
|
10% |
|
|
3/21/2018 |
|
2 years |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,363 |
|
|
|
5,363 |
|
|
|
442 |
|
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subtotal |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
14,800 |
|
|
$ |
14,800 |
|
|
$ |
1,553 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
43 |
|
|
$ |
16,113 |
|
|
$ |
15,077 |
|
|
$ |
1,633 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
(1) |
Dr. Niihara, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, is a co-owner with his wife and a director and the Chief Executive Officer of Hope International Hospice, Inc. |
|
(2) |
Officer |
|
(3) |
Director |
|
(4) |
Mr. Zen, one of our directors, is the sole owner of Profit Preview International Group, Ltd. |
72
The proceeds of the above loans were used working capital purposes.
Prior to the reverse capitalization transaction completed in July 2019, there were outstanding approximately $34.5 million principal amount of promissory notes convertible into shares of common stock of EMI Holding, Inc., or EMI, at conversion prices ranging from $3.05 to $10.00 per share. None of the convertible promissory notes originally provided for their conversion into Emmaus common stock or assumption by Emmaus connection with the reverse capitalization transaction. In order to facilitate the transaction and to satisfy its covenants in the merger agreement, EMI entered into negotiations with the holders of the convertible promissory notes to amend the terms thereof to provide that they would be converted automatically into shares of EMI common stock at their respective conversion prices immediately prior to the effective time of the reverse capitalization transaction, which shares would be outstanding immediately prior to the reverse capitalization transaction and would be converted into shares of Emmaus common stock in the same manner as other outstanding shares of EMI common stock based the exchange ratio. In connection with such amendments, the conversion price of up to approximately $15.1 million principal amount of EMI convertible promissory notes, including $14.4 million principal amount of EMI convertible promissory notes held by Wei Peu Zen, an Emmaus director and an affiliated company, were reduced from $10 a share to $8.25 a share. Also, in conjunction with the reverse capitalization transaction, approximately $357,000 principal amount and accrued interest under a promissory note held by Dr. Niihara was converted into shares of Emmaus commons stock at a conversion price of $10 per share.
On September 1, 2020, we issued a promissory note to Soomi Niihara, Dr. Niihara’s wife, in the amount of $395,000. The note bore interest at the rate of 12% per annum, with principal and accrued interest due upon demand. The note was repaid on October 1, 2020.
On September 1, 2020, we issued a promissory note to Hope International Hospice, Inc., of which Dr. Niihara and his wife are the sole shareholders and directors, in the amount of $189,000. The note bore interest at the rate of 12% per annum, with principal and accrued interest due upon demand. The note was repaid on October 1, 2020.
On October 28, 2020, we issued a promissory note to Soomi Niihara in the amount of $685,000. The note bore interest at the rate of 12% per annum, with principal and accrued interest due upon demand. The note was repaid on December 21, 2020.
On January 20, 2021, we issued a promissory note to Soomi Niihara in the amount of $700,000. The note bore interest at the rate of 12% per annum, with principal and accrued interest due upon demand.
Guarantee by Officer
On January 15, 2018, EMI Holding issued a convertible promissory note to Wealth Threshold Limited in the original principal amount of $5,000,000, repayment of which is personally guaranteed by Dr. Niihara. The unpaid principal amount of the note was $3,150,000 as of December 31, 2020.
Policy for Approval of Related Party Transactions
The Audit Committee of our Board of Directors is responsible for reviewing and approving all related party transactions.
Board Independence
Our board of directors has determined that each of Ian Zwicker, Masaharu Osato, Wei Peu Zen, Robert Dickey IV and Jane Pine Wood is an “independent” director as defined by The NASDAQ Marketplace Rules currently in effect and all applicable rules and regulations of the SEC.
The following table presents all fees, including reimbursements for expenses, billed for professional services rendered by Baker Tilly US, LLP (“Baker Tilly”), our independent registered public accounting firm for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018:
73
|
|
Years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 |
|
||
|
Audit Fees (1) |
|
$ |
275 |
|
|
Audit–Related Fees |
|
|
— |
|
|
Tax Fees |
|
|
— |
|
|
All Other Fees |
|
|
— |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
275 |
|
(1) Audit fees consisted of fees for services performed in the audits of our annual financial statements.
The engagement of Baker Tilly was approved by the Audit Committee of our Board of Directors on September 10, 2020.
The Audit Committee has adopted a formal policy on auditor independence requiring the advance approval by the Audit Committee of all audit and non-audit services provided by our independent registered public accounting firm. In determining whether to approve any services by our independent registered public accounting firm, the Audit Committee reviews the scope of and estimated fees for the services and considers whether the proposed services may adversely affect the firm’s independence. On an annual basis, our management reports to the Audit Committee all audit services performed during the previous 12 months and all fees billed by our independent registered public accounting firm for such services.
In fiscal 2019 and 2018, all audit services and the corresponding fees were approved by the Audit Committee.
74
|
|
1. |
Financial Statements: See “Index to Consolidated Financial Statements” on page F‑1 of this Annual Report. |
|
|
2. |
Financial Statement Schedule: See Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements starting on page F‑8 of this Annual Report. |
|
|
3. |
Exhibits: The exhibits listed in the following “Exhibit Index” are filed or incorporated by reference as part of this Annual Report. |
Exhibit Index
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
|||
|
Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/ |
|
1.1 |
8-K |
001-35527 |
1.1 |
March 3, 2010 |
|
|
|
2.1 |
424B3 |
333-229660 |
Annex A |
June 14, 2019 |
|
|
|
3.1 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
3.2 |
8-K |
001-35527 |
3.4 |
July 22, 2019 |
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
4.2+ |
MYnd Analytics, Inc. Amended and Restated 2012 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan |
DEF14A |
001-35527 |
Appendix A |
November 2, 2018 |
|
|
4.3+ |
10-K |
001-35527 |
4.4 |
December 22, 2016 |
|
|
|
4.4+ |
10-K |
001-35527 |
4.5 |
December 22, 2016 |
|
|
|
4.5+ |
10-K |
001-35527 |
4.6 |
December 22, 2016 |
|
|
|
4.6 |
10-Q |
000-142031 |
4.5 |
May 20, 2015 |
|
|
|
4.7 |
10-Q |
000-142031 |
4.3 |
August 19, 2016 |
|
|
|
4.8 |
10-Q |
000-142031 |
4.4 |
August 19, 2016 |
|
|
|
4.9 |
10-Q |
000-142031 |
4.3 |
November 14, 2016 |
|
|
|
4.10 |
10-K |
000-142031 |
4.32 |
April 16, 2018 |
|
|
75
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
|||
|
Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/ |
|
10-Q |
000-142031 |
4.1 |
May 15, 2018 |
|
||
|
4.12+ |
Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. Amended and Restated 2011 Equity Incentive Plan. |
DEF14A |
000-53072 |
Annex A |
September 19, 2014 |
|
|
4.13+
|
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.3a |
May 4, 2011 |
|
|
|
4.14+ |
Form of Incentive Stock Option Agreement (Time-Based Vesting) under 2011 Equity Incentive Plan. |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.3b |
May 4, 2011 |
|
|
4.15+ |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.3c |
May 4, 2011 |
|
|
|
4.16+
|
Form of Non-Qualified Stock Option Agreement (Time-Based Vesting) under 2011 Equity Incentive Plan. |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.3d |
May 4, 2011 |
|
|
4.17+ |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.3e |
May 4, 2011 |
|
|
|
4.18+ |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement (Time-Based Vesting) under 2011 Equity Incentive Plan. |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.3f |
May 4, 2011 |
|
|
4.19 |
10-K |
001-35527 |
10.14 |
December 11, 2018 |
|
|
|
4.20 |
8-K |
001-35527 |
4.1 |
January 28, 2019 |
|
|
|
4.21 |
8-K |
001-35527 |
10.2 |
April 3, 2018 |
|
|
|
4.22 |
8-K |
001-35527 |
4.1 |
February 27, 2020 |
|
|
|
4.23 |
Form of Second Amended and Restated Common Stock Purchase Warrant. |
8-K |
001-35527 |
4.2 |
February 27, 2020 |
|
|
10.1 |
8-K |
001-35527 |
10.1 |
April 3, 2018 |
|
|
76
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
|||
|
Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/ |
|
424B3 |
333-229660 |
Annex B |
June 14, 2019 |
|
||
|
10.3 |
10-Q |
001-35527 |
10.7 |
November 13, 2019 |
|
|
|
10.4+ |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.12 |
May 4, 2011 |
|
|
|
10.5+ |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.13 |
May 4, 2011 |
|
|
|
10.6+ |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.14 |
May 4, 2011 |
|
|
|
10.7+ |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.20 |
May 4, 2011 |
|
|
|
10.8 |
Letter of Intent by and between Ajinomoto Aminoscience LLC and Emmaus Medical, Inc. |
8-K/A |
000-142031 |
10.24 |
July 5, 2011 |
|
|
10.9 |
Form of Promissory Note issued to the persons indicated on Schedule A thereto. |
10-Q |
000-142031 |
10.1 |
August 19, 2016 |
|
|
10.10 |
10-Q |
000-142031 |
10.1 |
May 15, 2018 |
|
|
|
10.11 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
10.12 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
10.13 |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.1 |
September 17, 2018 |
|
|
|
10.14 |
8-K/A |
000-142031 |
10.6 |
October 5, 2018 |
|
|
|
10.15 |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.2 |
September 17, 2018 |
|
|
77
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
|||
|
Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/ |
|
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.3 |
September 17, 2018 |
|
||
|
10.17 |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.1 |
March 11, 2019 |
|
|
|
10.18 |
8-K |
000-142031 |
10.1 |
February 27, 2020 |
|
|
|
10.19 |
8-K |
001-35527 |
10.1 |
September 24, 2020 |
|
|
|
10.20 |
10-K |
001-35527 |
10.23(F) |
March 31, 2015 |
|
|
|
10.21 |
10-K |
000-142031 |
10.24a |
March 21. 2019 |
|
|
|
10.22 |
10-K |
000-142031 |
10.24b |
March 21. 2019 |
|
|
|
10.23 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
10.24
|
10-Q |
000-142031 |
10.3 |
November 14, 2017 |
|
|
|
10.25 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
78
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
|||
|
Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/ |
|
|
|
|
|
* |
||
|
10.27 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
10.28 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
10.29 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
10.30 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
10.31 |
8-K |
001-35527 |
1.1 |
March 3, 2020 |
|
|
|
10.32 |
8-K |
001-35527 |
10.1 |
March 3, 2020 |
|
|
|
10.33 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
10.34 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
10.35 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
10.36 |
Loan Agreement Dated October 28, 2020 Between Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. and EJ Holdings, Inc. |
8-K |
001-35527 |
10.1 |
November 13, 2020 |
|
79
|
|
|
Incorporated by Reference |
|
|||
|
Exhibit Number |
Exhibit Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date |
Filed/ |
|
|
|
|
|
* |
||
|
21.1 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
31.1 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
31.2 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
32.1 |
|
|
|
|
* |
|
|
101.INS |
XBRL Instance Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.SCH |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.CAL |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.DEF |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.LAB |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.PRE |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
____________________________________
+ Management contract or compensatory plan, contract or arrangement
* Filed herewith.
80
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the Registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Torrance, California, on January 22, 2021.
|
|
Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. |
|||
|
|
|
|||
|
|
By: |
|
/s/ Yutaka Niihara |
|
|
|
|
|
Name: |
Yutaka Niihara, M.D., M.P.H. |
|
|
|
|
Title: |
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Company in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
SIGNATURE |
|
TITLE |
|
DATE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Yutaka Niihara Yutaka Niihara, M.D., M.P.H.
|
|
Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) |
|
January 22, 2021 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Yasushi Nagasaki |
|
Interim Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and |
|
January 22, 2021 |
|
Yasushi Nagasaki |
|
Accounting Officer) |
|
|
|
/s/ Willis C. Lee |
|
Director |
|
January 22, 2021 |
|
Willis C. Lee |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Robert Dickey IV |
|
Director |
|
January 22, 2021 |
|
Robert Dickey IV |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Masaharu Osato |
|
Director |
|
January 22, 2021 |
|
Masaharu Osato, M.D. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Ian Zwicker |
|
Director |
|
January 22, 2021 |
|
Ian Zwicker |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Jane Pine Wood |
|
Director |
|
January 22, 2021 |
|
Jane Pine Wood |
|
|
|
|
81
INDEX TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
EMMAUS LIFE SCIENCES, INC.
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Stockholders and the Board of Directors of Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc.
Opinion on the Financial Statements
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. and subsidiaries (collectively, the Company) as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, changes in stockholders' equity (deficit), and cash flows, for the years then ended, and the related notes to the consolidated financial statements (collectively, the financial statements). In our opinion, the financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of the Company as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the two years in the period ended December 31, 2019, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
Going Concern Matter
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 2 to the financial statements, the Company has suffered recurring losses from operations and does not have sufficient liquidity to meet its expected operating and capital cash flow requirements. This raises substantial doubt about the Company's ability to continue as a going concern. Management's plans in regard to these matters also are described in Note 2. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
Restatement of Previously Issued Financial Statements
When originally issued, the Company’s December 31, 2018 consolidated financial statements were audited by another independent registered accounting firm whose report (dated March 21, 2019) expressed an unqualified opinion thereon and expressed substantial doubt as to the ability of the Company to continue as a going concern. Management subsequently determined that such financial statements included material departures from accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America; accordingly, the accompanying December 31, 2018 consolidated financial statements have been restated as more fully explained in Note 3.
Basis for Opinion
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s financial statements based on our audits. We are a public accounting firm registered with the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States) (PCAOB) and are required to be independent with respect to the Company in accordance with U.S. federal securities laws and the applicable rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission and the PCAOB.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the PCAOB. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement, whether due to error or fraud. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. As part of our audits we are required to obtain an understanding of internal control over financial reporting but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion.
Our audits included performing procedures to assess the risks of material misstatement of the financial statements, whether due to error or fraud, and performing procedures that respond to those risks. Such procedures included examining, on a test basis, evidence regarding the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. Our audits also included evaluating the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall presentation of the financial statements. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
F-2
We have served as the Company’s auditor since 2020.
San Diego, California
January 22, 2021
F-3
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
|
|
|
As of |
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 (As Restated) |
|
||
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
1,769 |
|
|
$ |
3,905 |
|
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
|
2,150 |
|
|
|
1,788 |
|
|
Inventories, net |
|
|
7,971 |
|
|
|
4,705 |
|
|
Investment in marketable securities |
|
|
27,929 |
|
|
|
49,343 |
|
|
Marketable securities, pledged to creditor |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
238 |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
1,402 |
|
|
|
634 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
|
41,221 |
|
|
|
60,613 |
|
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
151 |
|
|
|
152 |
|
|
Long-term investment at cost |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
538 |
|
|
Equity method investment |
|
|
13,325 |
|
|
|
13,569 |
|
|
Right of use assets |
|
|
4,474 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
285 |
|
|
|
406 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
59,456 |
|
|
$ |
75,278 |
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
$ |
11,498 |
|
|
$ |
8,235 |
|
|
Deferred rent, current portion |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
Operating lease liabilities, current portion |
|
|
991 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
|
5,748 |
|
|
|
5,342 |
|
|
Revolving line of credit to related party |
|
|
600 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Warrant derivative liabilities |
|
|
38 |
|
|
|
8,939 |
|
|
Notes payable, net of discount |
|
|
3,749 |
|
|
|
6,212 |
|
|
Notes payable to related parties |
|
|
193 |
|
|
|
468 |
|
|
Convertible debentures, net of discount |
|
|
7,015 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Convertible notes payable, net of discount |
|
|
2,995 |
|
|
|
11,253 |
|
|
Convertible notes payable to related parties, net of discount |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,089 |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
32,827 |
|
|
|
45,557 |
|
|
Deferred rent, less current portion |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
268 |
|
|
Operating lease liabilities, less current portion |
|
|
3,932 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other long-term liabilities |
|
|
33,750 |
|
|
|
36,222 |
|
|
Notes payable, net of discount, less current portion |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
925 |
|
|
Convertible notes payable, net of discount, less current portion |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,485 |
|
|
Convertible notes payable to related parties, net of discount |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8,529 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
70,509 |
|
|
|
96,986 |
|
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred stock — par value $0.001 per share, 15,000,000 shares authorized, no shares issued or outstanding |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Common stock — par value $0.001 per share, 250,000,000 shares authorized, 48,471,446 shares and 37,341,393 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2019 and at December 31, 2018, respectively |
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
215,207 |
|
|
|
149,682 |
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
(79 |
) |
|
|
(69 |
) |
|
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
(226,229 |
) |
|
|
(171,358 |
) |
|
Total stockholders’ deficit |
|
|
(11,053 |
) |
|
|
(21,708 |
) |
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit |
|
$ |
59,456 |
|
|
$ |
75,278 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-4
Consolidated Statements of operations and Comprehensive Loss
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
|
|
|
Years Ended December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
(As Restated) |
|
||
|
REVENUES, NET |
|
$ |
22,752 |
|
|
$ |
16,459 |
|
|
COST OF GOODS SOLD |
|
|
1,094 |
|
|
|
993 |
|
|
GROSS PROFIT |
|
|
21,658 |
|
|
|
15,466 |
|
|
OPERATING EXPENSES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
2,183 |
|
|
|
1,723 |
|
|
Selling |
|
|
6,975 |
|
|
|
4,733 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
17,012 |
|
|
|
17,464 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
26,170 |
|
|
|
23,920 |
|
|
LOSS FROM OPERATIONS |
|
|
(4,512 |
) |
|
|
(8,454 |
) |
|
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss on debt extinguishment |
|
|
(438 |
) |
|
|
(2,702 |
) |
|
Change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities |
|
|
3,545 |
|
|
|
4,476 |
|
|
Change in fair value of embedded conversion option |
|
|
131 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Net losses on investment in marketable securities and long-term investment |
|
|
(21,947 |
) |
|
|
(43,977 |
) |
|
Net losses on equity method investment |
|
|
(414 |
) |
|
|
(97 |
) |
|
Miscellaneous reverse merger costs |
|
|
(309 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Notes conversion costs |
|
|
(3,341 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Interest and other income |
|
|
232 |
|
|
|
1,002 |
|
|
Interest expense |
|
|
(27,625 |
) |
|
|
(22,796 |
) |
|
Total other expense |
|
|
(50,166 |
) |
|
|
(64,094 |
) |
|
LOSS BEFORE INCOME TAXES |
|
|
(54,678 |
) |
|
|
(72,548 |
) |
|
INCOME TAXES |
|
|
164 |
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
NET LOSS |
|
|
(54,842 |
) |
|
|
(72,587 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COMPONENTS OF OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
|
16 |
|
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
|
16 |
|
|
COMPREHENSIVE LOSS |
|
|
(54,852 |
) |
|
|
(72,571 |
) |
|
NET LOSS PER COMMON SHARE - BASIC and DILUTED |
|
|
(1.30 |
) |
|
|
(1.97 |
) |
|
WEIGHTED-AVERAGE COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING |
|
|
42,259,460 |
|
|
|
36,857,995 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-5
Consolidated Statements of changes IN stockholders’ equity (deficit)
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
|
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
Shares |
|
|
Amount |
|
|
Additional Paid-In Capital |
|
|
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
|
|
Accumulated Deficit |
|
|
Total Stockholders' Equity / (Deficit) |
|
|
||||||
|
Balance, December 31, 2017, as restated |
|
|
36,634,856 |
|
|
$ |
37 |
|
|
$ |
117,107 |
|
|
$ |
41,276 |
|
|
$ |
(140,132 |
) |
|
$ |
18,288 |
|
|
|
Cumulative effect adjustment on adoption of ASU 2016-01 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(41,361 |
) |
|
|
41,361 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
Beneficial conversion feature relating to convertible and promissory notes payable |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
13,374 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
13,374 |
|
|
|
Exercise of warrants |
|
|
1,741,720 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
18,455 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
18,456 |
|
|
|
Stock issued for cash |
|
|
131,268 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,275 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,275 |
|
|
|
Repurchase and cancellation of common stock |
|
|
(1,254,924 |
) |
|
|
(1 |
) |
|
|
(5,075 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(5,076 |
) |
|
|
Share-based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,546 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,546 |
|
|
|
Exercise of common stock options |
|
|
88,473 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation effect |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
Net loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(72,587 |
) |
|
|
(72,587 |
) |
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2018, as restated |
|
|
37,341,393 |
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
|
149,682 |
|
|
|
(69 |
) |
|
|
(171,358 |
) |
|
|
(21,708 |
) |
|
|
Cumulative effect adjustment on adoption of ASC 842 |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(29 |
) |
|
|
(29 |
) |
|
|
Beneficial conversion feature relating to convertible notes payable |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8,765 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8,765 |
|
|
|
Common stock issued for cash (net of issuance cost) |
|
|
1,677,013 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
8,587 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8,589 |
|
|
|
Common stock issued in merger |
|
|
2,330,548 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
(1,647 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(1,645 |
) |
|
|
Conversion of convertible notes payable and notes payable to common stock |
|
|
7,068,760 |
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
39,492 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
39,499 |
|
|
|
Exercise of stock options |
|
|
175 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
Exercise of warrants |
|
|
53,557 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
186 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
186 |
|
|
|
Warrant and conversion feature reclassified to equity |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
6,336 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
6,336 |
|
|
|
Fair value of replacement equity awards |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,438 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,438 |
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation effect |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(10 |
) |
|
|
Share-based compensation |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,367 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,367 |
|
|
|
Net loss |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(54,842 |
) |
|
|
(54,842 |
) |
|
|
Balance, December 31, 2019 |
|
|
48,471,446 |
|
|
$ |
48 |
|
|
$ |
215,207 |
|
|
$ |
(79 |
) |
|
$ |
(226,229 |
) |
|
$ |
(11,053 |
) |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-6
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In thousands)
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 (As Restated) |
|
||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss |
|
$ |
(54,842 |
) |
|
$ |
(72,587 |
) |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash flows used in operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
73 |
|
|
|
61 |
|
|
Impairment loss on long-term investment |
|
|
515 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Amortization of discount of notes payable and convertible notes payable |
|
|
23,781 |
|
|
|
18,234 |
|
|
Foreign exchange adjustments |
|
|
(115 |
) |
|
|
(297 |
) |
|
Net losses on investment in marketable securities |
|
|
21,432 |
|
|
|
43,977 |
|
|
Loss on equity method investment |
|
|
414 |
|
|
|
97 |
|
|
Loss on debt extinguishment |
|
|
438 |
|
|
|
2,702 |
|
|
Share-based compensation and fair value of replacement equity award |
|
|
3,805 |
|
|
|
4,545 |
|
|
Notes conversion costs |
|
|
3,341 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities |
|
|
(3,545 |
) |
|
|
(4,476 |
) |
|
Change in fair value of embedded conversion option |
|
|
(131 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Net changes in operating assets and liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable |
|
|
(361 |
) |
|
|
(1,761 |
) |
|
Inventories |
|
|
(3,267 |
) |
|
|
(4,079 |
) |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
(720 |
) |
|
|
(332 |
) |
|
Other non-current assets |
|
|
(4,364 |
) |
|
|
(241 |
) |
|
Income tax receivable and payable |
|
|
(64 |
) |
|
|
24 |
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
6,527 |
|
|
|
3,572 |
|
|
Deferred rent |
|
|
(317 |
) |
|
|
245 |
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
|
426 |
|
|
|
5,312 |
|
|
Other long-term liabilities |
|
|
2,451 |
|
|
|
(630 |
) |
|
Net cash flows used in operating activities |
|
|
(4,523 |
) |
|
|
(5,634 |
) |
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid in connection with the Merger |
|
|
(1,645 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Sale of marketable securities |
|
|
221 |
|
|
|
6,439 |
|
|
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
|
(60 |
) |
|
|
(94 |
) |
|
Purchase of marketable securities and investment at cost |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(469 |
) |
|
Capital contributions and loan to equity method investees |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(13,316 |
) |
|
Net cash flows used in investing activities |
|
|
(1,484 |
) |
|
|
(7,440 |
) |
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Repurchase of common stock and warrants |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(11,262 |
) |
|
Proceeds from notes payable issued, net of issuance cost and discount |
|
|
600 |
|
|
|
11,560 |
|
|
Proceeds from convertible notes payable issued, net of issuance cost and discount |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
17,816 |
|
|
Payments of notes payable |
|
|
(143 |
) |
|
|
(5,077 |
) |
|
Payments of convertible notes |
|
|
(5,348 |
) |
|
|
(20,000 |
) |
|
Proceeds from exercise of warrants |
|
|
186 |
|
|
|
111 |
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of common stock |
|
|
8,589 |
|
|
|
1,275 |
|
|
Net cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities |
|
|
3,884 |
|
|
|
(5,577 |
) |
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash |
|
|
(13 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
(2,136 |
) |
|
|
(18,651 |
) |
|
Cash, cash equivalent, beginning of period |
|
|
3,905 |
|
|
|
22,556 |
|
|
Cash, cash equivalents, end of period |
|
$ |
1,769 |
|
|
$ |
3,905 |
|
|
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES OF CASH FLOW ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest paid |
|
$ |
1,543 |
|
|
$ |
2,178 |
|
|
Income taxes paid |
|
$ |
227 |
|
|
$ |
3 |
|
|
NON-CASH INVESTMENT AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrant liabilities reclassified to equity |
|
$ |
6,337 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Exercised of warrants and options on cashless basis |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
18,345 |
|
|
Conversion of convertible notes and notes payable to common stock |
|
$ |
33,777 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Conversion of accrued interest payable to common stock |
|
$ |
5,722 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Initial recognition of right-of-use lease asset |
|
$ |
2,922 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-7
Notes to consolidated financial statements
NOTE 1—DESCRIPTION OF BUSINESS
Organization—On July 17, 2019 Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. (formerly, “MYnd Analytics, Inc.” and herein the “Company” or “Emmaus”) completed its merger transaction (the “Merger”) with EMI Holding, Inc., formerly known as Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. (“EMI Holding”) a wholly owned subsidiary of the Company merged into EMI Holding, with EMI Holding surviving the Merger as a wholly owned subsidiary. Immediately after completion of the Merger, the Company changed its name to “Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc.”
The Merger was treated as a reverse recapitalization under the acquisition method of accounting in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. (“GAAP”) For accounting purposed, EMI Holding was considered to have acquired the Company.
In connection with and prior to the Merger, the Company contributed and transferred to Telemynd, Inc. (“Telemynd”), a newly formed, subsidiary of the Company, all or substantially all of the Company’s historical business, assets and liabilities and the Company’s board of directors declared a stock dividend of one share of the Telemynd common stock held by the Company for each outstanding share of Company common stock after giving effect to a 1-for-6 reverse stock of the Company’s outstanding shares of common stock. The dividend, together with the contribution and transfer of the Company’s historical business, assets, and liabilities described above, is referred to as the spin-off.
As a result of the spin-off and the Merger, the Company’s ongoing business became EMI Holding’s business, which is that of a commercial-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on the development, marketing and sale of innovative treatments and therapies, including those in the rare and orphan disease categories.
References herein to the “Company” or “Emmaus” means Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. and its direct and direct subsidiaries.
Nature of Business—The Company is a commercial-stage biopharmaceutical company engaged in the discovery, development, marketing and sales of innovative treatments and therapies, primarily for rare and orphan diseases. On July 7, 2017, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, approved our lead product Endari® (prescription grade L-glutamine oral powder), to reduce the severe complications of sickle cell disease (“SCD”) in adult and pediatric patients five years of age and older. Endari® has received Orphan Drug designation from the FDA and Orphan Medicinal designation from the European Commission, or EC, which designations generally afford marketing exclusivity for Endari® for a seven-year period in the U.S. and for a ten-year period in the EU, respectively, following marketing approval. Endari® also will be entitled to an additional two years of marketing exclusivity in the EU based on Emmaus’ accepted pediatric investigation plan.
The Company commenced commercialization of Endari® in the U.S. in January 2018 in collaboration with a contract sales organization. Since January 2020, the Company has relied upon our in-house commercial sales team. Endari® is reimbursable by the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and every state provides coverage for Endari® for outpatient prescriptions to all eligible Medicaid enrollees within their state Medicaid programs. The Company has distribution agreements in place with the nation’s leading distributors, as well as physician group purchasing organizations and pharmacy benefits managers, making Endari® available at selected pharmacies nationwide. Prior to 2018, the Company had minimal revenues and relied upon funding from sales of equity securities and debt financings and loans, including loans from related parties to fund our business and operations.
On July 4, 2018, the FDA acknowledged receipt of the Company’s investigational new drug application, or IND, for the treatment of diverticulosis using the same prescription-grade L-glutamine oral powder used in Endari®. The Company subsequently received a “Study May Proceed” letter from the FDA, and in July 2019 the Company successfully enrolled 1st subject in a Pilot/Phase 1 study of the safety and efficacy of prescription-grade L-glutamine oral powder and expects to enroll 10 to 15 patients at multiple study sites. The study will evaluate the change in the number and size of colonic diverticula and assess safety.
F-8
NOTE 2—SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Basis of presentation—The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with GAAP codified in the Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) and Accounting Standards Updates (“ASU”) of the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”).
Going concern— The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the basis that the Company will continue as a going concern. The Company had net loss of approximately $54.8 million and $72.6 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. In addition, the Company has a significant amount of notes payable and other obligations due within the next twelve months and is projecting that its operating losses and expected capital needs, including the expected costs relating to the commercialization of Endari®, will exceed its existing cash balances and cash expected to be generated from operations for the foreseeable future. In order to meet the Company’s expected obligations, the Company will need to raise additional funds through equity and debt financings or licensing or other strategic agreements. The Company has no understanding or arrangement for any additional financing, and there can be no assurance that the Company will be able to complete any additional equity or debt financings on favorable terms, or at all, or enter into licensing or other strategic arrangements. Due to the uncertainty of the Company’s ability to meet its current operating and capital expenses, there is substantial doubt about the Company’s ability to continue as a going concern, as the continuation and expansion of its business is dependent upon obtaining further financing, successful and sufficient market acceptance of its products, and achieving a profitable level of operations. The consolidated financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of these uncertainties.
Principles of consolidation—The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company (and EMI Holding and its wholly‑owned subsidiary, Emmaus Medical Inc., and Emmaus Medical, Inc’s wholly‑owned subsidiaries. All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated.
Estimates—Financial statements prepared in accordance with GAAP require management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant assumptions made by management include those relating to revenue recognition on product sales, the estimated useful lives of equipment, impairment of assets, the variables used to calculate the valuation of conversion features, stock options and warrants, and estimated accruals on an ongoing basis. The Company’ base’s its estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that management believes to be reasonable under the circumstances. Actual results could differ from those estimates under different assumptions or conditions. To the extent there are material differences between these estimates and actuals, the Company’s financial statements will be affected.
Revenue recognition— Effective January 1, 2018, the Company adopted ASC 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers using the modified retrospective transition methods. The adoption of ASC 606 did not have a material impact on the measurement or on the recognition of revenue of contracts for which all revenue had not been recognized as of January 1, 2018, therefore no cumulative adjustment has been made to the opening balance of accumulated deficit at the beginning of 2018. Since January 2018, the Company has generated revenues primarily through the sale of Endari® as a treatment for SCD.
Net revenues from Endari® sales are recognized upon transfer to our distributors and specialty pharmacy providers. Distributors resell our products to other pharmacy and specialty pharmacy providers, health care providers, hospitals, and clinics. In addition to agreements with these distributors, we enter into contractual arrangements with specialty pharmacy providers, in-office dispensing providers, physician group purchasing organizations, pharmacy benefits managers and government entities that provide for government-mandated or privately negotiated rebates, chargebacks and discounts with respect to the purchase of our products. These various discounts, rebates, and chargebacks are referred to as “variable consideration.” Revenue from product sales is recorded net of variable consideration.
Under ASC 606, the Company recognizes revenue when its customers obtain control of the Company's product, which typically occurs on delivery. Revenue is recognized in an amount that reflects the consideration that the Company expects to receive in exchange for the product, or transaction price. To determine revenue recognition for contracts with customers within the scope of ASC 606, the Company performs the following 5 steps: (i) identify the contract(s) with a customer; (ii) identify the performance obligations in the contract; (iii) determine the transaction price; (iv) allocate the transaction price to the Company’s performance obligations in the contract; and (v) recognize revenue when (or as) the Company satisfies the relevant performance obligations.
Revenue from product sales is recorded at the transaction price, net of estimates for variable consideration consisting
F-9
of sales discounts, returns, government rebates, chargebacks and commercial discounts. Variable consideration is estimated using the expected-value amount method, which is the sum of probability-weighted amounts in a range of possible transaction prices. Actual variable consideration may differ from the Company's estimates. If actual results vary from the Company's estimates, the Company adjusts the variable consideration in the period such variances become known, which would affect net revenues in that period. The following are our significant categories of variable consideration:
Sales Discounts: The Company provides its customers prompt payment discounts and from time to time offers additional one-time discounts that are recorded as a reduction of revenues in the period the revenues are recognized.
Product Returns: The Company offers its distributors a right to return product purchased directly from the Company, which is principally based upon (i) overstocks, (ii) inactive product or non-moving product due to market conditions, and (iii) expired products. Product return allowances are estimated and recorded at the time of sale.
Government Rebates: The Company is subject to discount obligations under state Medicaid programs and the Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage gap program. The Company’s management estimates Medicaid and Medicare Part D prescription drug coverage gap rebates based upon a range of possible outcomes that are probability-weighted for the estimated payor mix. These reserves are recorded in the same period the related revenues are recognized, resulting in a reduction of product revenues and the establishment of a current liability that is included as an accounts payable and accrued expenses in our balance sheet. The liability for these rebates consists primarily of estimates of claims expected to be received in future periods related to recognized revenues.
Chargebacks and Discounts: Chargebacks for fees and discounts represent the estimated obligations resulting from contractual commitments to sell products to certain specialty pharmacy providers, in-office dispensing providers, group purchasing organizations, and government entities at prices lower than the list prices charged to distributors. The distributors charge the Company for the difference between what they pay for the products and the Company’s contracted selling price to these specialty pharmacy providers, in-office dispensing providers, group purchasing organizations, and government entities. In addition, we have contractual agreements with pharmacy benefit managers who charge us for rebates and administrative fee in connection with the utilization of product. These reserves are established in the same period that the related revenues are recognized, resulting in a reduction of revenues. Chargeback amounts are generally determined at the time of resale of products by the distributors.
Leases — The Company adopted ASU 2016-02 – Leases (Topic 842) (“ASC 842”) as of January 1, 2019. Pursuant to ASC 842, all of the Company’s leases outstanding on January 1, 2019 continued to be classified as operating leases. With the adoption of ASU 2016-02, the Company recorded a right-of-use asset and an operating lease liability on our balance sheet. Right-of-use assets represent our right to use the underlying asset during the lease term and the operating lease liabilities represent the Company commitment to make lease payments arising from the lease. Right-of-use assets and operating lease liabilities were recognized based on the present value of remaining lease payments over the lease term. As the Company’s leases do not provide an implicit rate, the Company has used an estimated incremental borrowing rate based on the information available at our adoption date in determining the present value of lease payments. Operating lease expense is recognized on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Variable lease costs such as common area costs and other operating costs are expensed as incurred. For all lease agreements, we combine lease and non-lease components. No right-of-use asset and related lease liability are recorded for leases with an initial term of 12 months or less.
Cash and cash equivalents—Cash and cash equivalents include short‑term securities with original maturities of less than ninety days. The Company maintains its cash and cash equivalents at insured financial institutions, the balances of which may, at times, exceed federally insured limits. Management believes that the risk of loss due to the concentrations is minimal.
Accounts Receivable— Accounts receivables are primarily due from product sales to customers. The Company makes judgements as to its ability to collect outstanding receivables and provides an allowance for receivables when collection becomes doubtful. Provisions are made based upon a specific review of all significant outstanding invoices and the quality and age of those invoices. The Company believes the credit risks associated with its customers are not significant.
Inventories—Inventories are valued based on first‑in, first‑out and at the lesser of cost or net realizable value. Work‑in‑process inventories consist of L‑glutamine for the Company’s products that has not yet been packaged and labeled for sale. All raw material purchases during the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 were from one vendor.
F-10
Prepaid expenses and other current assets— Prepaid expenses and other current assets consist primarily of cost paid for future services or refunds from vendors which will occur within a year. Prepaid expenses include prepayment in insurance, subscription services, consulting and other services which are being amortized over the contract terms or recognized upon services are performed.
Property and equipment— Equipment, Furniture and fixtures are recorded at historical cost and amortized on a straight‑line basis over their estimated useful lives of five to seven years. Leasehold improvements are recorded at historical cost and amortized on a straight‑line basis over the shorter of their estimated useful lives or the lease terms. Maintenance and repairs are expensed as incurred, while major additions and improvements are capitalized. Gains and losses on disposition are included in other income (expenses), if any.
Impairment of long‑lived assets—The Company evaluates the carrying value of its long‑lived assets for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that such carrying values may not be recoverable. The Management uses its best judgment based on the current facts and circumstances relating to the Company’s business when determining whether any significant impairment factors exist.
If the Company determines that the carrying values of long‑lived assets may not be recoverable based upon the existence of one or more indicators of impairment, the Company performs an undiscounted cash flow analysis to determine if impairment exists. If impairment exists, the Company measures the impairment based on the difference between the asset’s carrying amount and its fair value, and the impairment is charged to the consolidated statement of operations in the period in which the long‑lived asset impairment is determined to have occurred. No impairment existed as of December 31, 2019 and 2018.
Research and development—Research and development consists of expenditures for the research and development of new products and technologies, which primarily involve contract research, payroll‑related expenses and other related supplies. Research and development costs are expensed as incurred.
Share‑based compensation—The Company recognizes compensation cost for share‑based compensation awards over the service term of the recipients of the share‑based awards. The fair value of share‑based compensation is calculated using the Black‑Scholes‑Merton pricing model. The Black‑Scholes‑Merton model requires subjective assumptions regarding future stock price volatility and expected time to exercise, which greatly affect the calculated values. The expected term of awards granted is calculated using the simplified method allowed under the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) Staff Accounting Bulletin Nos. 107 and 110. The risk‑free rate selected to value any grant is based on the U.S. Treasury rate on the grant date that corresponds to the expected term of the award. Prior to the Merger, the Company common stock was not publicly traded. Therefore, the expected volatility was based on the historical volatility of common stock of comparable publicly traded companies.
Income taxes—The Company accounts for income taxes under the asset and liability method, wherein deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to the differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period the enactment occurs. A valuation allowance is provided for certain deferred tax assets if it is more likely than not that the Company will not realize tax assets through the generation of future taxable income for the related jurisdictions.
When tax returns are filed, it is highly probable that some positions taken would be sustained upon examination by the taxing authorities, while others are subject to uncertainty about the merits of the position taken or the amount of the position that would be ultimately sustained. The benefit of a tax position is recognized in the financial statements in the period during which, based on all available evidence, management believes it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of appeals or litigation processes, if any. Tax positions taken are not offset or aggregated with other positions. Tax positions that meet the more‑likely‑than‑not recognition threshold are recorded at the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50 percent likely of being realized upon examination by the applicable taxing authority. The portion of the benefits associated with tax positions taken that exceeds the amount measured as described above is reflected as a liability for unrecognized tax benefits along with any associated interest and penalties that would be payable to the taxing authorities upon examination.
F-11
As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company had no unrecognized tax benefits, and the Company had no positions which, in the opinion of management, would be reversed if challenged by a taxing authority. In the event the Company is assessed interest and/or penalties, such amounts will be classified as income tax expense in the financial statements.
Comprehensive income (loss)—Comprehensive income (loss) includes net loss and other comprehensive income (loss) relating to foreign translation adjustments of the Company’s subsidiaries.
Marketable securities— The Company to measure all equity investments that do not result in consolidation and are not accounted for under the equity method at fair value and recognize any changes in earnings. The Company uses quoted market prices to determine the fair value of equity securities with readily determinable fair values. For equity securities without readily determinable fair values, the Company has elected the measurement alternative under which the Company measures these investments at cost minus impairment, if any, plus or minus changes resulting from observable price changes in orderly transactions for the identical or a similar investment of the same issuer. Management assesses each of these investments on an individual basis. Additionally, on a quarterly basis, management is required to make a qualitative assessment of whether the investment is impaired; however, the Company is not required to determine the fair value of these investments unless impairment indicators existed. When impairment indicators exist, the Company generally uses discounted cash flow analyses to determine the fair value.
Equity Method Investment – The Company owns 40% of the capital shares of EJ Holdings. A variable interest entity (“VIE”) such as EJ Holdings is to be consolidated by its primary beneficiary if the Company has both a) the power to direct the activities of the VIE that most significantly impact the VIE’s economic performance and b) the obligation to absorb losses of, or the right to receive benefits from, the VIE that could potentially be significant to the VIE. The Company determined that it does not meet the power criterion for consolidating EJ Holdings and, accordingly, accounts for its variable interest in EJ Holdings under the equity method. See Note 6 for additional details.
Foreign Currency Translation—The Company’s reporting currency is the U.S. dollar. The functional currencies of its foreign subsidiaries are the primary currencies within the counties in which they operate. Assets and liabilities of their operations are translated into U.S. dollars at period‑end exchange rates, and revenues, if any, and expenses are translated into U.S. dollars at average exchange rates in effect during each reporting period. Adjustments resulting from the translation are reported in other comprehensive income or loss.
Financial Instruments—Financial instruments included in the financial statements are comprised of cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, investment in marketable securities, marketable securities pledged to creditor, long-term investment at cost, accounts receivable, note receivable, warrant derivative liabilities, accounts payable, certain accrued liabilities, convertible notes payable, notes payable, conversion feature liabilities and other contingent liabilities. The carrying amounts of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued liabilities approximate their fair values due to the short‑term nature of those instruments.
Fair value measurements—The Company defines fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. The Company measures fair value under a framework that provides a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the inputs to valuation techniques used to measure fair value. The hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities (Level 1 measurements) and the lowest priority to unobservable inputs (Level 3 measurements). The three levels of the fair value hierarchy are described as follows:
Level 1: Inputs to the valuation methodology are unadjusted quoted prices for identical assets or liabilities in active markets.
Level 2: Inputs to the valuation methodology include:
Quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets;
Quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in inactive markets;
Inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability;
Inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means.
F-12
If the asset or liability has a specified (contractual) term, the Level 2 inputs must be observable for substantially the full term of the asset or liability.
Level 3: Inputs to the valuation methodology are unobservable and significant to the fair value measurement.
The asset’s or liability’s fair value measurement level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of any input that is significant to the fair value measurement. Valuation techniques used need to maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The carrying values of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivables, other current assets, account payable and accrued expenses and revolving line of credit approximate fair value due to the short-term maturity of those instruments. The fair value assigned to marketable securities is determined by obtaining quoted prices on nationally recognized securities exchanges and are classified as Level 1 investments as of December 31, and. The fair value of the Company’s debt instruments is not materially different from their carrying values as presented. The fair value of the Company’s convertible debt instruments was determined based on Level 2 inputs. The carrying value of the debt was discounted based on allocating proceeds to other financial instruments within the arrangement as discussed in Note 8.
Beneficial conversion features of convertible notes payable - The convertible feature of certain notes payable provides for a conversion rate that is below market value. Such feature is normally characterized as a Beneficial Conversion Feature or BCF. The Company measures the estimated fair value of the BCF when the conversion feature is not required to be separately accounted from the notes payable. The value of BCF is recorded as a discount from the face amount of the notes and amortized to interest expense over the term of the notes.
Net loss per share—In accordance with ASC 260, “Earnings per Share,” the basic loss per common share is computed by dividing net loss available to common stockholders by the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding. Dilutive loss per share is computed in a manner similar to the basic loss per common share except that the denominator is increased to include the number of additional common shares that would have been outstanding if the potential common shares had been issued and if the additional common shares were dilutive. As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, there were 12,933,664 shares and 17,406,715 shares, respectively of potentially dilutive securities outstanding. None of the potentially dilutive securities were included in the calculation of diluted loss per share since their effect would be anti‑dilutive for all periods presented.
Segment reporting—The Company operates in one reportable segment.
Recent accounting pronouncements— In June 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-13—Financial Instruments – Credit Losses (Topic 326): Measurement of Credit Losses on Financial Instruments, which represents a new credit loss standard that will change the impairment model for most financial assets and certain other financial instruments. Specifically, this guidance will require entities to utilize a new “expected loss” model as it relates to trade and other receivables. In addition, entities will be required to recognize an allowance for estimated credit losses on available-for-sale debt securities, regardless of the length of time that a security has been in an unrealized loss position. This guidance was effective for annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2019, including interim periods within those annual reporting periods. Early adoption is permitted. The Company is evaluating the impact of this new standard on its financial statements and related disclosures.
In August 2018, the FASB issued ASU No. 2018-13, Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Disclosure Framework – Changes to the Disclosure Requirements for Fair Value Measurement (“ASU 2018-13”), which changes the fair value measurement disclosure requirements of ASC 820. The amendments in this Update removes some disclosures, modifies others, and add some new disclosure requirements. The amendments in this ASU are effective for all entities for fiscal years, and interim period within those fiscal years, beginning after December 15, 2019 with early adoption permitted. The Company is assessing the impact the adoption of ASU 2018-13 will have on its consolidated financial statements and accompanying footnote disclosures.
NOTE 3 – RESTATEMENT OF PREVIOUSLY ISSUED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
As previously disclosed in the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the SEC on July 8, 2020, the board of directors of the Company, based on the recommendation of the audit committee and in consultation with management and the Company’s predecessor independent registered public accounting firm, concluded that, because of errors identified in the previously issued audited financial statements of EMI Holding, Inc. as of and for the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company would restate the previously issued financial statements.
The restated financial statements correct the following errors:
F-13
|
|
2. |
EJ Holdings was incorrectly consolidated as a VIE and the Company’s variable interest in EJ Holdings should have been accounted for using the equity method. This error resulted in $13.2 million and $0.2 million overstatements of cash and other current assets, respectively, and a $13.5 million understatement of the equity method investment as of December 31, 2018. The error also resulted in a $0.2 million overstatement of loss from operations and a $0.1 million overstatement of loss before income taxes for the year ended December 31, 2018. |
|
|
3. |
The fair value of cashless warrants exercised in September 2018 upon their expiration of warrants should have been recorded in additional paid-in capital. The error resulted in a $18.3 million overstatement of change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities and an understatement of additional paid-in capital for the year ended December 31, 2018. |
|
|
4. |
Other adjustments: The restated financial statements also include adjustments to correct certain insignificant errors to the financial statements as of and for the year ending December 31, 2018. |
F-14
Consolidated Balance Sheet
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
As of December 31, 2018 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
As Restated |
|
|||
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
17,080 |
|
|
$ |
(13,175 |
) |
(b) |
$ |
3,905 |
|
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
|
1,351 |
|
|
|
437 |
|
(d) |
|
1,788 |
|
|
Inventories, net |
|
|
4,705 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,705 |
|
|
Investment in marketable securities |
|
|
49,343 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
49,343 |
|
|
Marketable securities, pledged to creditor |
|
|
238 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
238 |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
743 |
|
|
|
(109 |
) |
(b)(d) |
|
634 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
|
73,460 |
|
|
|
(12,847 |
) |
|
|
60,613 |
|
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
152 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
152 |
|
|
Long-term investment |
|
|
538 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
538 |
|
|
Equity method investment |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
13,569 |
|
(b) |
|
13,569 |
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
406 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
406 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
74,556 |
|
|
$ |
722 |
|
|
$ |
75,278 |
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
9,122 |
|
|
|
(887 |
) |
(b) |
|
8,235 |
|
|
Deferred rent, current portion |
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
|
5,181 |
|
|
|
161 |
|
(d) |
|
5,342 |
|
|
Warrant derivative liabilities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8,939 |
|
(a)(d) |
|
8,939 |
|
|
Notes payable, net of discount |
|
|
6,394 |
|
|
|
(182 |
) |
(a) |
|
6,212 |
|
|
Notes payable to related parties |
|
|
468 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
468 |
|
|
Convertible notes payable, net of discount |
|
|
11,253 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
11,253 |
|
|
Convertible notes payable to related parties, net of discount |
|
|
5,089 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,089 |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
37,526 |
|
|
|
8,031 |
|
|
|
45,557 |
|
|
Deferred rent, less current portion |
|
|
268 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
268 |
|
|
Other long-term liabilities |
|
|
36,222 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
36,222 |
|
|
Warrant derivative liabilities |
|
|
1,399 |
|
|
|
(1,399 |
) |
(d) |
|
— |
|
|
Notes payable, net of discount, less current portion |
|
|
1,021 |
|
|
|
(96 |
) |
(a) |
|
925 |
|
|
Convertible notes payable, net of discount, less current portion |
|
|
5,485 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,485 |
|
|
Convertible notes payable to related parties, net of discount, less current portion |
|
|
8,529 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
8,529 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
90,450 |
|
|
|
6,536 |
|
|
|
96,986 |
|
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY (DEFICIT) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred stock — par value $0.001 per share, 15,000,000 shares authorized, no shares issued or outstanding |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Common stock — par value $0.001 per share, 250,000,000 shares authorized, 37,341,393 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2018 |
|
|
37 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
140,903 |
|
|
|
8,779 |
|
(a)(c)(d) |
|
149,682 |
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
(69 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(69 |
) |
|
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
(156,668 |
) |
|
|
(14,690 |
) |
|
|
(171,358 |
) |
|
Stockholders’ deficit |
|
|
(15,797 |
) |
|
|
(5,911 |
) |
|
|
(21,708 |
) |
|
Noncontrolling interests |
|
|
(97 |
) |
|
|
97 |
|
(b) |
|
— |
|
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit |
|
$ |
74,556 |
|
|
$ |
722 |
|
|
$ |
75,278 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) Warrant adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in an increase of $7.5 million in warrant derivative liabilities and decreases of $182,000 in short-term notes payable, $96,000 in long-term notes payable and $9.7 million in additional paid-in capital.
(b) EJ Holdings adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in increases of $13.6 million in equity method investment, $58,000 in accounts payable and accrued expenses, and $97,000 in non-controlling interest and decreases of $13.2 million in cash and cash equivalent and $240,000 in prepaid expenses and other current assets.
(c) Cashless warrants adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in an increase of $18.3 million in additional paid-in capital.
(d) Corrections of other misstatement were as follows: (i) period adjustment and reclassification of variable consideration resulted in an increase of $436,000 in accounts receivable and a decrease of $946,000 in accounts payable and accrued expense. It also resulted a decrease of $10,000 in income tax receivable and an increase of $24,000 in income tax payable; (ii) correction of financing of insurance premium resulted in an increase of $141,000 in each of prepaid expenses and current liabilities; (iii) correction of stock modification accounting resulted in an increase of $52,000 in additional paid-in capital; and (iv) correction of accounting treatment for conversion feature of senior secured convertible promissory note resulted in an increase of $172,000 in additional paid-in capital.
F-15
Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc.
Consolidated Statement of operations and Comprehensive Loss
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
|
|
Years Ended December 31, 2018 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
As Restated |
|
|||
|
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF LOSS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
REVENUES, NET |
$ |
15,077 |
|
|
$ |
1,382 |
|
(d) |
$ |
16,459 |
|
|
COST OF GOODS SOLD |
|
764 |
|
|
|
229 |
|
(d) |
|
993 |
|
|
GROSS PROFIT |
|
14,313 |
|
|
|
1,153 |
|
|
|
15,466 |
|
|
OPERATING EXPENSES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
1,723 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,723 |
|
|
Selling |
|
4,813 |
|
|
|
(80 |
) |
(d) |
|
4,733 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
17,877 |
|
|
|
(413 |
) |
(b)(d) |
|
17,464 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
24,413 |
|
|
|
(493 |
) |
|
|
23,920 |
|
|
LOSS FROM OPERATIONS |
|
(10,100 |
) |
|
|
1,646 |
|
|
|
(8,454 |
) |
|
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss on debt extinguishment |
|
(3,245 |
) |
|
|
543 |
|
(d) |
|
(2,702 |
) |
|
Change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities |
|
20,674 |
|
|
|
(16,198 |
) |
(a) (c) |
|
4,476 |
|
|
Change in fair value of embedded conversion option |
|
466 |
|
|
|
(466 |
) |
(d) |
|
— |
|
|
Net losses on investment in marketable securities |
|
(43,977 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(43,977 |
) |
|
Net losses on equity method investment |
|
— |
|
|
|
(97 |
) |
(b) |
|
(97 |
) |
|
Interest and other income (loss) |
|
969 |
|
|
|
33 |
|
(b) |
|
1,002 |
|
|
Interest expense |
|
(22,825 |
) |
|
|
29 |
|
(a)(d) |
|
(22,796 |
) |
|
Total other income (expense) |
|
(47,938 |
) |
|
|
(16,156 |
) |
|
|
(64,094 |
) |
|
LOSS BEFORE INCOME TAXES |
|
(58,038 |
) |
|
|
(14,510 |
) |
|
|
(72,548 |
) |
|
INCOME TAXES |
|
6 |
|
|
|
33 |
|
(d) |
|
39 |
|
|
NET LOSS INCLUDING NONCONTROLLING INTEREST |
|
(58,044 |
) |
|
|
(14,543 |
) |
|
|
(72,587 |
) |
|
Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
|
146 |
|
|
|
(146 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
NET LOSS ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE COMPANY |
|
(57,898 |
) |
|
|
(14,689 |
) |
|
|
(72,587 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COMPONENTS OF OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
17 |
|
|
|
(1 |
) |
(b) |
|
16 |
|
|
Other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
17 |
|
|
|
(1 |
) |
|
|
16 |
|
|
COMPREHENSIVE LOSS |
|
(58,027 |
) |
|
|
(14,544 |
) |
|
|
(72,571 |
) |
|
Amounts attributable to noncontrolling interest: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
|
146 |
|
|
|
(146 |
) |
(b) |
|
— |
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE COMPANY |
$ |
(57,881 |
) |
|
$ |
(14,690 |
) |
|
$ |
(72,571 |
) |
|
NET LOSS PER COMMON SHARE - BASIC AND DILUTED |
|
(1.57 |
) |
|
|
(0.40 |
) |
|
|
(1.97 |
) |
|
WEIGHTED-AVERAGE COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING |
|
36,857,995 |
|
|
|
36,857,995 |
|
|
|
36,857,995 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) Warrant adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in an increase of $2.1 million in change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities and a decrease of $278,000 in interest expense.
(b) EJ Holdings adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in a decrease of $211,000 in general and administrative expense, an increase of $97,000 in loss on equity method investment and an increase in $32,000 in interest income.
(c) Cashless warrant adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in a decrease of $18.3 million in change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities.
(d) Corrections of other misstatement were as follows: (i) period adjustment of variable consideration resulted in increases of $1.4 million in revenue, net and $33,000 in income tax provision; (ii) reclassification of shipping cost and royalty expense to cost of sales resulted in an increase of $229,000 in cost of sales and decreases of $80,000 and $141,000 in selling expense and general and administrative expense, respectively; (iii) correction of stock modification accounting resulted in a decrease of $52,000 in general and administrative expense; and (iv) correction of accounting treatment for conversion feature resulted in an increase of $249,000 in interest expense and decreases of $543,000 and $466,000 in loss on debt extinguishment and change in fair value of embedded conversion option, respectively.
F-16
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows
(In thousands)
|
|
Year ended December 31, 2018 |
|
|||||||||
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
As Restated |
|
|||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss |
$ |
(58,044 |
) |
|
$ |
(14,543 |
) |
|
$ |
(72,587 |
) |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash flows used in operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
61 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
61 |
|
|
Amortization of discount of notes payable and convertible notes payable |
|
18,263 |
|
|
|
(29 |
) |
(d) |
|
18,234 |
|
|
Foreign exchange adjustments |
|
53 |
|
|
|
(350 |
) |
(b) |
|
(297 |
) |
|
Net losses on investment in marketable securities |
|
43,977 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
43,977 |
|
|
Loss on equity method investment |
|
— |
|
|
|
97 |
|
(b) |
|
97 |
|
|
Loss on debt extinguishment |
|
3,245 |
|
|
|
(543 |
) |
(d) |
|
2,702 |
|
|
Share-based compensation and fair value of replacement equity award |
|
4,597 |
|
|
|
(52 |
) |
(d) |
|
4,545 |
|
|
Change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities |
|
(20,674 |
) |
|
|
16,198 |
|
(a)(c) |
|
(4,476 |
) |
|
Change in fair value of embedded conversion option |
|
(466 |
) |
|
|
466 |
|
(d) |
|
— |
|
|
Net changes in operating assets and liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable |
|
(1,324 |
) |
|
|
(437 |
) |
(d) |
|
(1,761 |
) |
|
Inventories |
|
(4,079 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(4,079 |
) |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
(431 |
) |
|
|
99 |
|
(b)(d) |
|
(332 |
) |
|
Other non-current assets |
|
(241 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(241 |
) |
|
Income tax receivable and payable |
|
(10 |
) |
|
|
34 |
|
(d) |
|
24 |
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
4,631 |
|
|
|
(1,059 |
) |
(b)(d) |
|
3,572 |
|
|
Deferred rent |
|
245 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
245 |
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
5,174 |
|
|
|
138 |
|
(d) |
|
5,312 |
|
|
Other long-term liabilities |
|
(630 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(630 |
) |
|
Net cash flows used in operating activities |
|
(5,653 |
) |
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
(5,634 |
) |
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sale of marketable securities |
|
6,439 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
6,439 |
|
|
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
(94 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(94 |
) |
|
Purchase of marketable securities and investment at cost |
|
(469 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(469 |
) |
|
Capital contributions and loan to equity method investees |
|
— |
|
|
|
(13,316 |
) |
(d) |
|
(13,316 |
) |
|
Net cash flows provided by (used in) investing activities |
|
5,876 |
|
|
|
(13,316 |
) |
|
|
(7,440 |
) |
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Repurchase of common stock and warrants |
|
(11,262 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(11,262 |
) |
|
Proceeds from notes payable issued, net of issuance cost and discount |
|
11,560 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
11,560 |
|
|
Proceeds from convertible notes payable issued, net of issuance cost and discount |
|
17,645 |
|
|
|
171 |
|
(d) |
|
17,816 |
|
|
Payments of notes payable |
|
(5,077 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(5,077 |
) |
|
Payments of convertible notes |
|
(20,000 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(20,000 |
) |
|
Proceeds from exercise of warrants |
|
111 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
111 |
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of common stock |
|
1,275 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,275 |
|
|
Proceeds from noncontrolling interest |
|
48 |
|
|
|
(48 |
) |
(b) |
|
— |
|
|
Net cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities |
|
(5,700 |
) |
|
|
123 |
|
|
|
(5,577 |
) |
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash |
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Net increase (decrease) in cash, cash equivalents and restricted cash |
|
(5,477 |
) |
|
|
(13,174 |
) |
|
|
(18,651 |
) |
|
Cash, cash equivalents, beginning of period |
|
22,556 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
22,556 |
|
|
Cash, cash equivalents, end of period |
$ |
17,079 |
|
|
$ |
(13,174 |
) |
|
$ |
3,905 |
|
|
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES OF CASH FLOW ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest paid |
$ |
2,178 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
2,178 |
|
|
Income taxes paid |
$ |
3 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
3 |
|
|
Exercised of warrants and options on cashless basis |
$ |
1,712 |
|
|
$ |
16,633 |
|
(c) |
$ |
18,345 |
|
Refer to the descriptions of the adjustments and their impact on net loss in the Consolidated Balance Sheet and Statement of Comprehensive Loss as of and for the year ended December 31, 2018 above except for those below:
Cash flow classification adjustment related to EJ Holdings resulted in a net increase to cash flows provided by operating activities of $0.1 million and a decrease in net cash flows provided by investing activities of $13.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2018.
(d) Correction of unpaid deferred financing cost included in proceeds from convertible notes payable issued, net of issuance cost and discount resulted in a net increase to cash flow from financing activities and a net decrease to cash flow provided by operating activities of $171,000.
F-17
Revenues by category were as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
Year ended December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Endari® |
|
$ |
22,311 |
|
|
$ |
15,953 |
|
|
Other |
|
|
441 |
|
|
|
506 |
|
|
Revenues, net |
|
$ |
22,752 |
|
|
$ |
16,459 |
|
The following table summarizes the revenue allowance and accrual activities for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 (in thousands):
|
|
|
Trade Discounts, Allowances and Chargebacks |
|
|
Government Rebates and Other Incentives |
|
|
Returns |
|
|
Total |
|
||||
|
Balance as of December 31, 2017 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Provision related to sales in the current year |
|
|
926 |
|
|
|
1,535 |
|
|
|
99 |
|
|
|
2,560 |
|
|
Credit and payments made |
|
|
(842 |
) |
|
|
(737 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(1,579 |
) |
|
Balance as of December 31, 2018 |
|
|
84 |
|
|
|
798 |
|
|
|
99 |
|
|
|
981 |
|
|
Provision related to sales in the current year |
|
|
1,393 |
|
|
|
3,082 |
|
|
|
216 |
|
|
|
4,691 |
|
|
Credit and payments made |
|
|
(1,249 |
) |
|
|
(2,526 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(3,775 |
) |
|
Balance as of December 31, 2019 |
|
|
228 |
|
|
|
1,354 |
|
|
|
315 |
|
|
|
1,897 |
|
The following table sets forth information regarding customers that accounted for 10% or more of net revenues and account receivables:
|
|
|
Revenue for year ended December 31, |
|
|
Accounts receivables as of December 31, |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||||
|
AmerisourceBergen Specialty Group |
|
|
58 |
% |
|
|
78 |
% |
|
|
56 |
% |
|
|
57 |
% |
|
McKesson Plasma and Biologics LLC |
|
|
23 |
% |
|
|
14 |
% |
|
|
31 |
% |
|
|
25 |
% |
F-18
The Company is party to a distributor agreement with Telcon pursuant to which it granted Telcon exclusive rights to the Company’s PGLG oral powder for the treatment of diverticulosis in South Korea, Japan and China in exchange for Telcon’s payment of a $10 million upfront fee and agreement to purchase from us specified minimum quantities of the finished product. In a related license agreement with Telcon, the Company agreed to use commercially reasonable best efforts to obtain product registration in these territories within three years of obtaining FDA marketing authorization for PGLG in this indication. Telcon has the right to terminate the distributor agreement in certain circumstances for failure to obtain such product registrations, in which event the Company would be obliged to return to Telcon the $10 million upfront fee. The upfront fee of $10 million is included in other long-term liabilities as unearned revenue as of December 31, 2019 and 2018. Refer Note 13 for related party transaction details.
The Company received an upfront payment of $500,000 in connection with entering into a distribution agreement with a strategic partner in 2018 to distribute Endari® in the Middle East and North Africa region. The payment was recorded as unearned revenue and included in other long-term liabilities to be recognized as revenue when the performance obligations are satisfied. The upfront payment of $500,000 is included in other long-term liabilities as unearned revenue as of December 31, 2019 and 2018.
NOTE 5—SELECTED FINANCIAL STATEMENT CAPTIONS - ASSETS
Inventories consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|||||
|
Inventories by category |
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Raw materials and components |
|
$ |
1,145 |
|
|
$ |
171 |
|
|
Work-in-process |
|
|
2,187 |
|
|
|
2,471 |
|
|
Finished goods |
|
|
4,639 |
|
|
|
2,063 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
7,971 |
|
|
$ |
4,705 |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 (As Restated) |
|
||
|
Prepaid insurance |
|
$ |
735 |
|
|
$ |
223 |
|
|
Other prepaid expenses and current assets |
|
|
667 |
|
|
|
411 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
1,402 |
|
|
$ |
634 |
|
Property and equipment consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Equipment |
|
$ |
335 |
|
|
$ |
306 |
|
|
Leasehold improvements |
|
|
77 |
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
Furniture and fixtures |
|
|
95 |
|
|
|
79 |
|
|
Total property and equipment |
|
|
507 |
|
|
|
455 |
|
|
Less: accumulated depreciation |
|
|
(356 |
) |
|
|
(303 |
) |
|
Property and Equipment, net |
|
$ |
151 |
|
|
$ |
152 |
|
During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, depreciation expenses were approximately $59,000 and $47,000, respectively.
NOTE 6 — INVESTMENTS
Equity Securities— The Company held 6,643,559 shares of capital stock of Telcon RF Pharmaceutical, Inc., a Korean corporation (formerly, Telcon Inc. and herein “Telcon”), which were acquired in July 2017 for approximately $31.8 million. As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the closing prices per Telecon share on the Korean Securities Dealers Automated Quotations (“KOSDAC”) were approximately $4.20 and $7.43, respectively.
F-19
As of December 31,2019 and December 31, 2018, all shares of Telcon common stock were pledged to secure our obligation under the revised API agreement with Telcon. In December 2019, the API agreement was amended to permit the release the Telcon shares from the pledge and to permit the Company to sell the shares in exchange for the Company’s agreement that a portion of the net sale proceeds will be used to purchase at face value a 10-year convertible bond of Telcon in the principal amount of approximately $31.8 million to be substituted for the Telcon shares and pledged to Telcon to secure the Company’s obligations under the revised API Agreement between the Company and Telcon.
As of December 31, 2018, the Company held 39,250 shares of capital stock of CellSeed, Inc., Japanese Corporation (“CellSeed”), which shares were the remainder part of 147,100 shares acquired by the Company in January 2009 for approximately $1.1 million or $7.69 per share. As of December 31, 2018, the closing price per CellSeed share on the Tokyo Stock Exchange was approximately $6.07 and all the Company’s CellSeed shares were pledged to secure a $300,000 convertible note issued to Mitsubishi UFJ Capital III Limited Partnership that was due on demand and was classified as marketable securities, pledged to creditor in current assets. In June 2019, all the CellSeed shares were sold for net cash proceeds of approximately $221,000 after repayment of the secured convertible note.
Effective January 1, 2018, the Company adopted ASU 2016-01 which requires the Company to measure all equity investments that do not result in consolidation and are not accounted for under the equity method at fair value and recognize any changes in earnings. The Company uses quoted market prices to determine the fair value of equity securities with readily determinable fair values. For equity securities without readily determinable fair values, the Company has elected the measurement alternative under which the Company measures these investments at cost minus impairment, if any, plus or minus changes resulting from observable price changes in orderly transactions for the identical or a similar investment of the same issuer. Management assesses each of these investments on an individual basis. Additionally, on a quarterly basis, management is required to make a qualitative assessment of whether the investment is impaired; however, the Company is not required to determine the fair value of these investments unless impairment indicators existed. When impairment indicators exist, the Company generally uses discounted cash flow analyses to determine the fair value. For the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company recognized approximately $515,000 in impairment loss for equity securities without readily determinable fair value attributable to an investment in KPS Co., Ltd. No impairment loss was recognized during the year ended December 31, 2018. The Company recognized a cumulative effect adjustment of $41.4 million, net of $12.3 million income tax benefit, to increase the opening balance of accumulated deficit with an offset to accumulated other comprehensive income as of January 1, 2018, in connection with the adoption of ASU 2016-01.
The fair values of our equity securities were included in the following line items in the Consolidated Balance Sheets (in thousands):
|
|
|
As of December 31, 2019 |
|
|
As of December 31, 2018 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
Fair Value with Changes Recognized in Income |
|
|
Measurement Alternative - No Readily Determinable Fair Value |
|
|
Fair Value with Changes Recognized in Income |
|
|
Measurement Alternative - No Readily Determinable Fair Value |
|
||||
|
Marketable securities |
|
$ |
27,929 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
49,581 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Long-term investment at cost |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
538 |
|
|
Total equity securities |
|
$ |
27,929 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
49,581 |
|
|
$ |
538 |
|
Net unrealized losses on available-for-sale marketable securities held as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 were $21.4 million and $43.2 million, respectively.
Equity Method Investment – During 2018, the Company and Japan Industrial Partners, Inc., or JIP, formed EJ Holdings to acquire, own and operate an amino acids manufacturing facility in Ube, Japan. As part of the formation, the Company invested approximately $32,000 in exchange for 40% of EJ Holdings voting shares. JIP owns 60% of EJ Holdings voting shares. In October 2018, the Company entered into a loan agreement with EJ Holdings under which the Company made an unsecured loan to EJ Holdings in the amount of $13.6 million. The loan was valued at $13.8 million and $13.6 million as of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018 respectively. The loan proceeds were used by EJ Holdings to purchase the Ube facility in December 2019 and pay related taxes. The loan matures on September 30, 2028 and bears interest at the rate of 1% payable annually. The parties also contemplated that the Ube facility will eventually supply the Company with the facility’s output of amino acids, that the operation of the facility will be principally for our benefit and, as such, that major decisions affecting EJ Holdings and the Ube facility will be made by EJ Holdings’ board of directors, a majority of which are representatives of JIP.
F-20
EJ Holdings is engaged in phasing in the Ube facility, including obtaining FDA and other regulatory approvals for the manufacture of PGLG in accordance with cGMP. EJ Holdings has had no revenues since its inception, has depended on loans from the Company to acquire the Ube facility and fund its operations and will continue to be dependent on loans from us or other financing unless and until the Ube facility is activated and EJ Holdings can secure customers for its products.
The Company has determined that EJ Holdings is a variable interest entity, or VIE, based upon the facts that the Company provided the loan financing to acquire the Ube facility and the EJ Holdings activities at the facility are principally for the Company’s benefit. JIP, however, owns 60% of EJ Holdings and is entitled to designate a majority of EJ Holdings’ board of directors and its Chief Executive Officer and outside auditors, and, as such, controls the management, business and operations of EJ Holdings. Accordingly, the Company accounts for its variable interest in EJ Holdings under the equity method.
The Company’s share of the losses reported by EJ Holdings are classified as net losses from equity method investment. The investment is evaluated for impairment annually and if facts and circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable, an impairment charge would be recorded.
The following table sets forth certain financial information of EJ Holdings for years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 (in thousands):
|
|
|
As of |
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
||
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT ASSETS |
|
$ |
2,310 |
|
|
$ |
13,505 |
|
|
OTHER ASSETS |
|
|
10,654 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Total assets |
|
|
12,964 |
|
|
|
13,505 |
|
|
LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES |
|
$ |
296 |
|
|
$ |
33 |
|
|
LONG-TERM LIABILITIES |
|
|
13,870 |
|
|
|
13,634 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
14,166 |
|
|
|
13,667 |
|
|
NONCONTROLLING INTEREST |
|
|
(721 |
) |
|
|
(97 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Year Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
||
|
REVENUES, NET |
|
$ |
229 |
|
|
$ |
57 |
|
|
NET LOSS |
|
$ |
(1,035 |
) |
|
$ |
(243 |
) |
F-21
NOTE 7—SELECTED FINANCIAL STATEMENT CAPTIONS - LIABILITIES
Accounts payable and accrued expenses consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 (As Restated) |
|
||
|
Accounts payable: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Clinical and regulatory expenses |
|
$ |
232 |
|
|
$ |
83 |
|
|
Professional fees |
|
|
1,183 |
|
|
|
2,157 |
|
|
Selling expenses |
|
|
1,303 |
|
|
|
382 |
|
|
Manufacturing cost |
|
|
4,541 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other vendors |
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
844 |
|
|
Total accounts payable |
|
|
7,277 |
|
|
|
3,466 |
|
|
Accrued interest payable, related parties |
|
42 |
|
|
|
842 |
|
|
|
Accrued interest payable |
|
|
991 |
|
|
|
2,138 |
|
|
Accrued expenses: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payroll expenses |
|
|
891 |
|
|
|
713 |
|
|
Government rebates and other rebates |
|
|
1,355 |
|
|
|
933 |
|
|
Due to EJ Holdings |
|
|
238 |
|
|
|
57 |
|
|
Other accrued expenses |
|
|
704 |
|
|
|
86 |
|
|
Total accrued expenses |
|
|
3,188 |
|
|
|
1,789 |
|
|
Total accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
$ |
11,498 |
|
|
$ |
8,235 |
|
Other long-term liabilities consisted of the following (in thousands):
|
|
|
As of December 31, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Trade discount |
|
$ |
23,242 |
|
|
$ |
26,222 |
|
|
Unearned revenue |
|
|
10,500 |
|
|
|
10,000 |
|
|
Other long-term liabilities |
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Total other long-term liabilities |
|
$ |
33,750 |
|
|
$ |
36,222 |
|
On June 12, 2017, the Company entered into an API Supply Agreement, as subsequently amended (as so amended, the “API Agreement”), with Telcon pursuant to which Telcon advanced to the Company approximately $31.8 million as an advance trade discount in consideration of the Company’s agreement to purchase from Telcon the Company’s requirements for bulk containers of pharmaceutical grade L-glutamine (“PGLG”). The Company purchased $4.5 million and $1.0 million of PGLG from Telcon during years ended December 31, 2019, and 2018, respectively, of which $3.7 million and zero were reflected in accounts payable as of December 31, 2019 and 2018, respectively. See Note 12 for additional details.
F-22
Notes payable consisted of the following at December 31, 2019 and 2018 (in thousands except for conversion price and shares):
|
Year Issued |
|
Interest Rate Range |
|
|
Term of Notes |
|
Conversion Price |
|
|
Principal Outstanding December 31, 2019 |
|
|
Discount Amount December 31, 2019 |
|
|
Carrying Amount December 31, 2019 |
|
|
Shares Underlying Notes December 31, 2019 |
|
|
Principal Outstanding December 31, 2018 |
|
|
Discount Amount December 31, 2018 As Restated |
|
|
Carrying Amount December 31, 2018 As Restated |
|
|
Shares Underlying Notes December 31, 2018 |
|
||||||||||
|
Notes payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
2013 |
|
10% |
|
|
Due on demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
920 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
920 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
909 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
909 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2015 |
|
10% |
|
|
Due on demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2016 |
|
10% - 11% |
|
|
Due on demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
843 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
843 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
5% - 11% |
|
|
Due on demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,575 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,575 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
10% - 11% |
|
|
Due on demand- 18 months |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
12,311 |
|
|
|
9,511 |
|
|
|
2,800 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2019 |
|
11% |
|
|
Due on demand - 6 months |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,829 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,829 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
3,749 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
3,749 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
16,648 |
|
|
$ |
9,511 |
|
|
$ |
7,137 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
3,749 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
3,749 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
12,448 |
|
|
$ |
6,236 |
|
|
$ |
6,212 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-current |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
4,200 |
|
|
$ |
3,275 |
|
|
$ |
925 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Notes payable - related party |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
2016 |
|
10% - 11% |
|
|
Due on demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
20 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
20 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
270 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
270 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
10% |
|
|
Due on demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
39 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
11% |
|
|
Due on demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2019 |
|
10% |
|
|
Due on demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
193 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
193 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
468 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
468 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
193 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
193 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
468 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
468 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Convertible debentures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
2019 |
|
10% |
|
|
18 months |
|
$ |
9.52 |
|
|
$ |
10,200 |
|
|
$ |
3,185 |
|
|
$ |
7,015 |
|
|
|
1,080,415 |
|
(a) |
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
10,200 |
|
|
$ |
3,185 |
|
|
$ |
7,015 |
|
|
|
1,080,415 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
10,200 |
|
|
$ |
3,185 |
|
|
$ |
7,015 |
|
|
|
1,080,415 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Convertible notes payable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
2011 |
|
10% |
|
|
5 years |
|
$ |
3.05 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
300 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
300 |
|
|
|
98,285 |
|
|
|
2014 |
|
10% |
|
|
Due on demand - 2 years |
|
$3.05 - $3.60 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
519 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
519 |
|
|
|
183,648 |
|
||
|
2016 |
|
10% |
|
|
1 year |
|
$ |
4.50 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
61 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
61 |
|
|
|
16,753 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
10% |
|
|
Due on demand - 1 year |
|
$3.50 - $4.50 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,820 |
|
|
|
349 |
|
|
|
2,471 |
|
|
|
899,613 |
|
||
|
2018 |
|
6% - 10% |
|
|
Due on demand - 2 years |
|
$3.50 - $10.00 |
|
|
|
3,000 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
2,995 |
|
|
|
363,876 |
|
(b) |
|
19,556 |
|
|
|
6,169 |
|
|
|
13,387 |
|
|
|
3,661,427 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
3,000 |
|
|
$ |
5 |
|
|
$ |
2,995 |
|
|
|
363,876 |
|
|
$ |
23,256 |
|
|
$ |
6,518 |
|
|
$ |
16,738 |
|
|
|
4,859,726 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
3,000 |
|
|
$ |
5 |
|
|
$ |
2,995 |
|
|
|
363,876 |
|
|
$ |
16,604 |
|
|
$ |
5,351 |
|
|
$ |
11,253 |
|
|
|
3,981,232 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-current |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
6,652 |
|
|
$ |
1,167 |
|
|
$ |
5,485 |
|
|
|
881,210 |
|
|
Convertible notes payable - related party |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
2012 |
|
10% |
|
|
Due on demand |
|
$ |
3.30 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
200 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
200 |
|
|
|
74,182 |
|
|
|
2015 |
|
10% |
|
|
2 years |
|
$ |
4.50 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
58,350 |
|
|
|
2017 |
|
10% |
|
|
2 years |
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
311 |
|
|
|
4,689 |
|
|
|
532,671 |
|
|
|
2018 |
|
10% |
|
|
2 years |
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
9,400 |
|
|
|
871 |
|
|
|
8,529 |
|
|
|
971,963 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
14,800 |
|
|
$ |
1,182 |
|
|
$ |
13,618 |
|
|
|
1,637,166 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
5,400 |
|
|
$ |
311 |
|
|
$ |
5,089 |
|
|
|
665,203 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Non-current |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
9,400 |
|
|
$ |
871 |
|
|
$ |
8,529 |
|
|
|
971,963 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grand Total |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
17,142 |
|
|
$ |
3,190 |
|
|
$ |
13,952 |
|
|
|
1,444,291 |
|
|
$ |
55,172 |
|
|
$ |
17,211 |
|
|
$ |
37,961 |
|
|
|
6,496,892 |
|
|
(a) The notes are convertible into Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc. shares. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
|
(b) This note is convertible into EMI Holding Inc. shares. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
F-23
The average stated interest rate of notes payable was 10% for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018. The average effective interest rate of notes payable for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 was 66% and 35%, respectively, after giving effect to discounts relating to beneficial conversion features and deferred financing cost in connection with these notes.
Immediately prior to the completion of the Merger, all but one of the convertible notes payable were converted into shares of EMI common stock at their respective conversion prices. Upon completion of the Merger, the conversion shares were exchanged for shares of the Company common stock in the same manner as other outstanding shares of common stock of EMI based on the Merger “exchange ratio.” The unconverted convertible note payable of EMI is convertible into shares of common stock of EMI at conversion price of $10.00 per share and included in convertible notes payable.
The Company estimated the total fair value of any beneficial conversion feature and any accompanying warrants in allocating the proceeds from the sale of convertible notes payable. The proceeds allocated to the beneficial conversion feature were determined by taking the estimated fair value of shares underlying the convertible notes less the fair value of the number of shares that would be issued if the conversion rate equaled the fair value of common stock as of the date of issuance. In situations where the notes included both a beneficial conversion feature and a warrant, the proceeds were allocated to the beneficial conversion feature and the warrants based on the pro‑rata fair value.
The 10% Senior Secured Debentures were amended and restated immediately prior to the Merger to, among other things, make them convertible into shares of common stock of EMI and to provide for adjustments in the conversion shares issuable upon conversion of the debentures and the conversion price in the event of a merger, reorganization and similar events. Accordingly, upon completion of the Merger the debentures became convertible into shares of common stock of the Company and included in convertible notes payable.
The conversion feature of the amended and restated debentures was separately accounted for at fair value as derivative liabilities under guidance in ASC 815 that is remeasured at fair value on a recurring basis using Level 3 inputs, with any changes in the fair value of the conversion feature liabilities recorded in earnings. The following table sets forth the fair value of the conversion feature liabilities, which is included in the other current liabilities as of December 31, 2019 (in thousands):
The fair value and any changes in fair value of conversion feature liabilities are determined using a binominal lattice model. The model produces an estimated fair value based on changes in the price of the underlying common stock over successive periods of time. The fair values as of December 31, 2019 and as of the Merger date were based upon following assumptions:
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
July 17, 2019 |
|
||
|
Stock price |
|
$ |
1.97 |
|
|
$ |
7.02 |
|
|
Selected yield |
|
|
16.77 |
% |
|
|
19.82 |
% |
|
Expected volatility (peer group) |
|
|
50.00 |
% |
|
|
55.00 |
% |
|
Expected life (in years) |
|
|
0.81 |
|
|
|
1.26 |
|
|
Expected dividend yield |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
||
|
Risk-free rate |
|
Term structure |
|
|
Term structure |
|
||
|
Balance, end of period: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Conversion feature liabilities (in thousands) |
|
$ |
1 |
|
|
$ |
132 |
|
The Company is party to a revolving line of credit agreement with Dr. Niihara, the Company’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer. Under the agreement, at the Company’s request from time to time, Dr. Niihara may, but is not obligated to, loan or re-loan to the Company up to $1,000,000, including $600,000 loaned by him in December 2019. Outstanding amounts under the agreement are due and payable upon demand and bear interest, payable monthly, at a variable annual rate equal to the Prime Rate in effect from time to time plus 3%. In addition to the payment of interest, the Company is obligated to pay Dr. Niihara a “tax gross-up” intended to make him whole for federal and state income taxes payable by him with
F-24
respect to interest paid to him in the previous year. As of December 31, 2019, the outstanding balance under the revolving line of credit agreement of $600,000 was reflected in revolving line of credit, related party on the Consolidated Balance Sheet. With the tax-gross up, the effective interest rate on the outstanding balance as of December 31, 2019 was 10.4%. The revolving line of credit agreement will expire on November 22, 2022. Refer to Note 13 for related party transaction details.
NOTE 9—STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT
Purchase Agreement with GPB—On December 29, 2017, the Company entered into the Purchase Agreement with GPB Debt Holdings II, LLC (“GPB”), pursuant to which the Company issued to GPB a $13 million principal amount senior secured convertible promissory note (the “GPB Note”) for an aggregate purchase price of $12.5 million, reflecting a 4.0% original issue discount.
In connection with the issuance of GPB Note, the Company also issued to GPB a warrant (the “GPB Warrant”) to purchase up to 240,764 of common stock at an exercise price of $10.80 per share, with customary adjustments for stock splits, stock dividends and other recapitalization events and anti-dilution provisions set forth in the GPB Warrant. In the events of a “dilutive issuance” of common stock, the exercise price is to adjusted on a one-time basis to a 10% premium to the dilutive issuance price and the number of shares issuable under the GPB Warrant will be increased on a full ratchet basis. The GPB Warrant became exercisable six months after issuance and has a term of five years from the initial exercise date.
The Company determined that under ASC 815-40, GPB Warrant should be separately recognized at fair value as a liability upon issuance. The warrant liability is remeasured at fair value on a recurring basis using Level 3 inputs and any change in the fair value of the liability is recorded in earnings.
The following table sets forth the fair values of the warrants as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 (in thousands):
|
Warrant liability—GPB |
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
||
|
Balance, beginning of period |
|
$ |
1,399 |
|
|
$ |
1,882 |
|
|
Change in fair value included in the statement of comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
(1,361 |
) |
|
|
(483 |
) |
|
Balance, end of period |
|
$ |
38 |
|
|
$ |
1,399 |
|
Prior to the Merger, the value of warrant derivative liabilities and any change in fair value were determined using a Binominal Monte-Carlo Cliquet Option Pricing Model. After the Merger, the fair value of the warrant derivative liabilities was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing models.
The value as of the dates set forth the in the table below, were based on upon following assumptions:
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
||
|
Stock price |
|
$ |
1.97 |
|
|
$ |
9.10 |
|
|
Risk‑free interest rate |
|
|
1.64 |
% |
|
|
2.48 |
% |
|
Expected volatility (peer group) |
|
|
60.00 |
% |
|
|
70.00 |
% |
|
Expected life (in years) |
|
|
3.50 |
|
|
|
4.00 |
|
|
Expected dividend yield |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
Number outstanding |
|
|
252,802 |
|
|
|
240,764 |
|
|
Balance, end of period: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrant derivative liabilities (long-term) (in thousands) |
|
$ |
38 |
|
|
$ |
1,399 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchase Agreement with Holders of 10% Senior Secured Debentures - In October 2018, EMI sold and issued $12.2 million principal amount of 10% Senior Secured Debentures and common stock purchase warrants to purchase an aggregate of up to 1,220,000 shares of EMI common stock to a limited number of accredited investors. The net proceeds of the sale of the debentures and warrants were used to fund EMI’s loan to EJ Holdings, Inc in October 2018 reflected in the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
The debentures were amended and restated in their entirety in conjunction with the Merger on July 17, 2019 as described in Note 12. As originally issued, the debentures bore interest at the rate of 10% per annum, payable monthly commencing November 1, 2018, and were to mature on April 21, 2020. EMI was to be obligated to redeem $1 million principal amount of debentures monthly, commencing in May 2019 and to redeem the debentures in full upon a “subsequent financing” of at least $20 million, subject to certain exceptions, or in the “event of default” (as defined). EMI’s obligations
F-25
under the debentures are secured by a security interest in substantially all EMI assets and guaranteed by EMI’s U.S. subsidiaries.
The common stock purchase warrants also were amended and restated in their entirety in conjunction with the Merger. As originally issued, the common stock purchase warrants were exercisable for five years beginning April 22, 2019 at an initial exercise price of $11.30 per share, which was to be subject to reduction if EMI became a listed company or its common stock became listed or quoted on a trading market based upon the public offering price or “VWAP” of the common stock. The exercise price also was subject to adjustment in certain other customary circumstances In accordance with the fee agreement, EMI paid the placement agent a cash fee equal to 5% of the gross proceeds received from the purchasers, granted the warrants to purchase up to 120,000 shares of EMI common stock on the same terms as the common stock purchase warrants sold to the purchasers and reimbursed the agent for certain legal fees and expenses. Effective as of March 5, 2019, EMI entered into a securities amendment agreement with the debenture and warrant holders which amended in certain respects the original securities purchase agreement provided that the debentures and warrants were to be amended in certain respects and restated in their entirety immediately prior to and subject to the completion of the then-pending Merger. Pursuant to the terms of the securities amendment agreement, (i) the debenture holders waived their right to the monthly redemption of $1,000,000 principal amount of the debentures that was due May 1, 2019 and their right to accelerate the repayment of the debentures in connection with the proposed Merger and (ii) the provision of the debentures requiring their mandatory redemption in connection with any “subsequent financing” was eliminated. The debenture holders subsequently waived their rights to the monthly redemptions due June 1 and July 1, 2019 respectively.
The amended and restated debentures provide that the mandatory monthly redemption of $1,000,000 principal amount thereof would commence in November 2019 and that they would mature on October 21, 2020, six months later than the original maturity date of the debentures. Unlike the debentures, the amended and restated debentures were convertible at the option of each holder into shares of EMI common stock at a conversion price of $10.00 a share, subject to adjustment for stock splits, merger reorganizations and other customary events. The amended and restated warrants will be exercisable for up to an aggregate of up to 1,460,000 shares of EMI common stock, or 244,000 more shares than were previously purchasable under the original warrants, at an initial exercise price of $10.00 per share, or $1.30 less than the original exercise price of the warrants. The exercise price of the warrants was subject to reduction in connection with a “going public event” such as the Merger based upon the “VWAP” (i.e., volume-weighted average trading price) of the Company common stock at the time of the Merger. The exercise price also will be subject to adjustment for stock splits and other customary events. Upon completion of the Merger, the warrants became exercisable for shares of the Company common stock and the exercise price of the warrants and the number of underlying warrant shares were adjusted based upon exchange ratio in the Merger. Subsequent to the Merger, the exercise price of the warrants was adjusted in accordance with their terms to $5.87 per share based upon the VWAP of the Company common stock on the day following completion of the Merger.
The Company evaluated common stock purchase warrants issued in connection with the original issuance in October 2018 of the Company’s outstanding 10% Senior Secured Debentures under ASC 815-40 and concluded that the warrants should be separately recognized at fair value as a liability. The liability is remeasured at fair value on a recurring basis using Level 3 input and any changes in fair value is recorded in earnings. In 2019, the debentures were amended and restated to be convertible into Company common stock immediately prior to completion of the Merger, which resulted in the related warrants being reclassified to equity. The following table presents information regarding the warrants measured at fair value when reclassified to equity and as of December 31, 2018 (in thousands):
|
Liability instrument—10% Senior Secured Convertible Debentures |
|
July 19, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
||
|
Balance, beginning of period |
|
$ |
7,540 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Fair value at issuance date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9,686 |
|
|
Change in fair value included in the statement of comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
(1,204 |
) |
|
|
(2,146 |
) |
|
Fair value at reclassification to equity |
|
|
(6,336 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Balance, end of period |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
7,540 |
|
The fair value and change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities are determined using a Binominal Monte-Carlo Cliquet Option Pricing Model prior to the Merger. The model is similar to Black-Scholes option pricing models, except that the exercise price resets at certain dates in the future.
The fair value as of the dates set forth the in the table below were based upon following assumptions:
F-26
|
|
July 19, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 (As Restated) |
|
|||
|
Stock price |
|
$ |
6.86 |
|
|
$ |
9.00 |
|
|
Risk‑free interest rate |
|
|
1.79 |
% |
|
|
2.51 |
% |
|
Expected volatility (peer group) |
|
|
65.00 |
% |
|
|
70.00 |
% |
|
Expected life (in years) |
|
|
4.26 |
|
|
|
4.81 |
|
|
Expected dividend yield |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
||
|
Balance, end of period: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Warrant liabilities (in thousands) |
|
$ |
6,336 |
|
|
$ |
7,540 |
|
A summary of outstanding warrants as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 is presented below:
|
|
Year ended |
|
|
Year ended |
|
||
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
|||
|
Warrants outstanding, beginning of period |
|
3,436,431 |
|
|
|
5,265,432 |
|
|
Assumed as part of Merger |
|
1,044,939 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Deemed Granted |
|
500,729 |
|
(a) |
|
1,542,000 |
|
|
Exercised |
|
(51,000 |
) |
|
|
(2,385,317 |
) |
|
Cancelled, forfeited and expired |
|
— |
|
|
|
(985,684 |
) |
|
Warrants outstanding, end of period |
|
4,931,099 |
|
|
|
3,436,431 |
|
|
(a) |
Represents warrant shares issuable upon the Merger by reason of antidilution adjustments under former EMI warrants. |
A summary of outstanding warrants by year issued and exercise price as of December 31, 2019 is presented below.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Outstanding |
|
|
Exercisable |
|
||||||||||||||
|
Year issued |
Exercise Price |
|
|
Number of Warrants Issued |
|
|
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
|
|
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
|
|
Total |
|
|
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
|
||||||
|
Prior to January 1, 2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
$4.29-$10.28 |
|
|
|
1,937,407 |
|
|
|
1.57 |
|
|
$ |
5.43 |
|
|
|
1,937,407 |
|
|
$ |
5.43 |
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
|
|
1,937,407 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,937,407 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At December 31, 2018 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
10.76 |
|
|
|
210,553 |
|
|
|
3.61 |
|
|
$ |
10.76 |
|
|
|
210,553 |
|
|
$ |
10.76 |
|
|
|
$ |
5.87 |
|
|
|
1,407,000 |
|
|
|
3.81 |
|
|
$ |
5.87 |
|
|
|
1,407,000 |
|
|
$ |
5.87 |
|
|
|
2018 Total |
|
|
|
1,617,553 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,617,553 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
At December 31, 2019 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
6.12 |
|
|
|
32,391 |
|
|
|
4.41 |
|
|
$ |
6.12 |
|
|
|
32,391 |
|
|
$ |
6.12 |
|
|
|
$ |
12.00 |
|
|
|
76,575 |
|
|
|
3.73 |
|
|
$ |
12.00 |
|
|
|
76,575 |
|
|
$ |
12.00 |
|
|
|
$ |
14.04 |
|
(a) |
|
174,999 |
|
|
|
3.24 |
|
|
$ |
14.04 |
|
|
|
174,999 |
|
|
$ |
14.04 |
|
|
|
$ |
31.50 |
|
(a) |
|
737,975 |
|
|
|
2.57 |
|
|
$ |
31.50 |
|
|
|
737,975 |
|
|
$ |
31.50 |
|
|
|
$ |
36.24 |
|
(a) |
|
22,333 |
|
|
|
2.57 |
|
|
$ |
36.24 |
|
|
|
22,333 |
|
|
$ |
36.24 |
|
|
|
$ |
60.00 |
|
(a) |
|
666 |
|
|
|
1.00 |
|
|
$ |
60.00 |
|
|
|
666 |
|
|
$ |
60.00 |
|
|
|
$ |
5.87 |
|
|
|
256,200 |
|
|
|
3.83 |
|
|
$ |
5.87 |
|
|
|
256,200 |
|
|
$ |
5.87 |
|
|
|
$ |
7.68 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
|
4.55 |
|
|
$ |
7.68 |
|
|
|
75,000 |
|
|
$ |
7.68 |
|
|
|
2019 Total |
|
|
|
1,376,139 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,376,139 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grand Total |
|
|
|
4,931,099 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4,931,099 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
The exercise price of these warrants was reduced to $12 per share for the one-year period following the Merger. |
Stock Options – Upon completion of the Merger, the EMI Amended and Restated 2011 Stock Incentive Plan was assumed by the Company. The 2011 Stock Incentive Plan permits grants of incentive stock options to employees, including executive officers, and other share-based awards such as stock appreciation rights, restricted stock, stock units, stock bonus and unrestricted stock awards to employees, directors, and consultants for up to 9,000,000 shares of common stock. On February 28, 2013, the number of shares of common stock authorized for issuance under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan was increased from 3,000,000 shares to 6,000,000 shares. On July 14, 2014, the number of shares of common stock authorized for
F-27
issuance under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan was increased from 6,000,000 shares to 9,000,000 shares. Options granted under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan expire ten years after grant. Options granted to directors vest in quarterly installments, and all other option grants vest over a minimum period of three years, all based on continuous service with the Company. Each stock option outstanding under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan at the effective time of the Merger was automatically converted into a stock option exercisable for a number of shares of the Company’s common stock and at an exercise price calculated based on the exchange ratios in the Merger.
The Company also maintains a 2012 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan under which the Company may grant incentive stock options to selected employees including officers, non-employee consultants and non-employee directors. All outstanding stock options under the 2012 Omnibus Incentive Compensation Plan were fully vested prior to the Merger.
Management has valued stock options at their date of grant utilizing the Black‑Scholes‑Merton Option pricing model. The fair value of the underlying shares was determined by the market value of stock of similar companies and recent arm’s length transactions involving the sale of the Company’s common stock. Prior the Merger, the Company lacked company-specific historical and implied volatility information for its common stock. Therefore, the expected volatility was calculated using the historical volatility of a comparative public traded companies. The following table presents the assumptions used on recent dates on which options were granted by the Company.
|
|
|
6/19/2019 |
|
|
9/27/2018 |
|
|
8/8/2018 |
|
|
2/27/2018 |
|
||||
|
Stock Price |
|
$ |
10.30 |
|
|
$ |
11.10 |
|
|
$ |
11.30 |
|
|
$ |
11.40 |
|
|
Exercise Price |
|
$ |
10.30 |
|
|
$ |
11.10 |
|
|
$ |
11.30 |
|
|
$ |
11.40 |
|
|
Term |
|
6 years |
|
|
6 years |
|
|
6 years |
|
|
6 years |
|
||||
|
Risk-Free Rate |
|
1.83% |
|
|
|
2.99 |
% |
|
|
2.88 |
% |
|
|
2.75 |
% |
|
|
Dividend Yield |
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
|
— |
|
||||
|
Volatility |
|
|
67.16 |
% |
|
|
69.14 |
% |
|
|
66.09 |
% |
|
|
68.18 |
% |
The risk‑free interest rate is based on the implied yield available on U.S. Treasury issues with a term approximating the expected life of the options depending on the date of the grant and expected life of the respective options.
During the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company granted options to purchase 50,000 shares of common stock. The options have an exercise price of $10.30 per share. During the year ended December 31, 2018, the Company granted stock option to purchase up to 357,000 common stock. All of the options are exercisable with respect to one‑third (1/3) of the underlying shares on the first anniversary of the grant date and as to the remaining two‑thirds (2/3) of shares in twenty‑four (24) approximately equal monthly installments over a period of two years thereafter.
A summary of the Company’s stock option activity for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 is presented below:
|
|
|
December 31, 2019 |
|
|
December 31, 2018 |
|
||||||||||
|
|
|
Number of Options |
|
|
Weighted‑ Average Exercise Price |
|
|
Number of Options |
|
|
Weighted‑ Average Exercise Price |
|
||||
|
Options outstanding, beginning of period |
|
|
6,642,200 |
|
|
$ |
4.40 |
|
|
|
6,775,200 |
|
|
$ |
4.12 |
|
|
Granted or deemed issued |
|
|
636,683 |
|
(a) |
$ |
10.10 |
|
|
|
357,000 |
|
|
$ |
11.28 |
|
|
Exercised |
|
|
(167 |
) |
|
$ |
5.00 |
|
|
|
(170,000 |
) |
|
$ |
4.59 |
|
|
Cancelled, forfeited and expired |
|
|
(33,366 |
) |
|
$ |
11.29 |
|
|
|
(320,000 |
) |
|
$ |
6.06 |
|
|
Options outstanding, end of period |
|
|
7,245,350 |
|
|
$ |
4.68 |
|
|
|
6,642,200 |
|
|
$ |
4.40 |
|
|
Options exercisable at end of year |
|
|
7,001,680 |
|
|
$ |
4.47 |
|
|
|
5,958,783 |
|
|
$ |
3.87 |
|
|
Options available for future grant |
|
|
2,167,150 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2,357,800 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
(a) |
Upon the Merger, the exercise prices of outstanding EMI options were adjusted and additional options were deemed issued based upon the exchange ratio in the Merger. |
During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company recognized $3.7 million and $4.6 million, respectively, of share‑based compensation cost arising from stock option grants including $1.9 million of one-time adjustments resulting from the Merger. As of December 31, 2019, there was $1.4 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to unvested share‑based compensation arrangements granted under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan. That cost is expected to be recognized over the weighted-average remaining period of 1.8 years.
F-28
NOTE 10—INCOME TAXES
The provision for income taxes consists of the following for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 (in thousands):
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Current U.S. |
|
$ |
164 |
|
|
$ |
38 |
|
|
International |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
Deferred U.S. |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
International |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
$ |
164 |
|
|
$ |
39 |
|
Deferred tax assets consist of the following as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 (in thousands):
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Net operating loss carryforward |
|
$ |
16,773 |
|
|
$ |
19,573 |
|
|
General business tax credit |
|
|
9,888 |
|
|
|
9,342 |
|
|
Stock options |
|
|
5,723 |
|
|
|
5,997 |
|
|
Charitable contribution |
|
|
81 |
|
|
|
139 |
|
|
Accrued expenses |
|
|
166 |
|
|
|
364 |
|
|
Unearned revenue |
|
|
175 |
|
|
|
1,396 |
|
|
Allowance for bad AR |
|
|
2,373 |
|
|
|
173 |
|
|
Unrealized gain/ (loss) on LT investment |
|
|
1,400 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other |
|
|
1,629 |
|
|
|
352 |
|
|
Total gross deferred tax assets |
|
|
38,208 |
|
|
|
37,336 |
|
|
Less valuation allowance |
|
|
(38,019 |
) |
|
|
(34,193 |
) |
|
Net deferred tax assets |
|
$ |
189 |
|
|
$ |
3,143 |
|
Deferred tax liabilities consist of the following as of December 31, 2019 and 2018 (in thousands):
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Unrealized loss on long-term investment |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
(2,965 |
) |
|
Unrealized loss on foreign exchange translation and others |
|
|
(185 |
) |
|
|
(176 |
) |
|
Unrealized gain on marketable securities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Other |
|
|
(4 |
) |
|
|
(2 |
) |
|
Total deferred tax liabilities |
|
$ |
(189 |
) |
|
$ |
(3,143 |
) |
A valuation allowance for the net deferred tax assets is recorded when it is more likely than not that the Company will not realize these assets through future operations. The valuation allowance increased by approximately $3.8 million and $20.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 respectively.
As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company had net operating loss carryforwards for federal income tax purposes of approximately $62.9 million and $63.5 million, respectively, available to offset future federal taxable income, if any. Net operating loss generated in 2017 and prior years expire in various years through 2037. Net operating losses for federal income tax purpose generated in 2018 and after will be available indefinitely. In addition, the Company had net operating loss carryforwards for state income tax purposes of approximately $55.9 million and $55.1 million respectively, which expire in various years through 2039. As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company has general business tax credits of $9.9 million and $9.3 million, respectively, for federal income tax purposes. The tax credits are available to offset future tax liabilities, if any, through 2039. The Company’s utilization of net operating loss carryforwards could be subject to an annual limitation as a result of certain past or future events, such as stock sales or other equity events constituting a “change in ownership” under the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, and similar state provisions. The annual limitations could result in the expiration of net operating loss carryforwards and tax credits before they can be utilized.
F-29
The income tax provision differs from that computed using the statutory federal tax rate of 21% due to the following factors (in thousands):
|
|
|
2019 |
|
|
2018 |
|
||
|
Tax benefit at statutory federal rate |
|
$ |
(11,365 |
) |
|
$ |
(15,195 |
) |
|
State taxes, net of federal tax benefit |
|
|
(666 |
) |
|
|
(3,695 |
) |
|
Increase in valuation allowance |
|
|
3,411 |
|
|
|
6,340 |
|
|
Permanent items |
|
|
5,710 |
|
|
|
4,130 |
|
|
General business tax credit |
|
|
(545 |
) |
|
|
(431 |
) |
|
Other |
|
|
3,619 |
|
|
|
8,890 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
164 |
|
|
$ |
39 |
|
As of December 31, 2019 and December 31, 2018, the Company had no unrecognized tax benefits or position which, in the opinion of management, would be reversed if challenged by a taxing authority. In the event the Company is assessed interest or penalties, such amounts would be classified as income tax expense. As of December 31, 2019, all federal tax returns since 2016 are subject to audit. The expiration of the state returns varies by state, but the 2015 and subsequent years’ returns generally are subject to audit. No tax returns are currently being examined by taxing authorities.
NOTE 11—LEASES
Operating leases — During the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018, the Company leased its office space under operating leases with unrelated entities.
The Company leased 21,293 square feet of office space for its headquarters in Torrance, California, at a base rental of $78,908 per month, which the lease will expire on September 30, 2026, and leased an additional 1,600 square feet office space in Torrance, California, at a base rent of $2,240 per month and 2,986 square feet office space in New York, New York, at a base rent of $5,500, which leases expired on January 31, 2020 and December 30, 2019, respectively. Upon expiration of New York office lease in December 2019, the Company leased 1,850 square feet of new office space in New York, New York, at base rent of $8,479 per month, which the lease will expire on January 31, 2023.
The Company leased 1,322 square feet of office space in Tokyo, Japan, which the lease expired on September 30, 2020.
The rent expense for the years ended December 31, 2019 and 2018 amounted to approximately $926,000 and $669,000, respectively.
Future minimum lease payments were as follows as of December 31, 2019 (in thousands):
|
|
|
Amount |
|
|
|
2020 |
|
$ |
991 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
1,080 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
1,110 |
|
|
2023 |
|
|
1,043 |
|
|
2024 and thereafter |
|
|
2,983 |
|
|
Total lease payments |
|
|
7,207 |
|
|
Less: Interest |
|
|
(2,284 |
) |
|
Operating lease liabilities |
|
$ |
4,923 |
|
The Company adopted ASU 2016-02 on January 1, 2019 using a modified retrospective approach and elected the transition method and the practical expedients permitted under the transition guidance, which allowed to carryforward the historical lease classification and our assessment on whether a contract is or contains a lease. The Company also elected to combine lease and non-lease components, such as common area maintenance charges, as single lease, and elected to use the short-term lease exception permitted by the standard as noted in Note 2.
As a result of the adoption of Topic 842 on January 1, 2019, the Company recorded a $3.0 million in operating right-of-use asset and $3.3 million in lease liability and derecognized $287,000 of deferred rent as of the adoption date. These
F-30
were calculated using the present value of the Company’s remaining lease payments using an estimated incremental borrowing rate. The Company also recorded a $29,000 cumulative effect increase on our accumulated deficit as of January 1, 2019. As of December 31, 2019, the Company had an operating lease right-of-use asset of $4.5 million and lease liability of $4.9 million in the balance sheet. The weighted average remaining term of the Company’s leases as of December 31, 2019 was 6.1 years and the weighted-average discount rate was 11.8%.
Prior to the adoption, future minimum lease payments under non-cancellable leases at December 31, 2018 were as follows (in thousands):
|
|
|
Amount |
|
|
|
2019 |
|
$ |
730 |
|
|
2020 |
|
|
974 |
|
|
2021 |
|
|
973 |
|
|
2022 |
|
|
1,003 |
|
|
2023 and thereafter |
|
|
3,665 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
7,345 |
|
NOTE 12—COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Management Control Acquisition Agreement — On June 12, 2017, the Company entered into a Management Control Acquisition Agreement (the “MCAA”) with Telcon Holdings, Inc. (“Telcon Holdings”), a Korean corporation, and Telcon RF Pharmaceuticals, Inc. (formerly Telcon Inc.), (“Telcon”), a Korean-based public company whose shares are listed on KOSDAQ, a trading board of Korea Exchange in South Korea. In accordance with the MCAA, the Company invested approximately $31.8 million to purchase 6,643,559 shares of Telcon common stock at a purchase price of approximately $4.79 per share.
The MCAA was amended in certain respect and supplemented by an Agreement, dated as of September 29, 2017, among the parties. Pursuant to the September 2017 Agreement, among other things, Telcon purchased 4,444,445 shares of Company common stock from KPM Tech Co., Ltd and Hanil Vacuum Co., Ltd. at a price of $6.60 per share.
On July 2, 2018, the Company entered into an Additional Agreement with Evercore Investment Holdings Co., Ltd. (formerly Telcon Holdings Co., Ltd.), (“Evercore”), and Telcon. In the Additional Agreement, the Company agreed to use the proceeds from the sales of its KPM shares to repurchase shares of Company common stock from Telcon at a price of $7.60 a share, subject to certain exceptions, and Telcon granted the Company the right to purchase from Telcon all or a portion of its shares of the Company at a price of $7.60 a share until October 31, 2018 and at a price to be agreed upon after October 31, 2018. The Company repurchased 495,000 shares of the Company common stock from Telcon at a price of $7.60 a share in 2018.
API Supply Agreement — On June 12, 2017, the Company entered into an API Supply Agreement (the “API Agreement”) with Telcon pursuant to which Telcon paid the Company approximately $31.8 million in consideration of the right to supply 25% of the Company’s requirements for bulk containers of PGLG for a fifteen-year term. The amount was recorded as deferred trade discount. On July 12, 2017, the Company entered into a raw material supply agreement with Telcon which revised certain terms of the API supply agreement (the “revised API agreement”). The revised API agreement is effective for a term of five years and will renew automatically for 10 successive one-year renewal periods, except as either party may determine. In the revised API agreement, the Company has agreed to purchase a total of 940,000 kilograms of PGLG at $50 USD per kilogram, or a total of $47.0 million, over the term of the agreement. In September 2018, the Company entered into an agreement with Ajinomoto and Telcon to facilitate Telcon’s purchase of PGLG from Ajinomoto for resale to the Company under the revised API agreement.
On June 16, 2019, the Company entered into an agreement with Telcon to adjust the price payable to Telcon under the revised API agreement from $50 per kilogram of PGLG to $100 per kilogram from July 1, 2019 through June 30, 2020, with the price payable after June 30, 2020 to be subject to agreement between the parties. The PGLG raw material purchased from Telcon is recorded in inventory at net realizable value and the excess purchase price is recorded against deferred trade discount. Refer to Note 13 for related party transaction details.
F-31
NOTE 13—RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The following table sets forth information relating to our loans from related persons outstanding at any time during the year ended December 31, 2019 (in thousands except for conversion rate and share information).
|
Class |
Lender |
|
Interest Rate |
|
|
Date of Loan |
|
Term of Loan |
|
Principal Amount Outstanding at December 31, 2019 |
|
|
Highest Principal Outstanding |
|
|
Amount of Principal Repaid or Converted into Stock |
|
|
Amount of Interest Paid |
|
|
Conversion Rate |
|
|
Shares Underlying Notes December 31, 2019 |
|
|||||||
|
Current, Promissory note payable to related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Lan T. Tran (2) |
|
10% |
|
|
4/29/2016 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
$ |
20 |
|
|
$ |
20 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Hope International Hospice, Inc. (1) |
|
10% |
|
|
6/3/2016 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
78 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Lan T. Tran (2) |
|
10% |
|
|
2/9/2017 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Yutaka Niihara (2)(3) |
|
10% |
|
|
9/14/2017 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
904 |
|
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Lan T. Tran (2) |
|
11% |
|
|
2/10/2018 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Lan T. Tran (2) |
|
10% |
|
|
2/9/2019 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
14 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subtotal |
|
$ |
193 |
|
|
$ |
1,359 |
|
|
$ |
277 |
|
|
$ |
82 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Current, Convertible notes payable to related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Yasushi Nagasaki (2) |
|
10% |
|
|
6/29/2012 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
200 |
|
|
$ |
200 |
|
|
$ |
56 |
|
|
$ |
3.30 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Yutaka & Soomi Niihara (2)(3) |
|
10% |
|
|
11/16/2015 |
|
2 years |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
73 |
|
|
$ |
4.50 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Wei Peu Zen (3) |
|
10% |
|
|
11/6/2017 |
|
2 years |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
597 |
|
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Profit Preview International Group, Ltd. (4) |
|
10% |
|
|
2/1/2018 |
|
2 years |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,037 |
|
|
|
4,037 |
|
|
|
385 |
|
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Profit Preview International Group, Ltd. (4) |
|
10% |
|
|
3/21/2018 |
|
2 years |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
5,363 |
|
|
|
5,363 |
|
|
|
442 |
|
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subtotal |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
14,800 |
|
|
$ |
14,800 |
|
|
$ |
1,553 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
193 |
|
|
$ |
16,159 |
|
|
$ |
15,077 |
|
|
$ |
1,635 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
F-32
The following table sets forth information relating to our loans from related persons outstanding at any time during the year ended December 31, 2018 (in thousands except for conversion rate and share information).
|
Class |
Lender |
|
Interest rate |
|
|
Date of loan |
|
Term of Loan |
|
Principal Amount Outstanding at December 31, 2018 |
|
|
Highest Principal Outstanding |
|
|
Amount of Principal Repaid |
|
|
Amount of Interest Paid |
|
|
Conversion Rate |
|
|
Shares Underlying Notes at December 31, 2018 |
|
|||||||
|
Current, Promissory note payable to related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Masaharu & Emiko Osato (3) |
|
11% |
|
|
12/29/2015 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
300 |
|
|
$ |
300 |
|
|
$ |
76 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Lan T. Tran (2) |
|
11% |
|
|
2/10/2016 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
131 |
|
|
|
131 |
|
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Masaharu & Emiko Osato (3) |
|
11% |
|
|
2/25/2016 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
400 |
|
|
|
400 |
|
|
|
94 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Lan T. Tran (2) |
|
10% |
|
|
4/29/2016 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Hope International Hospice, Inc. (1) |
|
10% |
|
|
6/3/2016 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
250 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Lan T. Tran (2) |
|
10% |
|
|
2/9/2017 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
12 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Yutaka Niihara (2)(3) |
|
10% |
|
|
9/14/2017 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
27 |
|
|
|
904 |
|
|
|
877 |
|
|
|
95 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
Lan T. Tran (2) |
|
11% |
|
|
2/10/2018 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
159 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subtotal |
|
$ |
468 |
|
|
$ |
2,176 |
|
|
$ |
1,708 |
|
|
$ |
294 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Current, Convertible notes payable to related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Yasushi Nagasaki (2) |
|
10% |
|
|
6/29/2012 |
|
Due on Demand |
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
3.30 |
|
|
|
74,182 |
|
|
|
|
Yutaka & Soomi Niihara (2)(3) |
|
10% |
|
|
11/16/2015 |
|
2 years |
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
200 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
$ |
4.50 |
|
|
|
58,350 |
|
|
|
|
Wei Peu Zen (3) |
|
10% |
|
|
11/6/2017 |
|
2 years |
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
5,000 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
250 |
|
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
532,671 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subtotal |
|
$ |
5,400 |
|
|
$ |
5,400 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
250 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
665,203 |
|
|
Non Current, Convertible notes payable to related parties: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
Profit Preview International Group, Ltd. (4) |
|
10% |
|
|
2/1/2018 |
|
2 years |
|
|
4,037 |
|
|
|
4,037 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
202 |
|
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
420,456 |
|
|
|
|
Profit Preview International Group, Ltd. (4) |
|
10% |
|
|
3/21/2018 |
|
2 years |
|
|
5,363 |
|
|
|
5,363 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
268 |
|
|
$ |
10.00 |
|
|
|
551,507 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Subtotal |
|
$ |
9,400 |
|
|
$ |
9,400 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
470 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
971,963 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
15,268 |
|
|
$ |
16,976 |
|
|
$ |
1,708 |
|
|
$ |
1,014 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,637,166 |
|
|
(1) |
Dr. Niihara, the Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer of the Company, is co-owner with his wife Soomi Niihara, a director and the Chief Executive Officer of Hope International Hospice, Inc. |
|
(2) |
Officer |
|
(3) |
Director |
|
(4) |
Mr. Zen, a director of the Company, is the sole owner of Profit Preview International Group, Ltd. |
See Note 8 for a discussion of the Company’s revolving line of credit agreement with Dr. Niihara.
|
See Notes 4 and 12 for a discussion of the Company’s distribution and supply agreements with Telcon, which holds 4,844,622 shares of the Company common stock, or approximately 8.5% of the common stock outstanding as of December 31, 2019. As of December 31, 2019, the Company held 6,643,559 shares Telcon stock as discussed in Note 6. |
F-33
Subsequent to the year ended December 31, 2019, the Company issued the following securities:
|
|
|
Dollar Amount |
|
|
Number of Shares Issued |
|
||
|
Common stock |
|
$ |
200,000 |
|
|
|
100,000 |
|
On February 27, 2020, the Company and EMI entered into a securities amendment agreement (the “February 2020 Amendment”) with the holders of $9.2 million principal amount of EMI’s outstanding amended and restated 10% Senior Secured Convertible Debentures and related outstanding amended and restated common stock purchase warrants to purchase up to 1,663,200 shares of the Company common stock. Pursuant to the terms of the February 2020 Amendment, the debenture holders waived their rights to the monthly redemption of $1,000,000 in principal amount of the debentures for the six-month period beginning February 2020 and ending July 2020. The monthly redemptions were to resume beginning in August 2020. In connection with the February 2020 Amendment, the maturity date of the Debentures was extended by six months to April 21, 2021, and the conversion price of the debentures and the exercise price of the related warrants were reduced to $3.00 per share from $9.52 and $5.87, respectively, per share. The debentures and related warrants provide for so-called full-ratchet anti-dilution adjustments in the event we sell or issue shares of common stock or common stock equivalents at an effective price per share less than the conversion price of the debentures or the exercise price of the warrants, subject to certain exceptions. The conversion price of the debentures and the exercise price of the related warrants were reduced to $2.00 a share as a result of the Company’s sale of 100,000 shares of common stock at a price of $2.00 a share under the Purchase Agreement Lincoln Park Capital LLC described below. The conversion price of the debenture and the exercise prices of the related warrants are also subject to adjustment for stock splits and other customary events.
On February 28, 2020, the Company entered into a Purchase Agreement with Lincoln Park Capital Fund, LLC (“LPC”), pursuant to which we may elect to sell to LPC up to $25,000,000 of shares of the Company common stock, subject to certain limitations and conditions set forth in the Purchase Agreement, including 100,000 initial shares that the Company sold to LPC at a price of $2.00 per share in connection with entering into the Purchase Agreement. Pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, on any business day over the 36-month term of the Purchase Agreement the Company has the right at our discretion and subject to certain conditions to direct LPC to purchase up to 20,000 shares of the Company common stock, which amount is subject to increase under certain circumstances based upon increases in the market price of the common stock. The purchase price of the common stock will be based upon the prevailing market price of the common stock at the time of the purchase without any fixed discount. In addition, the Company may direct LPC to purchase additional amounts as accelerated purchases and additional accelerated purchases under certain circumstances. Apart from the initial sale of shares described above, the Company is not obliged to sell any shares of common stock pursuant to the Purchase Agreement, and the Company will control the timing and amount of any such sales, but in no event will LPC be required to purchase more than $1,000,000 of common stock in any single regular purchase (excluding accelerated or additional accelerated purchases).
On May 8, 2020, the Company received a loan in the amount of $797,840 under the Small Business Administration Paycheck Protection Program (“PPP”). The PPP, established as part of the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security Act (“CARES Act”), provides for loans to qualifying businesses for amounts up to 2.5 times of the average monthly payroll expenses of the qualifying business. The loan, which was in the form of a Promissory Note dated April 29, 2020, matures on April 29, 2022 and bears interest at a rate of 1% per annum, payable monthly commencing on December 8, 2020 unless the PPP loan is forgiven prior to the date of the first monthly payment. The Note may be prepaid by the Company at any time prior to maturity with no prepayment penalties. The loan and accrued interest are forgivable after a specific period as long as the Company uses the loan proceeds for eligible purposes, including payroll, benefits, rent and utilities, and maintains its payroll levels. The amount of loan forgiveness would be reduced if the Company were to terminate employees or reduce salaries during such period. The Company believes it has used the entire loan amount for purposes consistent with the PPP and has applied for forgiveness of the loan.
On June 15, 2020, the holder of a convertible promissory note in the principal amount of $3,150,000 agreed to an extension of the maturity date to June 15, 2023. The interest for the note was increased from 11% to 12%. In conjunction with this amendment, the Company issued to the holder of note five-year common stock purchase warrants to purchase a total of up to 1,250,000 shares of the Company common stock at an exercise price of $2.05 a share.
On September 22, 2020, the Company and EMI entered into a securities amendment agreement (the “September 2020 Amendment”) with the holders of EMI’s outstanding debentures described above. The September 2020 Amendment amends in
F-34
certain respects the securities purchase agreement among EMI and the debenture holders originally entered into on September 8, 2018, as amended by the February 2020 Amendment, and provides that the debentures are to be amended in certain respects as set forth in the form of Allonge Amendment No. 1 to the debentures included in the September 2020 Agreement (the “Allonge”). Pursuant to the Allonge, the aggregate monthly redemption payments under the debentures were reduced to $500,000 from $1,000,000 in principal amount and the maturity date of the debentures was extended from April 21, 2021 to August 31, 2021. The monthly redemption payments resumed in September 2020 and will continue on the first day of each month thereafter commencing October 1, 2020. The remaining principal balance of the debentures will be due and payable upon maturity, subject to mandatory prepayment in connection with certain “Capital Events” as defined.
In consideration of the debenture holder’s financial accommodations to the Company, the Company issued to the holders, pro rata based upon the relative principal amounts of their debentures, five-year common stock purchase warrants to purchase a total of up to 1,840,000 shares of the Company common stock at an exercise price of $2.00 a share. The warrants provide for so-called full-ratchet anti-dilution adjustments in the event the Company sells or issues shares of common stock or common stock equivalents at an effective price per share less than the exercise price of the warrants, subject to certain exceptions. The exercise price also remains subject to adjustment for stock splits and other customary events. In October 2018, the Company granted to T.R. Winston and its affiliates for services relating to the September 2020 Amendment common stock purchase warrants to purchase up to 75,000 shares of the Company common stock at an exercise price of $2.10 a share and otherwise on terms identical to the warrants issued to the debenture holders described above.
On September 28, 2020, the Company entered into a convertible bond purchase agreement with Telcon pursuant to which it purchased on October 16, 2020 at face value a convertible bond of Telcon in the principal amount of approximately $26.1 million, on the terms described in the purchase agreement. The Company purchased the convertible bond with a portion of the net proceeds from the sale of Telcon common shares owned by us as reported in our October 14, 2020 press release announcing the sale the Telcon shares. The sale of the Telcon shares and purchase of the Telcon convertible bond was in accordance with our December 23, 2019 agreement with Telcon. As contemplated by the December 23, 2019 agreement, the convertible bond and any proceeds therefrom, including proceeds from any exercise of the call option or early redemption right described below, replace the Company’s former Telcon shares and proceeds therefrom as collateral under the revised API Supply Agreement with Telcon.
The Telcon convertible bond matures on October 16, 2030 and bears interest at the rate of 2.1% a year, payable quarterly. Beginning on October 16, 2021, the holder of the convertible bond will be entitled on a quarterly basis to call for early redemption of all or any portion of the principal amount of the convertible bond. To the extent not previously redeemed, the principal amount of the bond will be due upon maturity. The convertible bond is convertible at the holder’s option at any time and from time to time into common shares of Telcon at an initial conversion price of approximately $8.00, per share. The conversion price is subject to antidilution adjustments in the event of the issuance of Telcon shares or share equivalents at a price below the market price of Telcon shares, a merger or similar reorganization of Telcon or a stock split, reverse stock split, stock dividend or similar event.
In connection with the purchase of the convertible bond, the Company entered into a call option agreement dated September 28, 2020 with Telcon pursuant to which Telcon or its designee is entitled to repurchase, at par, up to 50% in principal amount of the convertible bond commencing October 16, 2021 and prior to maturity. If the Company transfers the convertible bond, it will be obliged under the call option agreement to see to it that the transferee is bound by such call option.
On October 28, 2020, the Company entered into a loan agreement with EJ Holdings pursuant to which it agrees to loan to EJ Holdings a total of approximately $6.5 million, in monthly instalments through March 2021, including approximately $4.0 million, loaned through December 31, 2020. The loans will be unsecured general obligations of EJ Holdings, will bear interest at a nominal annual rate payable on September 30 of each year beginning in 2021 and will be due and payable in a lump sum at maturity on September 30, 2020. The proceeds of the loans will be used by EJ Holdings to fund its activities and operations at its Ube facility as described under “Equity Method Investment” in Note 6 above.
F-35
NOTE 15—QUARTERLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (UNAUDITED)
Set forth below are the Consolidated Financial Statement of the Company as previously reported and as restated to reflect adjustments:
Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheet
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
|
|
|
As of September 30, 2019 (Unaudited) |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
As Restated |
|
|||
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
13,546 |
|
|
|
(12,220 |
) |
(b) |
$ |
1,326 |
|
|
Accounts receivable, net |
|
|
1,900 |
|
|
|
82 |
|
(c) |
|
1,982 |
|
|
Inventories, net |
|
|
7,491 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
7,491 |
|
|
Investment in marketable securities |
|
|
27,643 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
27,643 |
|
|
Marketable securities, pledged to creditor |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
1,194 |
|
|
|
347 |
|
(b)(c) |
|
1,541 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
|
51,774 |
|
|
|
(11,791 |
) |
|
|
39,983 |
|
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
163 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
163 |
|
|
Equity method investment |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
13,407 |
|
(b) |
|
13,407 |
|
|
Right of use assets |
|
|
4,118 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4,118 |
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
427 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
427 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
56,482 |
|
|
$ |
1,616 |
|
|
$ |
58,098 |
|
|
LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
$ |
10,706 |
|
|
|
220 |
|
(b) |
$ |
10,926 |
|
|
Operating lease liabilities, current portion |
|
|
844 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
844 |
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
|
5,676 |
|
|
|
357 |
|
(a)(c) |
|
6,033 |
|
|
Warrant derivative liabilities |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
91 |
|
(a) |
|
91 |
|
|
Notes payable, net of discount |
|
|
3,886 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,886 |
|
|
Notes payable to related parties |
|
|
193 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
193 |
|
|
Convertible debentures, net of discount |
|
|
11,000 |
|
|
|
(4,530 |
) |
(a) |
|
6,470 |
|
|
Convertible notes payable, net of discount |
|
|
2,928 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,928 |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
35,233 |
|
|
|
(3,862 |
) |
|
|
31,371 |
|
|
Operating lease liabilities, less current portion |
|
|
3,714 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,714 |
|
|
Other long-term liabilities |
|
|
34,585 |
|
|
|
(29 |
) |
(a) |
|
34,556 |
|
|
Convertible debentures, net of discount less current portion |
|
|
1,200 |
|
|
|
(494 |
) |
(a) |
|
706 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
74,732 |
|
|
|
(4,385 |
) |
|
|
70,347 |
|
|
STOCKHOLDERS’ DEFICIT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred stock — par value $0.001 per share, 15,000,000 shares authorized, no shares issued or outstanding |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Common stock — par value $0.001 per share, 250,000,000 shares authorized, 47,671,446 shares issued and outstanding at September 30, 2019 |
|
|
47 |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
48 |
|
|
Additional paid-in capital |
|
|
199,395 |
|
|
|
13,224 |
|
(a)(b) |
|
212,619 |
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
|
|
(51 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(51 |
) |
|
Accumulated deficit |
|
|
(216,916 |
) |
|
|
(7,949 |
) |
|
|
(224,865 |
) |
|
Stockholders’ deficit |
|
|
(17,525 |
) |
|
|
5,276 |
|
|
|
(12,249 |
) |
|
Noncontrolling interests |
|
|
(725 |
) |
|
|
725 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ deficit |
|
$ |
56,482 |
|
|
$ |
1,616 |
|
|
$ |
58,098 |
|
(a) Senior secured debentures adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in decreases of $4.5 million in short-term convertible notes payable and $0.5 million in long-term convertible notes payable. Also, it resulted in a decrease of $5.6 million in additional paid-in capital, $263,000 million in short-term conversion feature liabilities and $29,000 in long-term conversion feature liabilities.
(b) EJ Holdings adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in increases of $13.4 million in equity method investment, $220,000 in accounts payable and accrued expenses, and $725,000 in non-controlling interest, as well as decreases of $12.2 million in cash and cash equivalents and $241,000 in prepaid expenses and other current assets.
(c) Corrections to other misstatements were as follows: (i) period adjustment and reclassification of variable consideration resulted in increases of $82,000 in accounts receivable and $22,000 in current liabilities; (ii) correction of financing of insurance premium resulting in an increase of $598,000 in prepaid expenses and other current liabilities; (iii) correction relating of debt modification resulting in an increase of $1.1 million in additional paid-in capital; (iv) correction relating to GPB warrant classification resulting in an increase of $91,000 in warrant derivative liabilities and a decrease of $776,000 in additional paid-in capital.
F-36
Emmaus Life Sciences, Inc.
Consolidated Statement of operations and Comprehensive Loss
(In thousands, except share and per share amounts)
|
|
|
Three months ended September 30, 2019 ( Unaudited) |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
As Restated |
|
|||
|
REVENUES, NET |
|
$ |
6,084 |
|
|
$ |
(324 |
) |
(c) |
$ |
5,760 |
|
|
COST OF GOODS SOLD |
|
178 |
|
|
|
70 |
|
(c) |
|
248 |
|
|
|
GROSS PROFIT |
|
|
5,906 |
|
|
|
(394 |
) |
|
|
5,512 |
|
|
OPERATING EXPENSES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
|
725 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
725 |
|
|
Selling |
|
|
1,789 |
|
|
|
(11 |
) |
|
|
1,778 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
|
6,991 |
|
|
|
65 |
|
(b)(c) |
|
7,056 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
|
9,505 |
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
9,559 |
|
|
LOSS FROM OPERATIONS |
|
|
(3,599 |
) |
|
|
(448 |
) |
|
|
(4,047 |
) |
|
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss on debt extinguishment |
|
|
(6,427 |
) |
|
|
5,989 |
|
(a)(c) |
|
(438 |
) |
|
Change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities |
|
|
424 |
|
|
|
3,152 |
|
(a)(c) |
|
3,576 |
|
|
Change in fair value of embedded conversion option |
|
|
342 |
|
|
|
(211 |
) |
(a) |
|
131 |
|
|
Net losses on equity investment in marketable securities and long-term investment |
|
|
(5,248 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(5,248 |
) |
|
Net loss on equity method investment |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
36 |
|
(b) |
|
36 |
|
|
Miscellaneous reverse merger costs |
|
|
(309 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(309 |
) |
|
Note conversion costs |
|
|
(3,906 |
) |
|
|
565 |
|
(c) |
|
(3,341 |
) |
|
Interest and other income (loss) |
|
|
(17 |
) |
|
|
35 |
|
(b) |
|
18 |
|
|
Interest expense |
|
|
(7,318 |
) |
|
|
(1,396 |
) |
(a) |
|
(8,714 |
) |
|
Total other income (expenses) |
|
|
(22,459 |
) |
|
|
8,170 |
|
|
|
(14,289 |
) |
|
LOSS BEFORE INCOME TAXES |
|
|
(26,058 |
) |
|
|
7,722 |
|
|
|
(18,336 |
) |
|
INCOME TAXES |
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
NET LOSS INCLUDING NONCONTROLLING INTEREST |
|
|
(26,083 |
) |
|
|
7,722 |
|
|
|
(18,361 |
) |
|
Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
|
|
(54 |
) |
|
|
54 |
|
(b) |
|
— |
|
|
NET LOSS ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE COMPANY |
|
|
(26,137 |
) |
|
|
7,776 |
|
|
|
(18,361 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COMPONENTS OF OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
(6 |
) |
|
|
5 |
|
|
Other comprehensive loss |
|
|
11 |
|
|
|
(6 |
) |
|
|
5 |
|
|
COMPREHENSIVE LOSS |
|
|
(26,072 |
) |
|
|
7,716 |
|
|
|
(18,356 |
) |
|
Amounts attributable to noncontrolling interests: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
|
|
(54 |
) |
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
|
(6 |
) |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
Comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
|
|
(60 |
) |
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
COMPREHENSIVE LOSS ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE COMPANY |
|
$ |
(26,132 |
) |
|
$ |
7,776 |
|
|
$ |
(18,356 |
) |
|
NET LOSS PER COMMON SHARE - BASIC and DILUTED |
|
$ |
(0.57 |
) |
|
$ |
0.17 |
|
|
$ |
(0.40 |
) |
|
WEIGHTED-AVERAGE COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING |
|
|
46,020,507 |
|
|
|
45,986,629 |
|
|
|
45,986,629 |
|
(a) Senior secured debentures adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in decreases of $6.3 million in loss on debt extinguishment and $211,000 in change in fair value of embedded conversion option and increases of $2.4 million in change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities and $1.4 million in interest expenses.
(b) EJ Holdings adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in increases of $125,000 in general and administrative expense, $36,000 in loss on equity method investment and an increase in $35,000 in interest and other income (loss).
(c) Corrections to other misstatement were as follows: (i) period adjustment of variable consideration resulted in a decrease of $324,000 in revenue, net; (ii) reclassification of shipping cost and royalty expense to cost of sales resulted in an increase of $71,000 in cost of sales and decreases of $11,000 and $60,000 in selling cost and general and administrative expense, respectively; (iii) correction relating to stock modification accounting resulted in an increase of $52,000 in general and administrative expense; (iv) correction relating to accounting for debt modification resulted in a decrease of $320,000 in loss on debt extinguishment; and (v) correction relating to the GPB warrant classification resulted in an increase of $685,000 in change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities.
F-37
|
Nine months ended September 30, 2019 (Unaudited) |
|
||||||||||
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
As Restated |
|
|||
|
REVENUES, NET |
$ |
17,260 |
|
|
$ |
(1,300 |
) |
(c) |
$ |
15,960 |
|
|
COST OF GOODS SOLD |
|
573 |
|
|
|
198 |
|
(c) |
|
771 |
|
|
GROSS PROFIT |
|
16,687 |
|
|
|
(1,498 |
) |
|
|
15,189 |
|
|
OPERATING EXPENSES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Research and development |
|
1,778 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1,778 |
|
|
Selling |
|
5,177 |
|
|
|
(29 |
) |
|
|
5,148 |
|
|
General and administrative |
|
14,523 |
|
|
|
(1,048 |
) |
(b)(c) |
|
13,475 |
|
|
Total operating expenses |
|
21,478 |
|
|
|
(1,077 |
) |
|
|
20,401 |
|
|
LOSS FROM OPERATIONS |
|
(4,791 |
) |
|
|
(421 |
) |
|
|
(5,212 |
) |
|
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Loss on debt extinguishment |
|
(6,427 |
) |
|
|
5,989 |
|
(a)(c) |
|
(438 |
) |
|
Change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities |
|
623 |
|
|
|
2,869 |
|
(a)(c) |
|
3,492 |
|
|
Change in fair value of embedded conversion option |
|
342 |
|
|
|
(211 |
) |
(a) |
|
131 |
|
|
Net losses on equity investment in marketable securities and long-term investment |
|
(22,242 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(22,242 |
) |
|
Net loss on equity method investment |
|
— |
|
|
|
(413 |
) |
(b) |
|
(413 |
) |
|
Miscellaneous reverse merger costs |
|
(309 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(309 |
) |
|
Note conversion costs |
|
(3,906 |
) |
|
|
565 |
|
(c) |
|
(3,341 |
) |
|
Interest and other income (loss) |
|
146 |
|
|
|
102 |
|
(b) |
|
248 |
|
|
Interest expense |
|
(22,757 |
) |
|
|
(2,396 |
) |
(a)(c) |
|
(25,153 |
) |
|
Total other income (expenses) |
|
(54,530 |
) |
|
|
6,505 |
|
|
|
(48,025 |
) |
|
LOSS BEFORE INCOME TAXES |
|
(59,321 |
) |
|
|
6,084 |
|
|
|
(53,237 |
) |
|
INCOME TAXES |
|
242 |
|
|
|
(1 |
) |
(c) |
|
241 |
|
|
NET LOSS INCLUDING NONCONTROLLING INTEREST |
|
(59,563 |
) |
|
|
6,085 |
|
|
|
(53,478 |
) |
|
Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
|
620 |
|
|
|
(620 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
NET LOSS ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE COMPANY |
|
(58,943 |
) |
|
|
5,465 |
|
|
|
(53,478 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
COMPONENTS OF OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
10 |
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
Other comprehensive loss |
|
10 |
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
COMPREHENSIVE LOSS |
|
(59,553 |
) |
|
|
6,093 |
|
|
|
(53,460 |
) |
|
Amounts attributable to noncontrolling interests: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
|
620 |
|
|
|
(620 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
8 |
|
|
|
(8 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Comprehensive loss attributable to noncontrolling interest |
|
628 |
|
|
|
(628 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
COMPREHENSIVE LOSS ATTRIBUTABLE TO THE COMPANY |
$ |
(58,925 |
) |
|
$ |
5,465 |
|
|
$ |
(53,460 |
) |
|
NET LOSS PER COMMON SHARE - BASIC and DILUTED |
$ |
(1.46 |
) |
|
$ |
0.14 |
|
|
$ |
(1.32 |
) |
|
WEIGHTED-AVERAGE COMMON SHARES OUTSTANDING |
|
40,474,847 |
|
|
|
40,443,124 |
|
|
|
40,443,124 |
|
(a) Senior secured debentures adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in decreases of $6.3 million in loss on debt extinguishment and $211,000 in change in fair value of embedded conversion option as well as in increases of $2.1 million in change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities and $1.0 million in interest expenses.
(b) EJ Holdings adjustments: The correction of this misstatement resulted in a decrease of $930,000 in general and administrative expense, and increases of $36,000 in loss on equity method investment and $102,000 in interest income.
(c) Corrections to other misstatement were as follows: (i) period adjustment of variable consideration resulted in decreases of $1.3 million in revenue, net and $1,000 income tax provision (ii) reclassification of shipping cost and royalty expense to cost of sales resulted in an increase of $199,000 in cost of sales and decreases of $29,000 and $170,000 in selling cost and general and administrative expense, respectively; (iii) correction relating to stock modification accounting resulted in an increase of $52,000 in general and administrative expense; (iv) correction relating to accounting for debt modification resulted in an increase of $1.3 million in interest expenses and a decrease of $320,000 in loss on debt extinguishment; and (v) correction relating to GPB warrant classification resulted in an increase of $685,000 in change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities.
F-38
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In thousands)
|
|
|
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2019 (Unaudited) |
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Previously Reported |
|
|
Adjustments |
|
|
As Restated |
|
|||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net loss |
|
$ |
(59,563 |
) |
|
$ |
6,085 |
|
|
$ |
(53,478 |
) |
|
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash flows used in operating activities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
Impairment loss on long-term investment |
|
|
524 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
524 |
|
|
Amortization of discount of convertible notes and notes payable |
|
|
19,479 |
|
|
|
2,396 |
|
|
|
21,875 |
|
|
Foreign exchange adjustments on convertible notes and notes payable |
|
|
49 |
|
|
|
(256 |
) |
|
|
(207 |
) |
|
Net losses on equity investment in marketable securities |
|
|
21,718 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
21,718 |
|
|
Loss on equity method investment |
|
|
0 |
|
|
|
413 |
|
|
|
413 |
|
|
Loss on debt extinguishment |
|
|
6,427 |
|
|
|
(5,989 |
) |
|
|
438 |
|
|
Share-based compensation and fair value of replacement equity award |
|
|
3,541 |
|
|
|
52 |
|
|
|
3,593 |
|
|
Note conversion costs |
|
|
3,906 |
|
|
|
(565 |
) |
|
|
3,341 |
|
|
Change in fair value of warrant derivative liabilities |
|
|
(623 |
) |
|
|
(2,869 |
) |
|
|
(3,492 |
) |
|
Change in fair value of embedded conversion option |
|
|
(342 |
) |
|
|
211 |
|
|
|
(131 |
) |
|
Net changes in operating assets and liabilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable |
|
|
(548 |
) |
|
|
355 |
|
|
|
(193 |
) |
|
Inventories |
|
|
(2,787 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(2,787 |
) |
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
(426 |
) |
|
|
(599 |
) |
|
|
(1,025 |
) |
|
Other non-current assets |
|
|
(4,150 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(4,150 |
) |
|
Accounts payable and accrued expenses |
|
|
4,857 |
|
|
|
1,109 |
|
|
|
5,966 |
|
|
Deferred revenue |
|
|
500 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
500 |
|
|
Deferred rent |
|
|
(287 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(287 |
) |
|
Other current liabilities |
|
|
230 |
|
|
|
598 |
|
|
|
828 |
|
|
Other long-term liabilities |
|
|
2,363 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,363 |
|
|
Net cash flows used in operating activities |
|
|
(5,078 |
) |
|
|
941 |
|
|
|
(4,137 |
) |
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash paid in connection with the Merger |
|
|
(1,641 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(1,641 |
) |
|
Purchases of property and equipment |
|
|
(55 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(55 |
) |
|
Sales of marketable securities |
|
|
221 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
221 |
|
|
Net cash flows provided by (used in) investing activities |
|
|
(1,475 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(1,475 |
) |
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Payments of convertible notes |
|
|
(3,368 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(3,368 |
) |
|
Proceeds from exercise of warrants |
|
|
186 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
186 |
|
|
Proceeds from issuance of common stock |
|
|
6,210 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
6,210 |
|
|
Net cash flows provided by (used in) financing activities |
|
|
3,028 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
3,028 |
|
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash |
|
|
(8 |
) |
|
|
13 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
(3,533 |
) |
|
|
954 |
|
|
|
(2,579 |
) |
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period |
|
|
17,079 |
|
|
|
(13,174 |
) |
|
|
3,905 |
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of period |
|
$ |
13,546 |
|
|
|
(12,220 |
) |
|
$ |
1,326 |
|
|
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURES OF CASH FLOW ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Interest paid |
|
$ |
1,239 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
1,239 |
|
|
Income taxes paid |
|
$ |
242 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
242 |
|
|
Warrant liabilities reclassified to equity |
|
$ |
776 |
|
|
$ |
5,561 |
|
|
$ |
6,337 |
|
|
Conversion of convertible notes and notes payable to common stock |
|
$ |
33,777 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
33,777 |
|
|
Conversion of accrued interest payable to common stock |
|
$ |
2,381 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
2,381 |
|
|
Initial recognition of right-of-use lease asset |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
2,922 |
|
|
$ |
2,922 |
|
Refer to descriptions of the adjustments and their impact on net loss in the Consolidated Statement of Operation and Comprehensive Loss for the nine months ended September 30, 2018 above.
Cash flow classification adjustment related to EJ Holdings in 2019 resulted in a net increase to cash flows provided by operating activities of $940,000.
No other misstatements impacted the classifications between net operating, net investing or net financing cash flow activities for the nine months ended September 30, 2019.
F-39